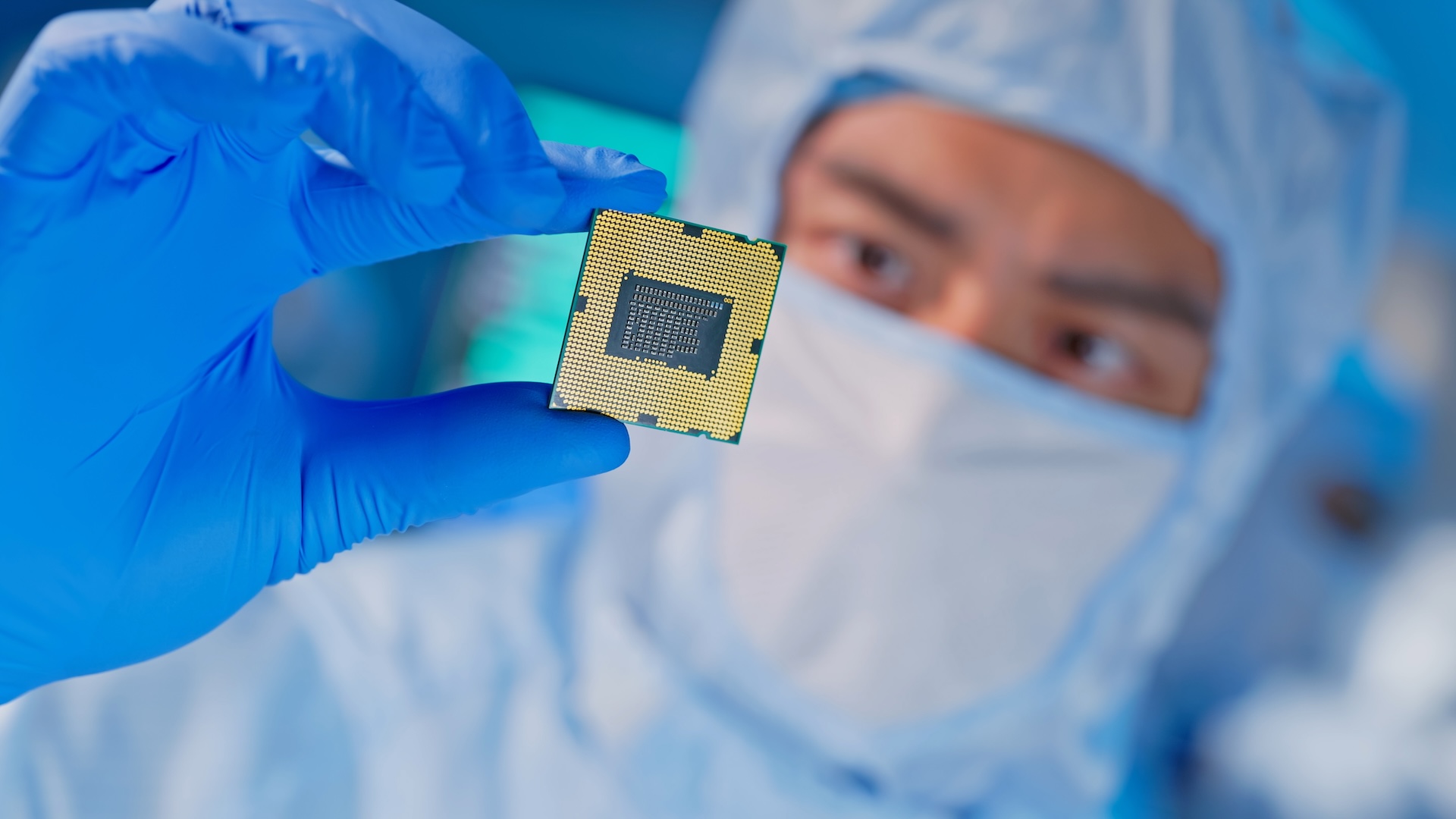
When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Scientists have created a wireless charge gadget that could be inserted under the skin . So far , it ’s only been tested in rodent , but if follow - up enquiry in humans is successful , it could mean medical implant ditch the unwieldy battery and wiring that come with them .
