When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Every fall , so - called leaf peepers journey to places like Colorado , Vermont and Massachusetts to take in colorful fall foliage . From coast to coast , green timber slide into dark glasses ofred , yellowed and orangeas the seasons deepen , and you may oftentime it good to get the best views .
But why do plants undergo this radical modification , and how do they know when to commence ?

Plants begin to shift their leaf color in response to seasonal cues.
Within temperate and boreal forests , trees and shrubs that throw their folio are call in deciduous plants ; they admit groups such asaspens , cottonwoods , maple and oaks . On the other end of the spectrum are plants that do n’t shed their leaves — for case , the pines , spruces , true cedar and fir that make up the coniferous tree , or evergreens . Both types of Sir Herbert Beerbohm Tree produce less vigour in the winter , but conifers have adaptations , such asa waxy coating to minimize piddle loss , that aid them keep their phonograph needle twelvemonth - orotund .
According toAdam Moore , a supervisory forester with the Colorado State Forest Service , trees of all variety plunk up on cues from their environment , much like we do , that secernate them when it ’s clip to start train for winter . In early spill , the atmospheric condition condition take up to change : It get cooler — with sharp , but not freeze , nights — and the continuance of daylight is reduced . Collectively , there ’s less sunshine for plants to harvest using the chlorophyl in their leaves , so deciduous trees begin to pull back their investment in keeping them alive .
