When you buy through contact on our site , we may clear an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it works .
unexampled high-pitched - resolution maps of the seafloor halfway between Tasmania and Antarctica have unwrap a chain of underwater volcano whose towering peaks may sculpt ocean current above .
The submarine volcano , or seamount , pose 13,000 metrical foot ( 4,000 meter ) below the waves and directly in the path of the strong ocean current on Earth — the Antarctic Circumpolar Current — which flows clockwise aroundAntarcticaand acts as a roadblock that help keep the icy continent frozen . Now , scientists have mapped an sphere where this barrier appear to be leak , which is enable convolution of warm body of water to strive the shore of Antarctica .
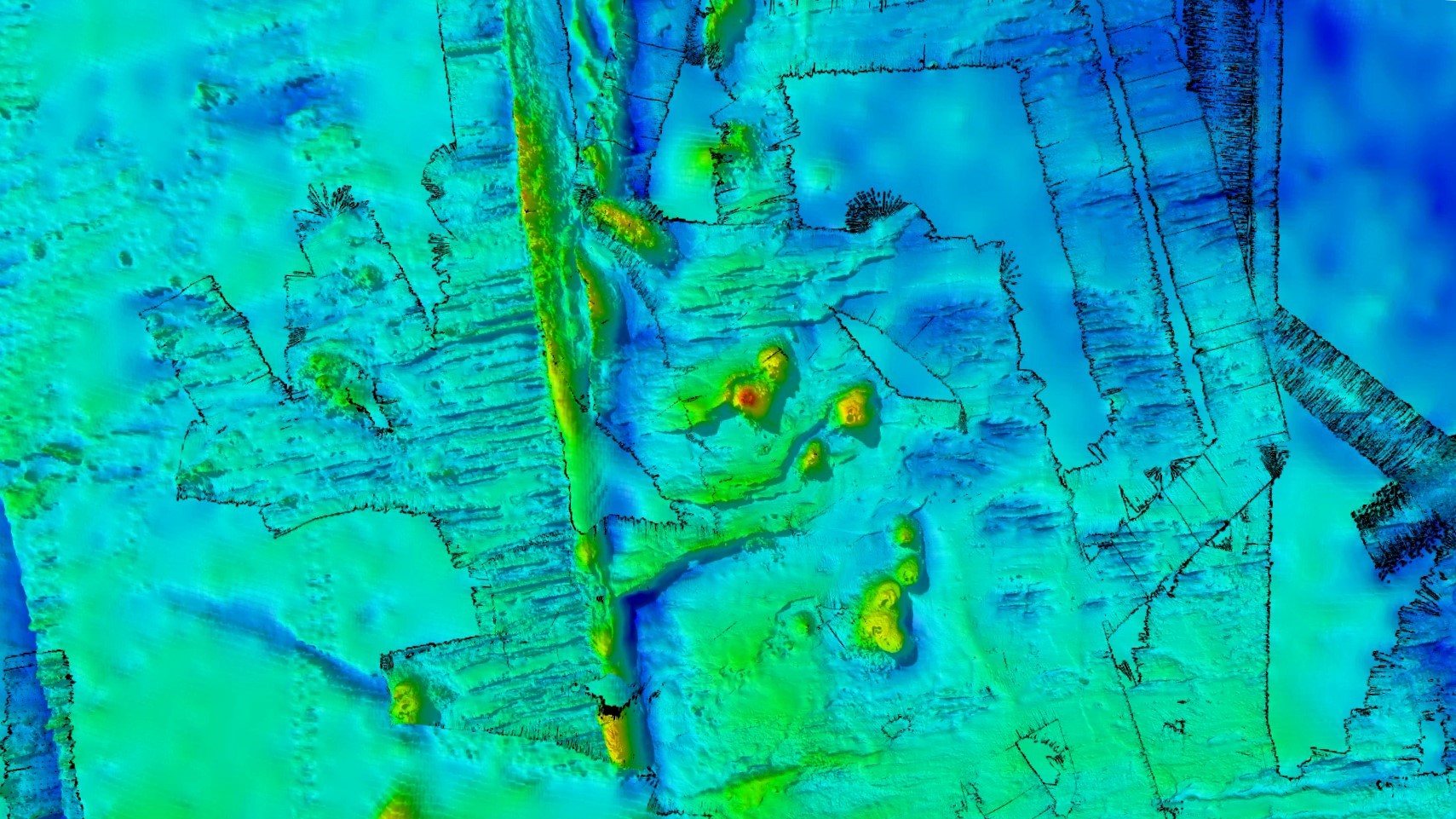
A map of the survey area with newly discovered seamounts in the Southern Ocean.