Most bioelectronic devices , such as sensors or drug - obstetrical delivery organization , are often throttle by the capacity of onboard batteries . They can also often be hooked up to an extraneous power supply — but this risks get transmission , specially if the patient needs surgical procedure to take away or supercede persona .
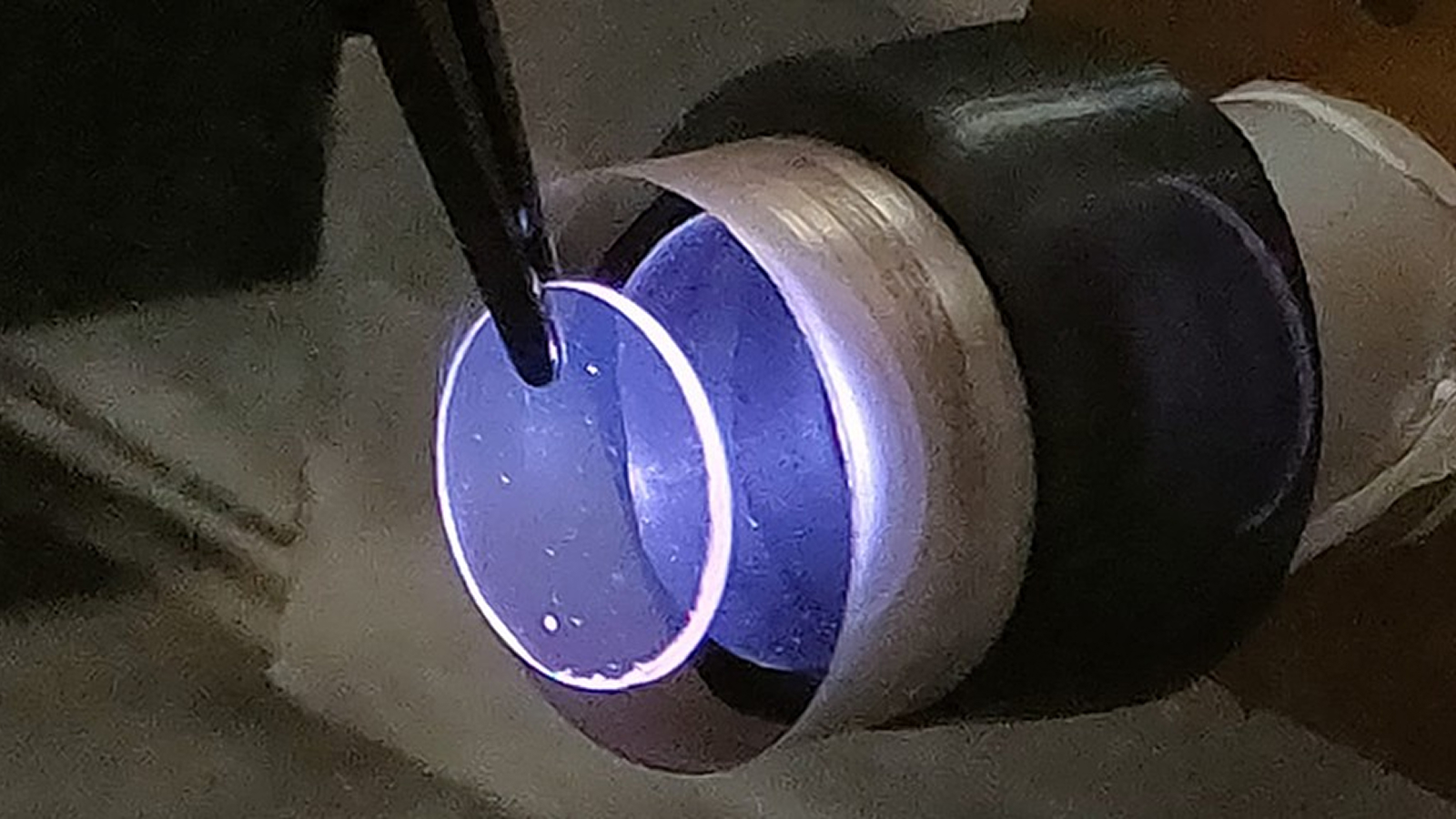
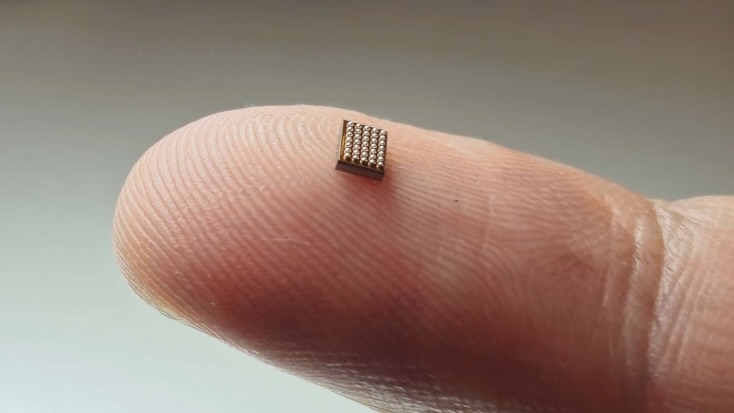
A wireless charger that sits under the skin could power medical devices before dissolving into the body.
To get around this problem , scientists built a prototype radio set charging chip that can be embed under the skin . The prototype , tested in puke , can either wirelessly transfer energy through the body or harvest Department of Energy from the physical structure .
The pliable and diffuse under - the - skin chip can also adapt to the form of tissue paper during a subprogram , and it ’s biodegradable , investigator wrote in a composition published Nov. 15 in the journalScience Advances .
Related:4D implant redeem babies with respiration trouble
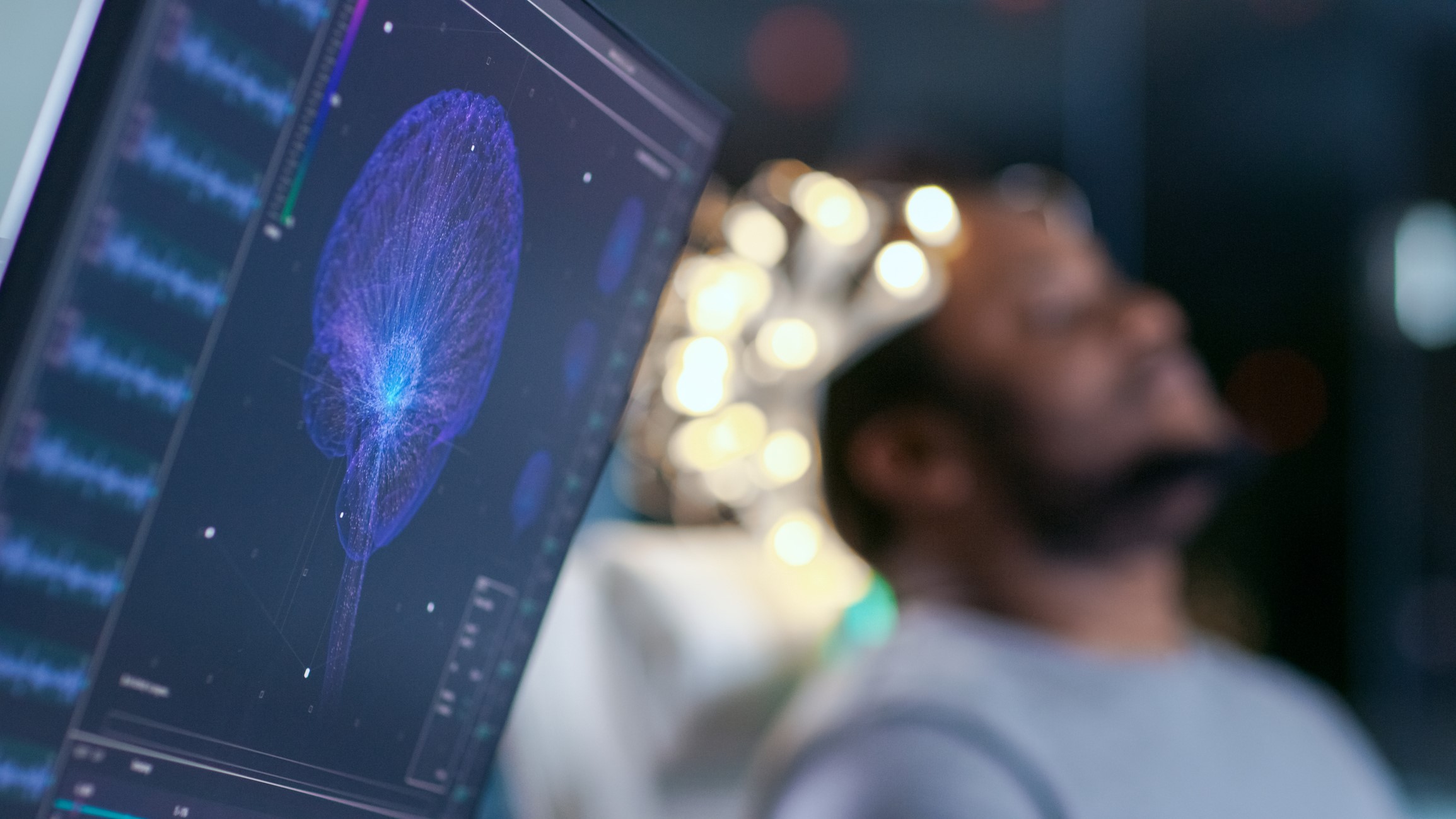
If the device proves successful in humans, it could mean medical implants ditch the clunky batteries and wiring that come with them.
