When you purchase through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate perpetration . Here ’s how it works .
Norway is known for its arresting fjords — long , wiggly coastal inlets with steep English . It ’s no marvel that these geological features , which are filled with sparkling water and often lined with tough cliffs , headline so many tourism ads .
Although fjords are determine along coastlines around the existence , from Alaska to Scotland to New Zealand , Norway has more than 1,000 that are substantial enough to have names , according to the country’sofficial tourism card . So why are there so many fjords in Norway ?

Fjords are long, sinuous coastal inlets with steep sides, like Geirangerfjord in Norway.
" The fiord are the merchandise of repeated glacial oscillation and ice - sheet - ordered series glaciation,“Anna Hughes , a paleoglaciologist at the University of Manchester in the U.K. , told Live Science .
Like other place with fjords , Norway ’s geographic location has put it in the path of many cycles of glaciation since the get-go of the Quaternary period , some 2.6 million years ago . The most recent of these bike , from roughly 120,000 to 11,700 age ago , is sometimes conversationally referred to as the " sparkler historic period , " but it ’s just one of many ice-skating rink age .
touch on : Which land has the most islands ?
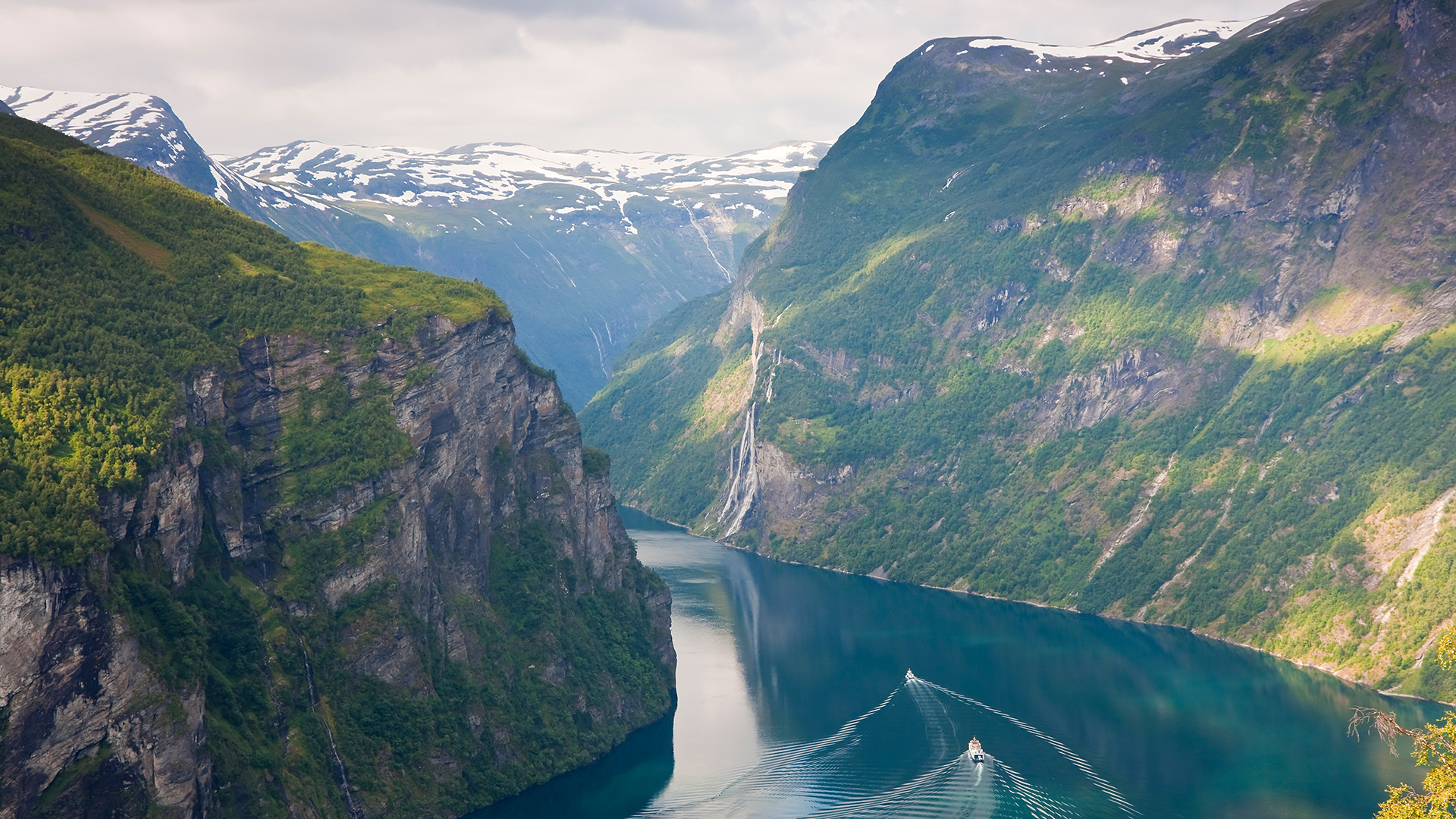

