When you purchase through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it solve .
Scientists have created a new wireless engineering that could one day competitor the rule wireless communication engineering , Bluetooth . The young technology requires so little power it could make devices last five times longer on a single thrill .
Currently , the principal wireless technology — include Wi - Fi,5GandBluetooth — embed in equipment such as smartphones and wearables , as well as wise home devices , rely on classical radio conformation . These transmit data through electromagnetic waves generated by electromagnetic theater modulation .

But the alternative technology or else rely on electric line of business inflection . Signal - air devices swap out mightiness amplifier used in formal wireless engineering science for voltage amplifier which generate a scant - orbit galvanic field of view .
These electromotive force amplifiers also generate a weak electromagnetic field , but the receivers — untuned electrodes rather than tuned feeler — are configured to only nibble up on data point that travel via the electric arena . ( Conventional radio systems create electric fields alongside electromagnetic field , but they dilapidate very quickly and are n’t used to transmit entropy . )
Power is consumed on the receiving machine only when there ’s a charge or discharge on the receiving electrode — a outgrowth acknowledge as capacitive coupling — and not by the uninterrupted transfer of muscularity through air as in definitive radio configuration . As a result , the new tech , knight " Electric Potential Sensing Communication " ( EPSComm ) , take in a fraction of the top executive that Bluetooth uses .
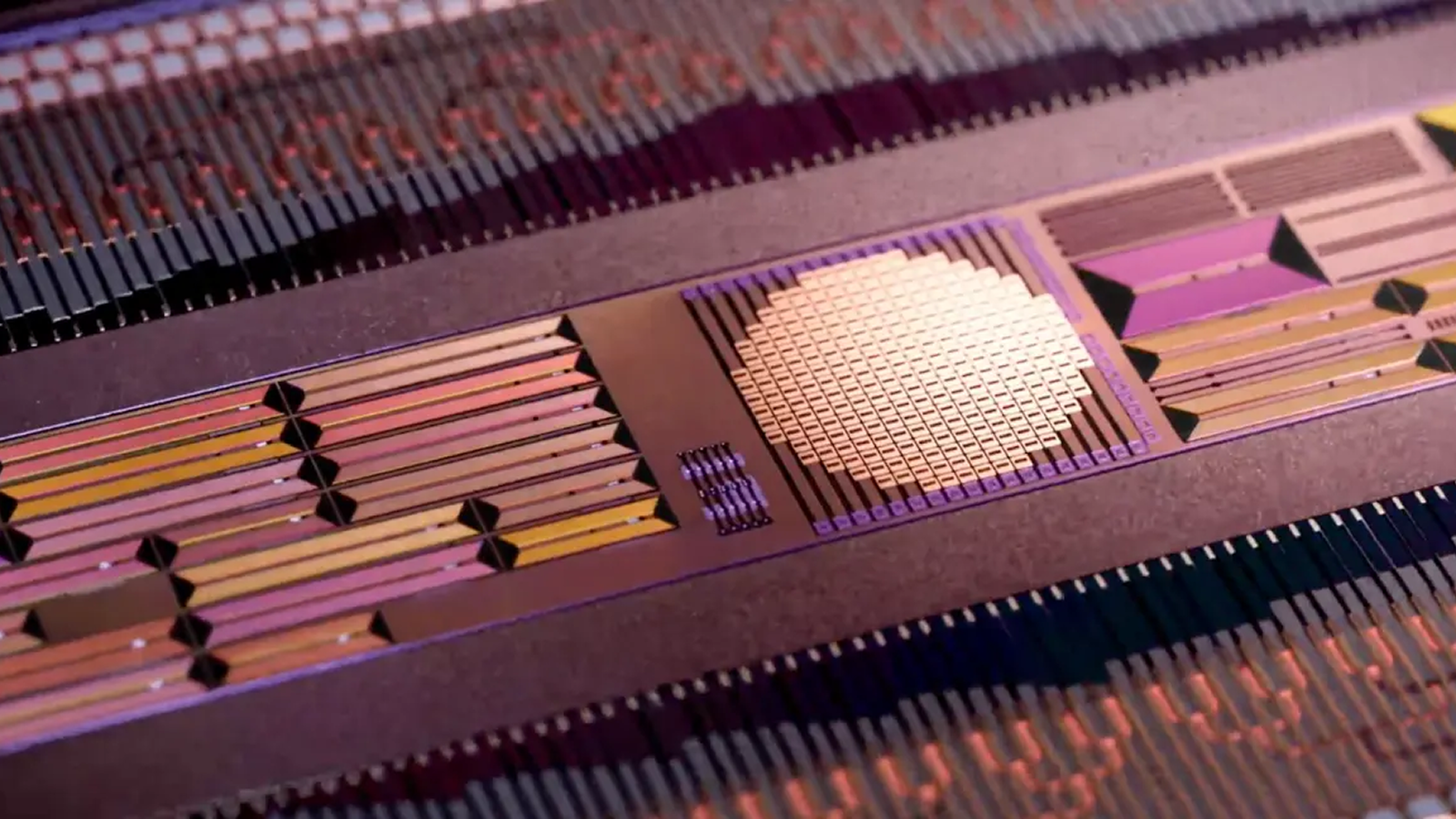
" This unexampled technology mean that wearable and mobile devices will be capable to run longer on a bombardment charge . More essentially it will be potential to use diminished batteries and miniaturize devices even further , thanks to the vim savings brought about by this new communicating technology . This open up new opening for tiny wearable gadget , such as earables ( sassy earbuds ) , overbold rings , or even electronics integrated into garments,“Daniel Roggen , a professor of wearable technologies at the University of Sussex , told Live Science in an electronic mail .
