When you purchase through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
rough 80 years ago , the world was at warfare . Under a shroud of privateness , scientists in the U.K. , Germany and the U.S. were create the first electronic computers . These computers filled rooms , demanded huge amount of electrical energy and enabled previously impossible calculations . Few of the people postulate could have imagined that ten later , computing gadget orders of magnitude more powerful would check in a back pack — yet that ’s exactly what happened .
So , as we sit on the threshold of truly usefulquantum computing , could we ever see quantum laptop computer ? " I recollect it ’s possible,“Mario Gely , a quantum computing researcher at the University of Oxford , severalize Live Science . " It ’s extremely risky , but I ca n’t think of a central reason why a quantum laptop would not be potential . "

Will quantum computers ever be as small as laptops?
Here are some of the dance step that will be needed to get there .
Scaling up qubit number
Before scientist can make a quantum laptop computer , they take to make a utile quantum computer , full point . Questions remain over how manyqubits — quantum equivalents to digital bits — are needed to create a authentically utile quantum computer , or one that can clear a scope of utile , real - world problem that eludethe best superclassical computers . But it ’s definitely higher than is currently potential .
Stephen Bartlett , a theoretic quantum physicist and director of the University of Sydney ’s Nano Institute , thinks we could see genuinely useful quantum computers by the death of this 10 . " There ’s a caboodle of exposed scientific challenge , which make that pathway a bit murky , but we ’re get tight , " Bartlett told Live Science .
Related : What is the largest have it off prime number ?

Will quantum computers ever be as small as laptops?
For instance , new developed quantumcharge - coupled gadget ( QCCD ) architecturecould be used to make two - dimensional arrays of qubits rather than one - dimensional ones — which would increase the density , and potentially the phone number , of qubits .
Reducing the errors in quantum computers
But scaling brings another challenge in ramp up a miniature quantum computer : correcting errors , or " noise . " " Our existing quantum components are noisy , so we need error fudge factor , and that call for a big amount of redundancy , " Bartlett read . Scientists need to either reduce errors or build error correction into quantum computers , and that requires even more qubits . Many scientists are trying to solve this trouble .
For example , aDecember 2023 studytried to reduce misplay by building a quantum computer with " logical qubits . " Inanother paper , published in April 2024 , scientist design a new type of qubit that behave like an wrongdoing - correcting logical qubit . Some scientists have even proposed using photon ( light particles ) as qubits , includinganother studythat used a optical maser pulse . According to Peter van Loock , a professor of theoretic quantum optic at Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz in Germany and cobalt - author of the study , this approach has an " constitutional capacity to correct error " .
So if , within a decennary or two , herculean and utilitarian quantum computers exist , the next step would be miniaturisation .