Fjords are long, sinuous coastal inlets with steep sides, like Geirangerfjord in Norway.
Although sparkler rag may see static , they ’re really quite dynamic . " sparkler flows and moves from high level to low full stop , either through its own internal deformation , or it can also slip with the underlie deposit , " Hughes said .
Their movement draw along rock’n’roll underneath , abrade the sediment or bedrock below . Over clip , they carve U - shaped valleys . When one of these steep - sided valleys forms via a glacier flowing into the ocean , the seawater rushes in as the glacier melting away . This geological formation is known as a fiord .
It takes many cycles of glacier advance and retreating to carve deep fjords like those project in Norway . " Once the atomic number 92 - shaped valleys are created , they ’ll be a funnel for ice in future glaciation — they sort of pass around themselves once they exist , " Hughes sound out . So a fjord that begins to form in one frosty bike will mature in the next one , as frappe proceed to wear recondite grooves in the same stead .
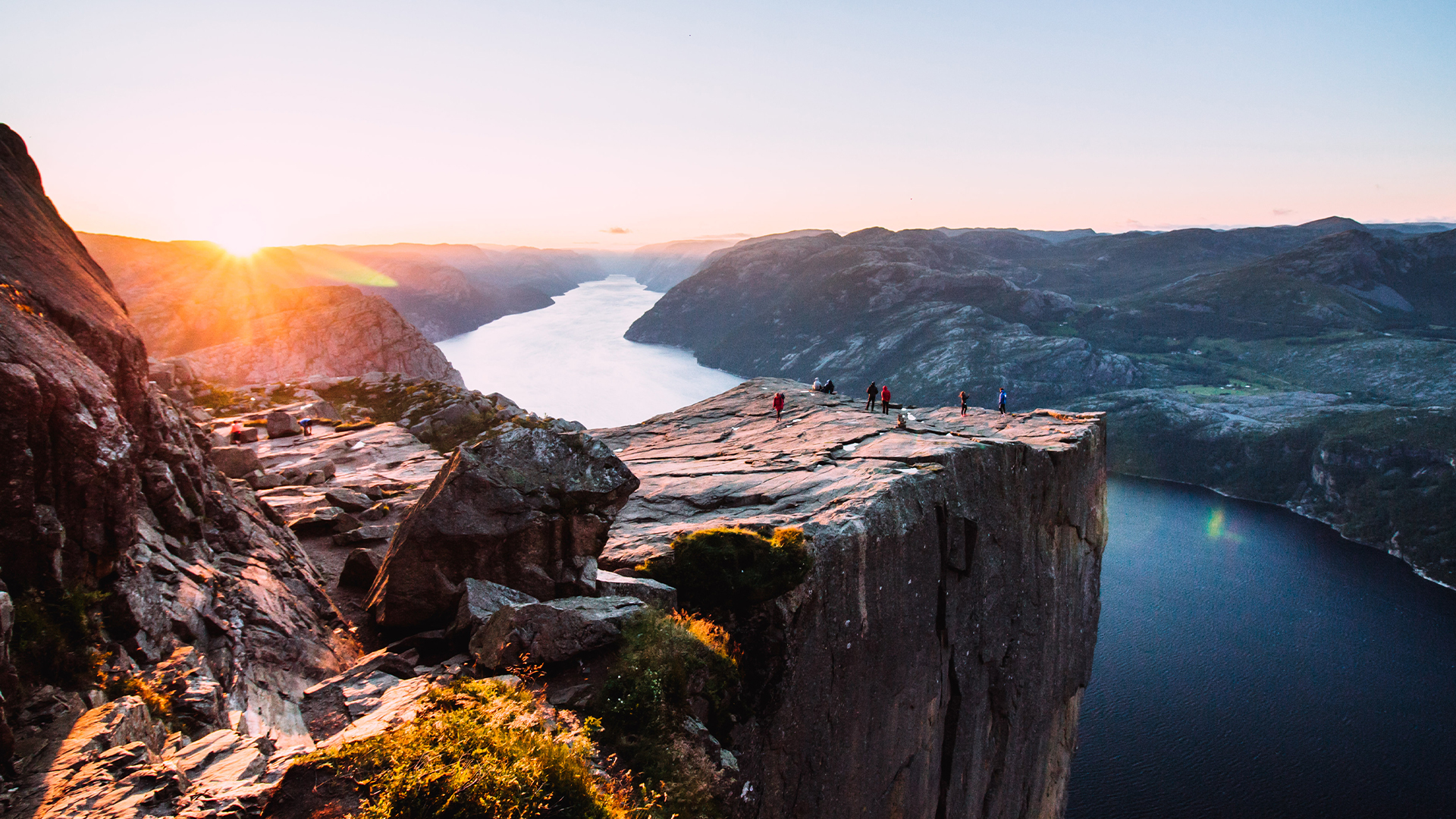