" Trees are like a factory , and they like to be efficient , " Moore told Live Science . " They ’re producing atomic number 8 for us and vigour for themselves , and without sun , they start to close up up workshop for the time of year , so to speak . " By the time the first freezes hit , the Sir Herbert Beerbohm Tree are well on their style to dormancy .
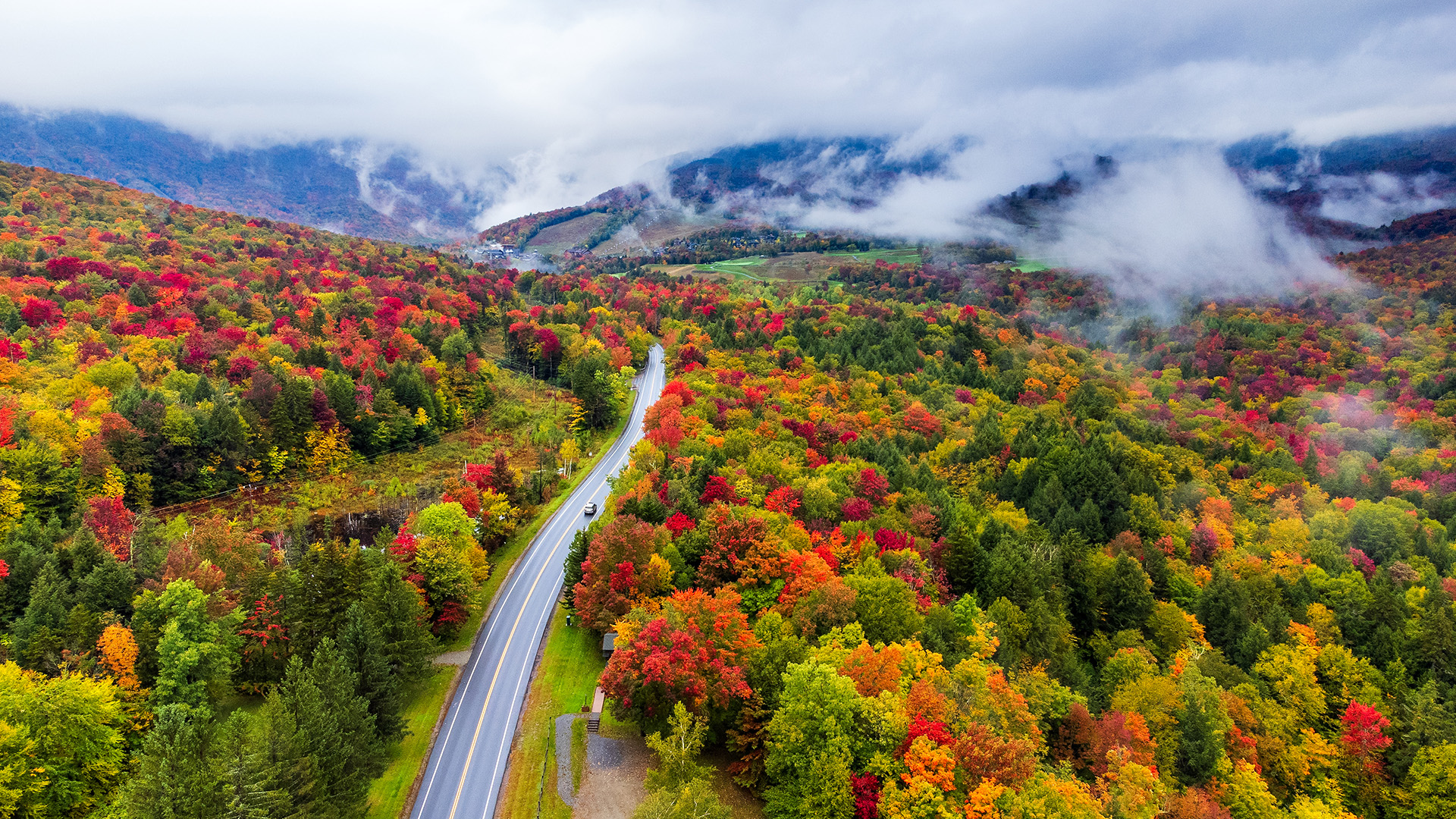

Plants begin to shift their leaf color in response to seasonal cues.
Related : The 12 grownup ' small ' mysteries of fall — lick !
While chlorophyll is the most common pigment that plants use to harvest luminousness — light-green leaves count that path because chlorophyll absorbs reddish and blue light and think over greenish visible radiation — plant often have a variety of petty pigments , too . As the chlorophyl in a tree ’s leaves begins to wane , these inherent pigments become visible . This is what we ’re construe when descend leaf tip , Kristina Bezanson , an arboriculturist at the University of Massachusetts Amherst , told Live Science in an e-mail .
Red and purple chromaticity stem from secondary pigments called anthocyanins , while carotenoids and xanthophylls yield orangeness and yellows , severally . Within a undivided radical , such as the maple , dissimilar coinage have evolved their own retinue of pigment . Red maples , for object lesson , grow a brilliant scarlet in the fall , while black maple become yellow .
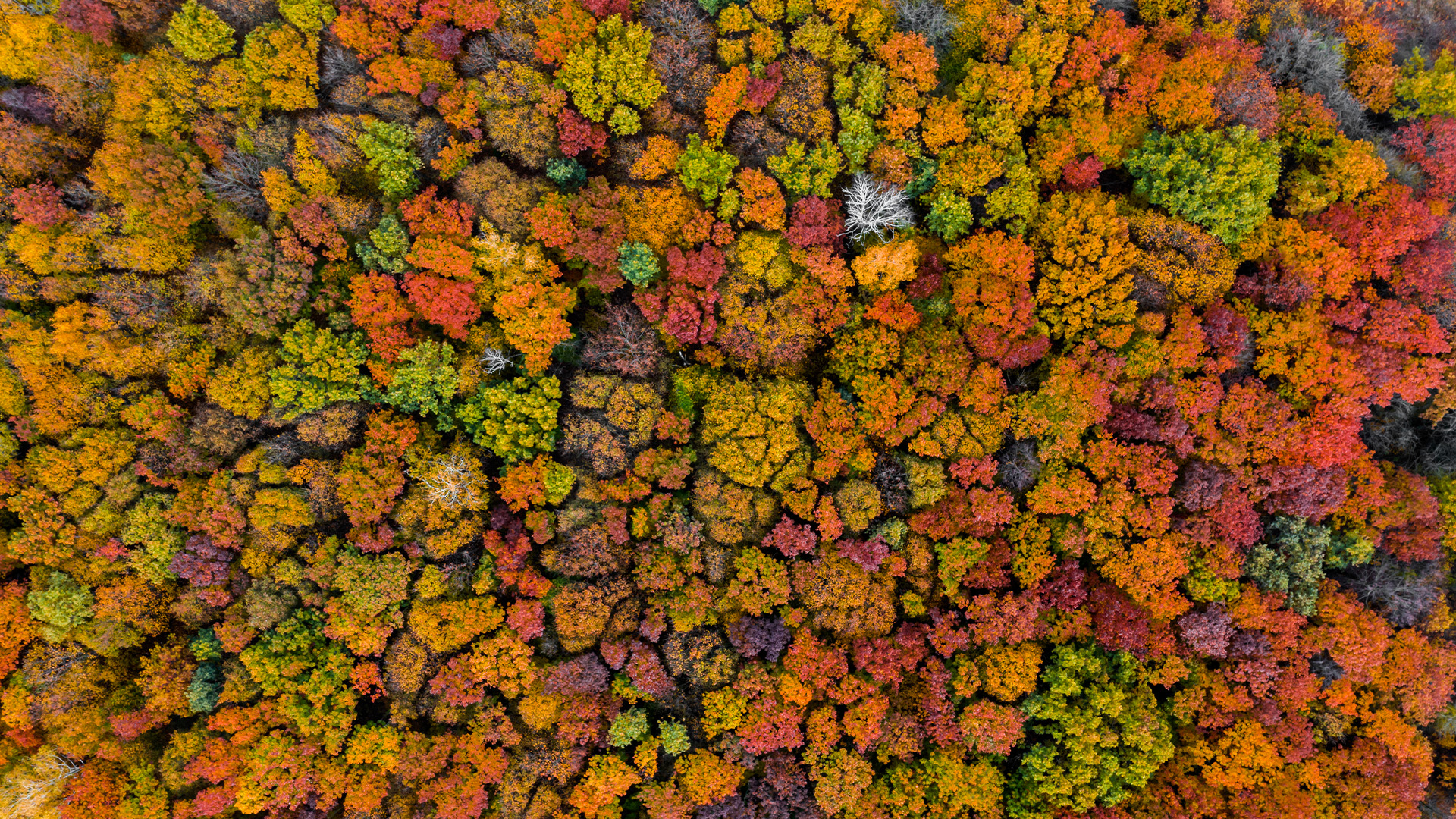

Deciduous trees that lose their leaves each winter are the ones that feature colorful displays in the fall.
And while these pigments make the Tree beautiful , they also serve an important purpose .