Will quantum computers ever look like laptops?
Choosing different types of qubits
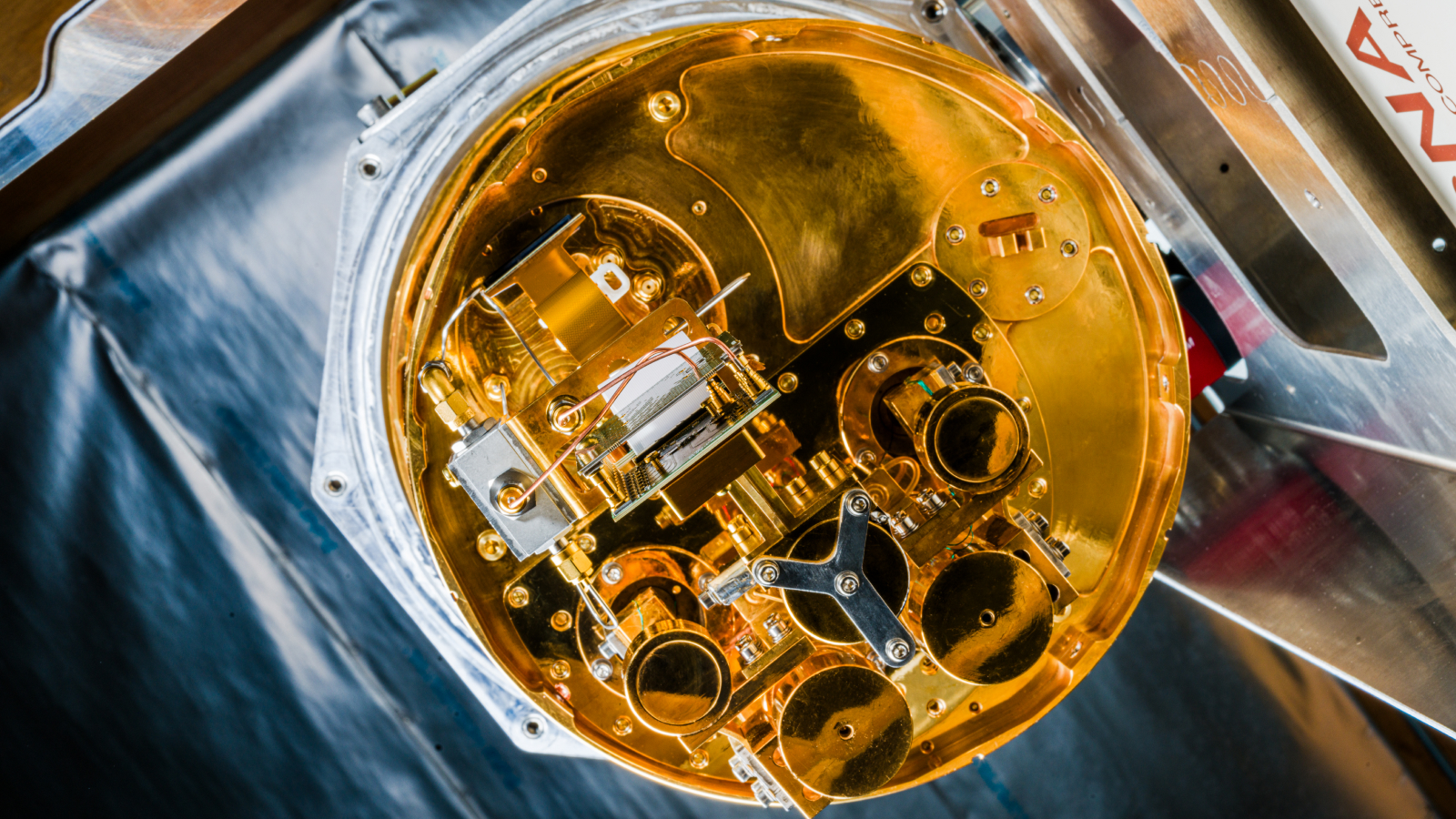
But to get really small , quantum reckoner may need to focalise on a different case of qubit than is currently popular . Some of the most innovative quantum computers today — such as those made by IBM and Google — rely onquantum processing unitsfilled with superconducting qubits . But the first quantum laptop computer probably wo n’t expend this applied science .
That ’s because , by their nature , superconducting qubits must be cool to a fraction aboveabsolute zero — around 20 millikelvin — and that requires filling a room with dilution icebox . And company like IBM are n’t trying to get around this size of it constraint . For example , IBM ’s currentquantum computing roadmapsets out goals that admit a 2,000 - qubit quantum computer by 2033 — which would fill many way rather than one .
Quantum laptops may or else rely on trapped ion qubits , charged subatomic particle that exist in multiple states at once and that are suspended using electromagnetic fields , Bartlett and Gely explained . Although trap ion systems work at way temperature and do n’t rely on room - sized refrigerators , the lasers they use are gigantic .
" At the import , our optical maser system occupies more or less a three-dimensional meter [ 35 three-dimensional understructure ] , " Gely said . " If we take that ion traps are the future , then we need the lasers to become smaller . "
And lasers must not only shrink but also become more advanced . Current systems are geared to constrain 100 ions . " How many qubits you’re able to see with this mass of laser equipment is ill-defined , " Gely say . " you could check more qubits than we have today , but certainly not the millions of qubits of a in full fledged quantum computer . "
However , two late advances could facilitate with miniaturization . First , future QCCDs could help miniaturization by increasing qubit tightness . Second , in July , Stanford researchers createdtitanium - cerulean lasers that are 10,000 clip smallerthan the ones they replace .
Related : How does a secure earphone line of reasoning work ?
Miniaturization efforts will ramp up
the right way now , scientists are focalise on making quantum computers more hefty , not on shrinking them . " The drive for miniaturization is not as strong at the moment as the drive for performance , and that mimics the early twenty-four hours of conventional information processing system when we had mainframes , " Bartlett said . " citizenry thought of the most sinewy computers as taking up a building . And you eff , why would anyone seriously consider carrying one around in your backpack ? "
Thehistory of computerssuggests quantum computing equipment will roll up out first for industrial , military machine and government applications before shifting to consumer . The apocryphal 1943 citation fromThomas Watson Sr.that there would be a " human beings market place for peradventure five computers " springs to mind .
Of course , the world market place for microcomputer and laptops is vast , so could there ever be a similar explosion of requirement for quantum PC and laptops ? " The query I always get in my quantum computing socio-economic class is , you know , ' When can I dally Doom on a quantum calculator ? ' " Bartlett said . " But why would you require to when you may play Doom perfectly well on your figurer today ? "
— Google ’s Sycamore quantum computer chip can now outmatch the fastest supercomputer , new study suggests
— New quantum computer bang up ' quantum supremacy ' phonograph recording by a factor of 100 — and it consumes 30,000 times less power
— History of quantum computer science : 12 central moments that form the future tense of computers

alternatively , Bartlett intimate there might be " quantum personal apps like finance or something niche around information security department " — but the truth is , nobody knows . Gely made the alternate suggestion of a quantum mainframe sitting alongside a Graeco-Roman processor . " It could be like you have a computer graphic card , but it would only be utile for certain tasks , " Gely said .
It ’s not yet clear that quantum laptops would be useful for consumers . What expert can say with a high story of confidence is that all of the hardware obstruction — scale the number of qubits , even up error cand miniaturise components — can be overcome . And yet , a succeeding quantum laptop in all likelihood wo n’t roleplay Doom .