When you purchase through liaison on our situation , we may garner an affiliate perpetration . Here ’s how it works .
Women are up to four time more potential than men to be affected byautoimmune disease , conditions in which theimmune systemmistakenly attack the body ’s own cells . Now , scientists recollect they know why : Women ’s outsized risk may be attach to how the organic structure manipulate its X chromosome .
Humans have two types of sexchromosomes : X and Y. Most female carry two XTC chromosomes in each cell , while most males have an 10 and a Y. The X chromosome is larger than the Y and contains far more gene that code for proteins . But in people with two X chromosome , only one involve to enter in protein output — otherwise , cell could soon be overwhelmed with too many protein . To forbid this , one ex chromosome in each cell is " silenced " in femalesduring embryonic developing .
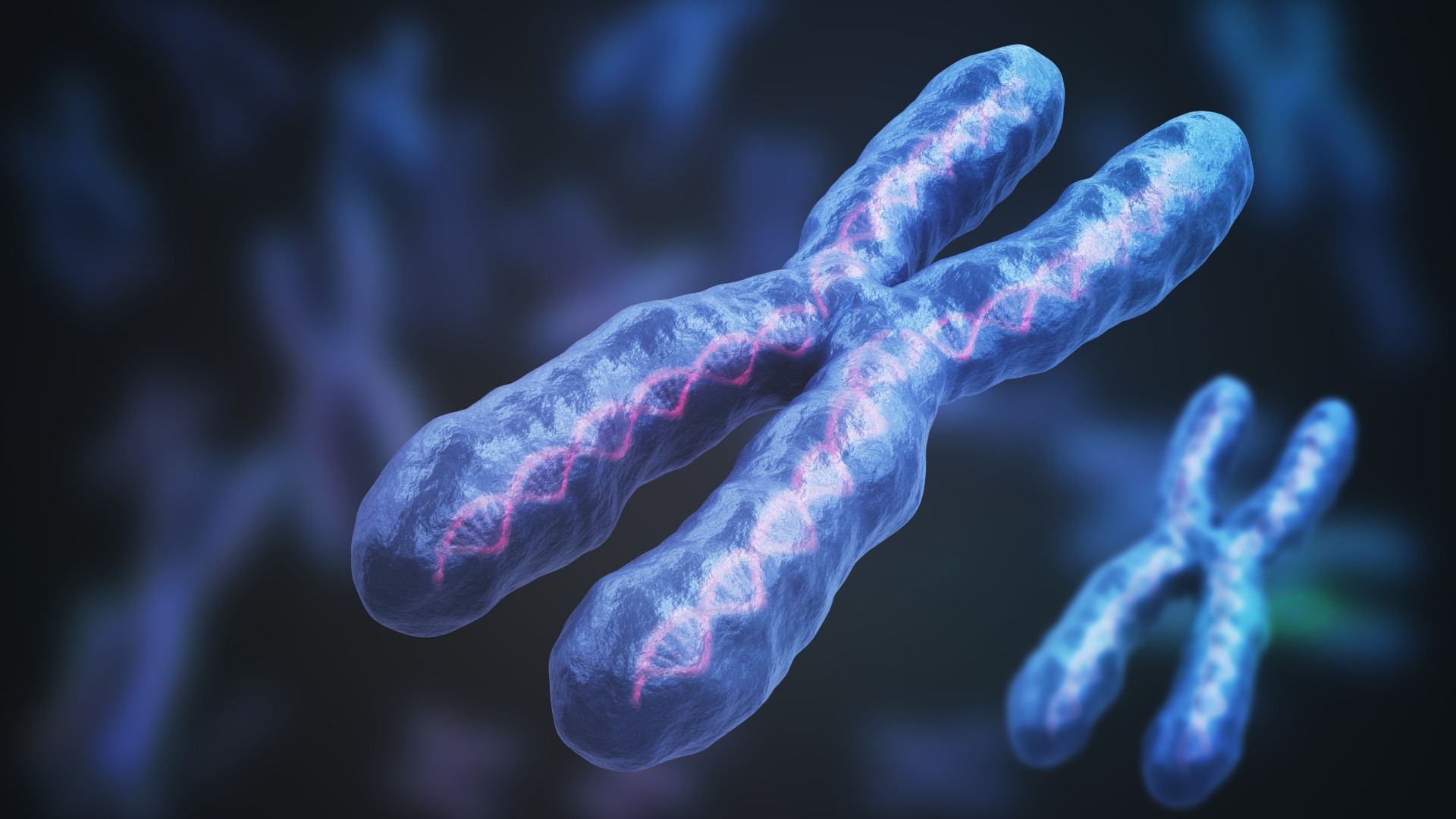
A new study suggests that females may be at a higher risk of developing autoimmune disease because of the way their two X chromosomes, illustrated above, are regulated.
A farseeing molecule ofRNA — the genetic cousin ofDNA — forebode Xist execute this silencing by latch onto one X chromosome . It grow out , however , that many protein are prone to sticking to Xist , and these big building complex of RNA and protein may predispose female to autoimmune disease .