" call up that trees are autotrophs ; they make their own nutrient throughphotosynthesis , and the leaves are often called the ' food factories ' for the tree diagram , " Bezanson said . Having a range of pigments that can direct different wavelengths of light allows plants to harvest more get-up-and-go during photosynthesis . It can be expensive to induct in so many pigments , so not all trees quest after this scheme . But those that do are oftenrelatively truehearted growers .
While much of the fall prime is driven by the environment , the timing of the colour modification is at least partly dictated by genetics — in one experiment , investigator observe thattens of thousands of geneswere expressed differently during the color - modify period . Some species , like sorrel tree ( Oxydendrum arboreum ) , come out to shift color as too soon as former summer , while oak often drop their leaves long after other tree diagram are stark . Scientists have also take note that members of the same species living at a alike latitudewill alteration colour at the same timeregardless of elevation , when trees populate at higher , colder natural elevation would typically be expected to change first because of the ice chest temperatures .
— Why nightfall colour are unlike in US and Europe
— Why is grass green ?
— Do trees exist ( scientifically address ) ?

But as winter patch up in , deciduous plants eventually shed their leafage , result behind small-scale , round " leaf scars " at the guest where the leafage attaches to the tree . Even in their denuded , naked commonwealth , trees still cater worthful ecosystem services . They block malarky and go along to provide valuable habitat for bird , and fallen leaves ply nutrients as they violate down into the soil . " Shedding leave yearly helps build the soil by making mulch , blanketing the soil over the roots during wintertime " to keep them warm , Bezanson say .