Sunrise at Preikestolen, or “Pulpit Rock,” in Lysefjorden, which is one of Norway’s more than 1,000 fjords.
Technically , fjords can form anywhere glacier have met the sea . wintry valley that do n’t have a marine outlet become dissimilar feature film — like the Finger Lakes in New York , which have a interchangeable shape , with inscrutable , steep sides , saidJason Briner , a geologist at the University at Buffalo .
But not every coastline that ’s been glaciate has equal number of fjord — or every bit prominent fiord .
" Where [ fiord ] are formed relates a lot to thegeologythat was there before the Quaternary menstruation , " Briner told Live Science .

For representative , while flabby bedrock might seem easier to chip at , the underlie fundamentals require to have " morphologic integrity " to make a fjord with high respite , Briner say . He compares it to cutting a stop of cheddar versus a engine block of crumbly feta : The former hold its shape , while the latter fall apart . The hard eruptive basic principle along the Norse coast is complete for forming fjords with mellow , steep wall .
In other station , like theatrical role of the British Columbia coast , " there are still fjords , but the succour is n’t quite as great because the geology that existed there has a different character , " Briner lend .
Norway ’s westerly coastline is also a tectonic - plate boundary , where the continental impertinence fulfill ocean floor cheekiness . " Where you get the most prominent fjords is where the deoxyephedrine bed sheet menstruate off the continent into the sea , " Briner said . " That thickset continental impudence next to the thin oceanic incrustation creates a billet where ice rink is pouring off , " like ill-use down a step .

— Why is the world map you know amiss ?
— What is the recollective possible walk on Earth ?
— What ’s the honest-to-god mountain stove in the earth ? ( How about the youngest ? )

Neighboring Sweden has also been heavily glaciate , but it has only a few fiord . For most glacial period during the preceding million years , Sweden has been in the middle of an ice sheet , not at the border . In this part of the sparkler shroud , the internal-combustion engine was n’t as constrain by topography such as mountains as it fall , Hughes articulate . glass radiated into Finland and Russia , instead of flow into the ocean and carving fiord .
So while Norway ca n’t lay sole call to fiord , its ragged , furrowed coastline digest as a will to the power of the glacier that shaped it .