That ’s because the complexes can set off an resistant chemical reaction in which the body lay down antibody against the protein within it , according to a new written report in mice and humans issue Thursday ( Feb. 1 ) in the journalCell .
" So besides it ’s [ Xist ] job in controlling factor activity , there ’s really a major immunological embossment that maybe had n’t previously been recognized,“Dr . Howard Chang , co - senior study author and a professor of cancer inquiry and genetic science at Stanford University , told Live Science .
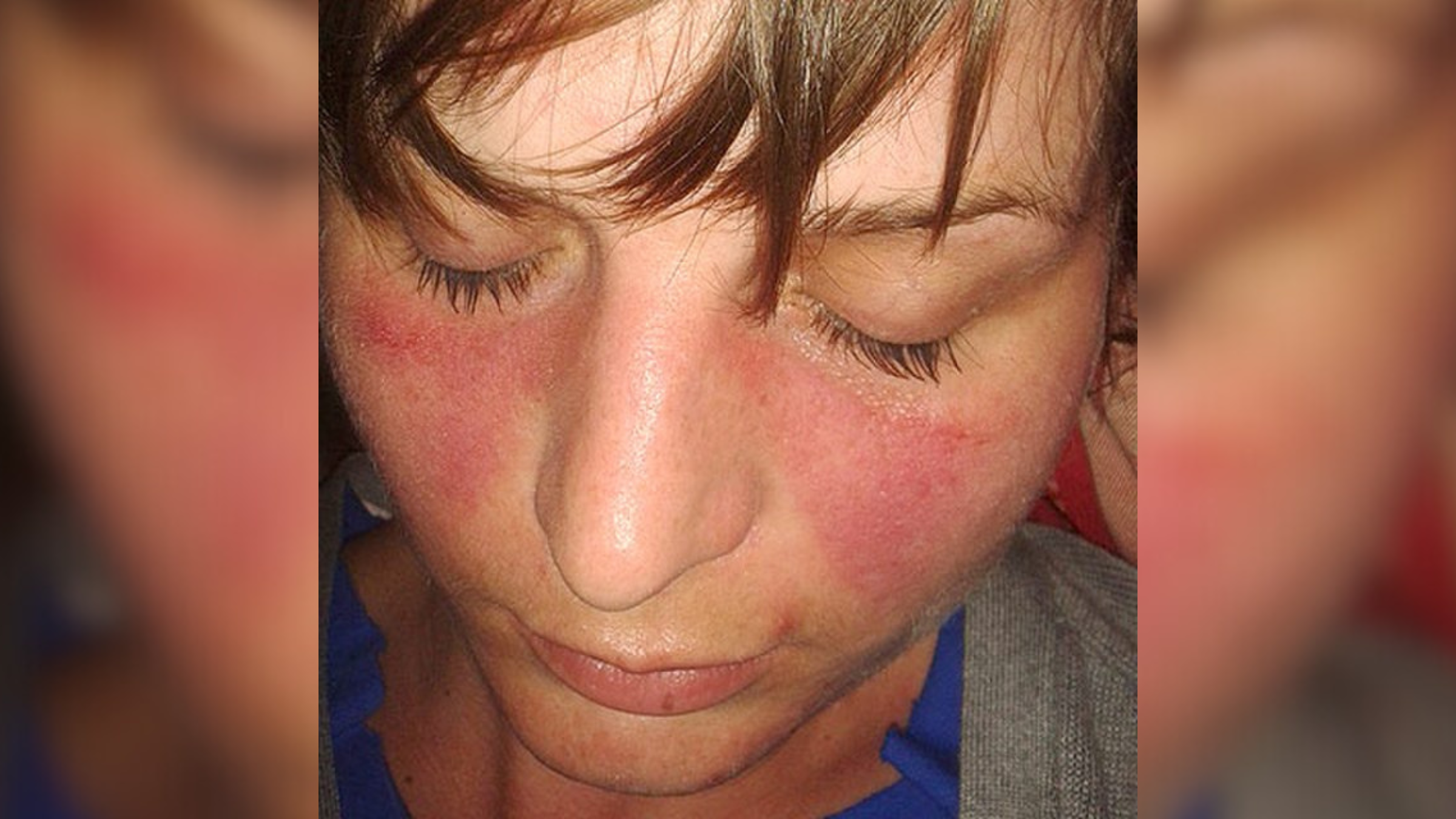
The researchers studied the Xist complex in a mouse model of lupus, which, in humans, can cause joint pain, stiffness and a characteristic butterfly-shaped rash on the face, pictured above.
These findings could therefore open up new avenues for research into discourse for autoimmune diseases , he said .
Related:‘If you do n’t have inflammation , then you ’ll snuff it ' : How scientists are reprogramming the body ’s natural world power
Autoimmune diseases , which affectmore than 23.5 million Americans , are triggered by a combining ofgeneticandenvironmental triggers . scientist have proposedmany theoriesto explain why womanhood are more likely to develop the conditions , pointing to their hormones and the microbes inside and on them , but none of these mind have been conclusively confirmed .