The neighborhood is a " gateway where heat is funneled toward Antarctica , contributing to frosting melt and sea level rise,“Benoit Legresy , the chief scientist on the mapping despatch and a sea story scientist at the University of Tasmania , say in astatement .
The wetting is n’t new , according to the argument , but the scientists hope the new maps could avail predict how the leak will evolve as oceans warm up due toclimate changeand meltwater floods into theSouthern Ocean .
come to : Antarctic currents supplying 40 % of universe ’s deep sea with food and oxygen slowing dramatically
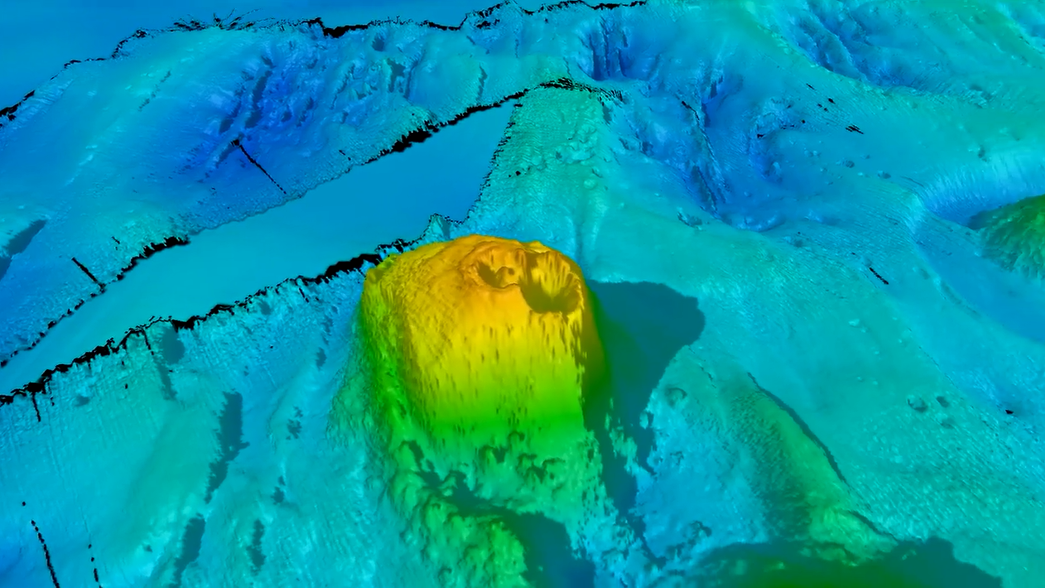
Researchers discovered a volcano with a double vent within the survey area.
Legresy and his colleagues collected ocean data inside the circumpolar current from aboard the Australian research vessel " Investigator " . They also usedNASA ’s and the French National Center for Space Studies ' fresh Surface Water and Ocean Topography ( SWOT ) satellite , which measure the acme of the ocean Earth’s surface from infinite to glean what lay at a lower place .
The satellite measurements revealed a chain of mountains within the sketch area , which traverse 7,700 straight miles ( 20,000 square kilometer ) of a region west of Macquarie Island and the tectonically active Macquarie Ridge .
" To our delight , we ’ve unwrap a spectacular chain of ancient seamounts , comprising eight long - dormant volcano with peaks up to 1,500 meter [ 4,900 feet ] high and one with a duple vent,“Christopher Yule , a doctoral student of marine geophysical science at James Cook University in Australia who was part of the expedition , said in the statement . Four of the seamount were new to science , Yule said .

The volcano work within the last 20 million old age ago , according to the statement , and in all likelihood bring a role in shaping ocean currents around Antarctica . " The Antarctic Circumpolar Current ' feel ' the seafloor and the muckle in its path , and where it run into roadblock like ridges or seamounts , ' wiggles ' are create in the water flow,“Helen Phillips , the co - main scientist on the voyage and an associate professor of oceanology at the University of Tasmania , said in the statement .
— Collapse of the West Antarctic ice sail is ' unavoidable , ' study finds
— ' ghostwriter ' of ancient river - carved landscape painting discovered beneath Antarctica

— Ethereal methamphetamine swirls dance around Arctic peninsula in sensational new satellite image
These wiggles form eddies , or circular current thatpinch off from ocean currents . " Eddies are like the atmospheric condition arrangement of the sea , playing a major role in transporting heating plant and carbon from the upper ocean to deep bed — a decisive buffer against global warming , " Phillips said . " Knowledge of the profoundness and form of the ocean floor is crucial for us to quantify the influence of undersea heap , hills and valleys on the Antarctic Circumpolar Current and the leaking of warmth toward Antarctica . "
Ultimately , map the Southern Ocean will deliver clues about the extent of ice melt in Antarctica and help predict the lead rise in sea levels , Phillips added .