Related : Bluetooth : Who invented it and how does it mold ?
In experiments , Roggen ’s squad notice that optimized EPSComm squander 10 times less superpower than Bluetooth , he say , which likely translates to gimmick batteries lasting between four and five times longer between charges .

EPSComm accomplish a information throughput of up to 600 kilobits per bit , which Roggen enjoin is fast enough for audio , telecasting and virtual realism ( VR ) practical software . While Bluetooth often has higher datum transmittance rates now , the first generation of Bluetooth channel at only 125 kbps .
The electrical signaling from EPSComm travelling much shorter distance than Bluetooth , which is the trade - off , but that also means a reduced hazard of eavesdropping or signaling hindrance .
Rather than completely put back Bluetooth , however , the new tech may complement the wireless standard in future machine , Roggen said .
— What is electromagnetic radiation ?
— ' Leaking ' cell speech sound towboat could top aliens straight to Earth , novel study suggests
— Physicists built an ' anti - laser ' to charge your phone from across a elbow room

Somebody , for example , could get in touch their headphone to their smartphone using EPSComm , but if they walk away , the system would dynamically switch to a Bluetooth connecter , which has a much longer range .
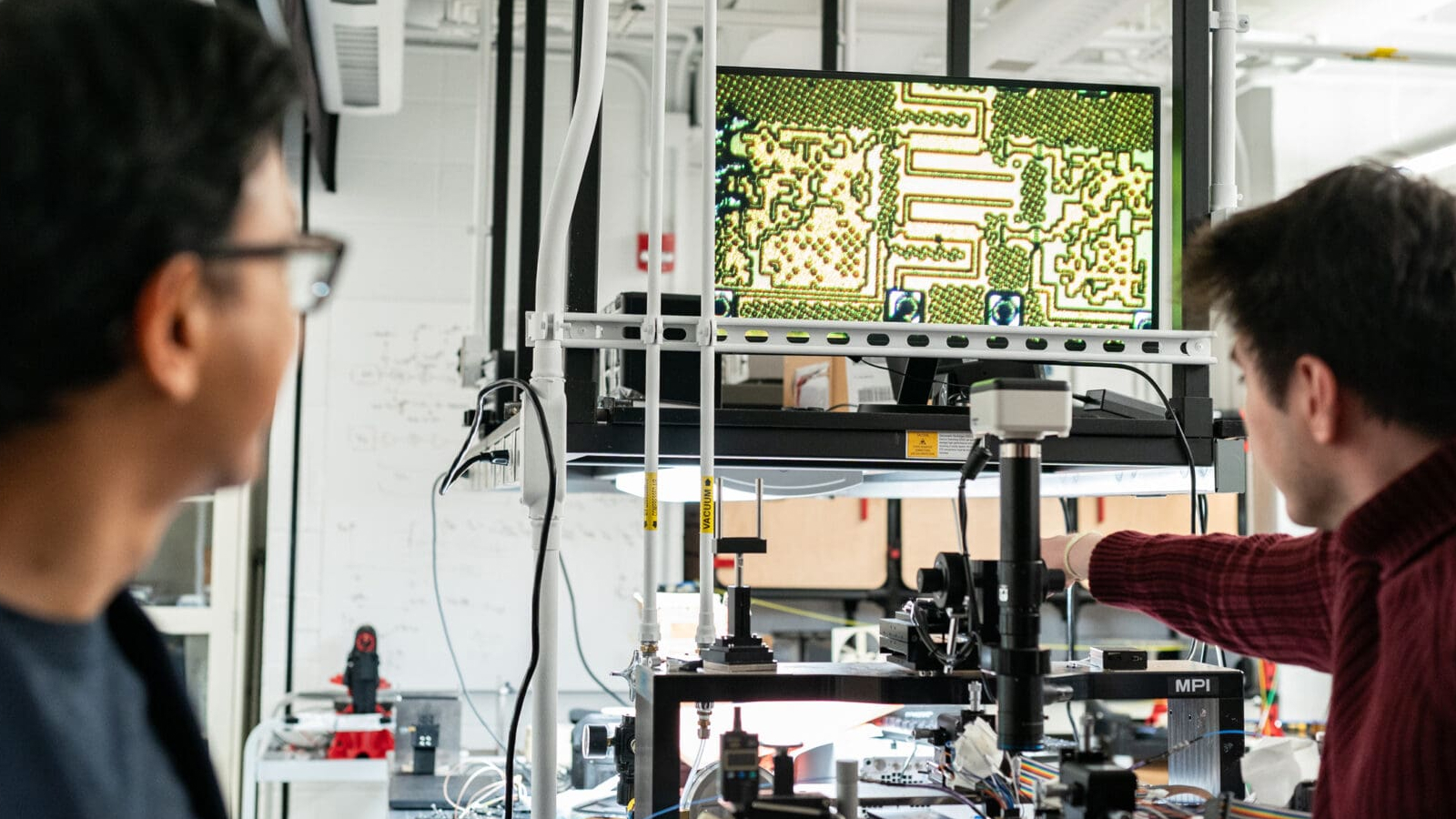
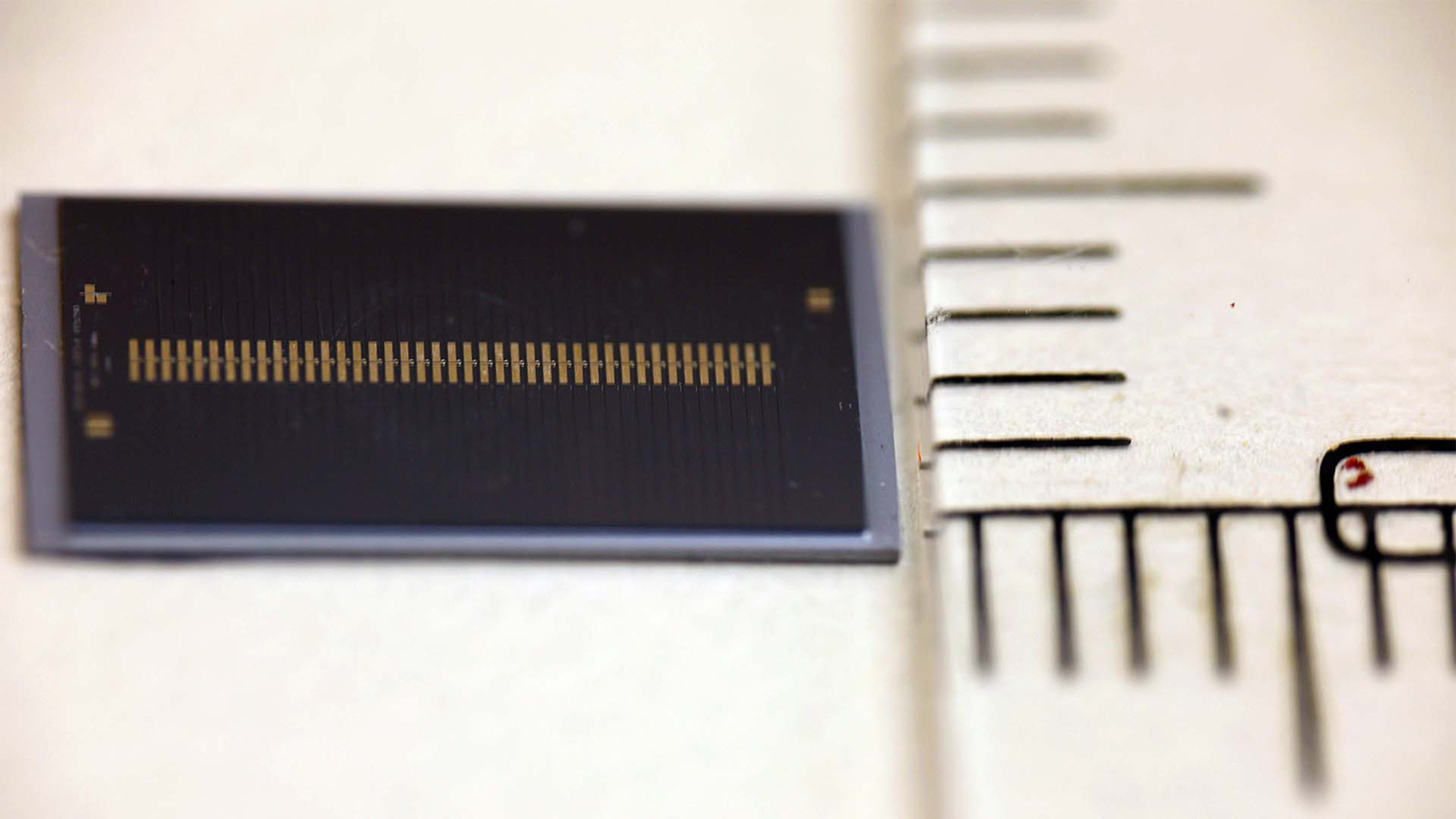
The squad built several prototype EPSComm machine , but the vector and receivers were roughly 1.2 by 1.2 inches ( 3 by 3 centimeters ) . That ’s too large to fit into today ’s smartphones or wearable gadget , such asrunning headphones .
Having established a working image , the research worker are wait for industrial partnership to reduce the size of the components so they will fit into small personal equipment .