Earlier researchby Chang and colleagues suggested that the Xist complex may drive sex - biased autoimmunity , as many proteins associated with autoimmune disease could hold to it . But Xist needed to be studied in closing off , without other component , such as internal secretion , that could potentially block out its influence .
So the squad genetically direct two strains of male mice to make Xist : one that was genetically susceptible to autoimmune symptoms similar to those oflupusand another that was tolerant — the comparison radical . In the lupus - prostrate variant , female mouse were more prostrate to symptoms than male mice were , so the squad theorized that Xist would bring the male ' levels of disease up to that of female .
In their experiment , the squad run up a peculiar version of the Xist gene into the genome of male mice that could be switched on but would n’t hush up their only X chromosome . To stimulate autoimmune disease , they had to expose the lupus - prostrate mice to a specific chemical .

Related : ignition is a ' mismatch between our evolutionary chronicle and modernistic environment , ' says immunologist Ruslan Medzhitov
Once Xist was activated and lupus was induce , the team see that male mice that expressed Xist developed disease at a similar rate to females and had more severe disease than mouse without Xist .
However , requiring both the environmental chemical initiation and a hereditary sensitivity to lupus was an important control , Chang say . That made the shiner experiment more relevant to humankind .

" If someone is born with a inherited susceptibleness , then the presence of Xist has some impact but also , very significantly , this environmental trigger [ is necessary ] , " Chang said . Carrying Xist does n’t warrant a individual will have an autoimmune condition ; the Xist complex may just account for the variant in case counts between the sex .
— unexampled ' opposite vaccine ' could pass over out autoimmune diseases , but more research is postulate
— Teen ’s class - long case of depression and seizures due to brain - injure autoimmune disease

— COVID-19 yoke to 40 % gain in autoimmune disease peril in huge study
To back up their computer mouse results , the team analyzed blood sample from more than 100 patient with autoimmune disease , including lupus , and 20 without autoimmune disease . They discovered that the patients with autoimmunity had more Xist autoantibody in their blood than the individual without autoimmunity did .
The types and number of autoantibody in different mass were disease - specific , which may help with the next diagnosis and treatment of these conditions , Chang tell . For example , someday , taking these autoantibody profiles could aid doctors decipher which disease a patient has or promise the flight of their precondition , he say .

This article is for informational role only and is not meant to offer medical advice .
Ever wonder whysome people build musculus more easily than othersorwhy freckle come out in the Lord’s Day ? Send us your motion about how the human body function tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject melodic phrase " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your interrogative answered on the website !
Twin study break signs of MS that might be perceptible before symptom

Scientist who discovered torso ’s ' fire alarm ' against infest bacterium succeed $ 250,000 Lasker plunder
The unremitting surveillance of advanced living could worsen our brain function in ways we do n’t fully understand , disturbing studies suggest