" Our prototyped power supply organisation represents an of import pace forward in advancing a wide ambit of biodegradable implantable aesculapian gadget with its potential to provide in force and reliable energy solution , " field co - authorWei Lan , a prof of electronics in the School of Physical Science and Technology at Lanzhou University inChina , told Live Science in an email .
The prototype superpower supply uses a magnesium coil that charges when a second coil is place above the tegument . Power drop dead through a circuit and then introduce an zip - computer memory faculty made of zinc - ion intercrossed capacitors .
Unlike bombardment , which salt away energy in chemic physique , these supercapacitors hive away index as electrical vim . They also have a high power density and can discharge a large amount of energy at once , even though they hive away less vigor per unit than batteries do .

The researcher embedded this prototype in a biodegradable , poker chip - same implant that combined energy harvest and energy computer storage . When the epitome was attached to a medical implant , power go on through the circuit directly to the machine and into the condenser to ensure a unvarying power supply .
In so-and-so , the wireless implant work for up to 10 days and dissolved completely within two month — proving its biodegradability . But it could potentially last longer if the squad thickened the protective polymer and wax layers incase the system , Lan said .
The investigator also essay the wireless charger as a drug - delivery system and delivered anti - instigative medicine to rats with a fever . After 12 hours , the rats that had no implant had much high physical structure temperatures than those with the fleck , suggesting the machine was successfully delivering the music .

— Elon Musk ’s Neuralink ' nous chips ' cleared for 1st in - human trials
— 1st patient role with new ' head - read ' gadget uses brain signals to write
— Who was the first bionic man ?

The newfangled prototype would require to overcome several hurdles before it ’s ready to be test in humans , however . In the drug - delivery experiments , some rats were also given uncharged implant twine with anti - inflammatories — and their temperatures spend , which suggest some passive drug liberation . The squad also has n’t control turn the machine on or off ; it cease work only when it runs out of power .
Future research will also call for to address the gadget ’s size and full biodegradability .
" At present , the size of it of the scheme is still relatively bombastic and arrest a small rectifier mental faculty [ which convert between AC and DC ] , and stability needs to be further meliorate , " Lan said . " There is still a certain distance to accomplish material biomedical applications . "