When you purchase through link on our website , we may clear an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
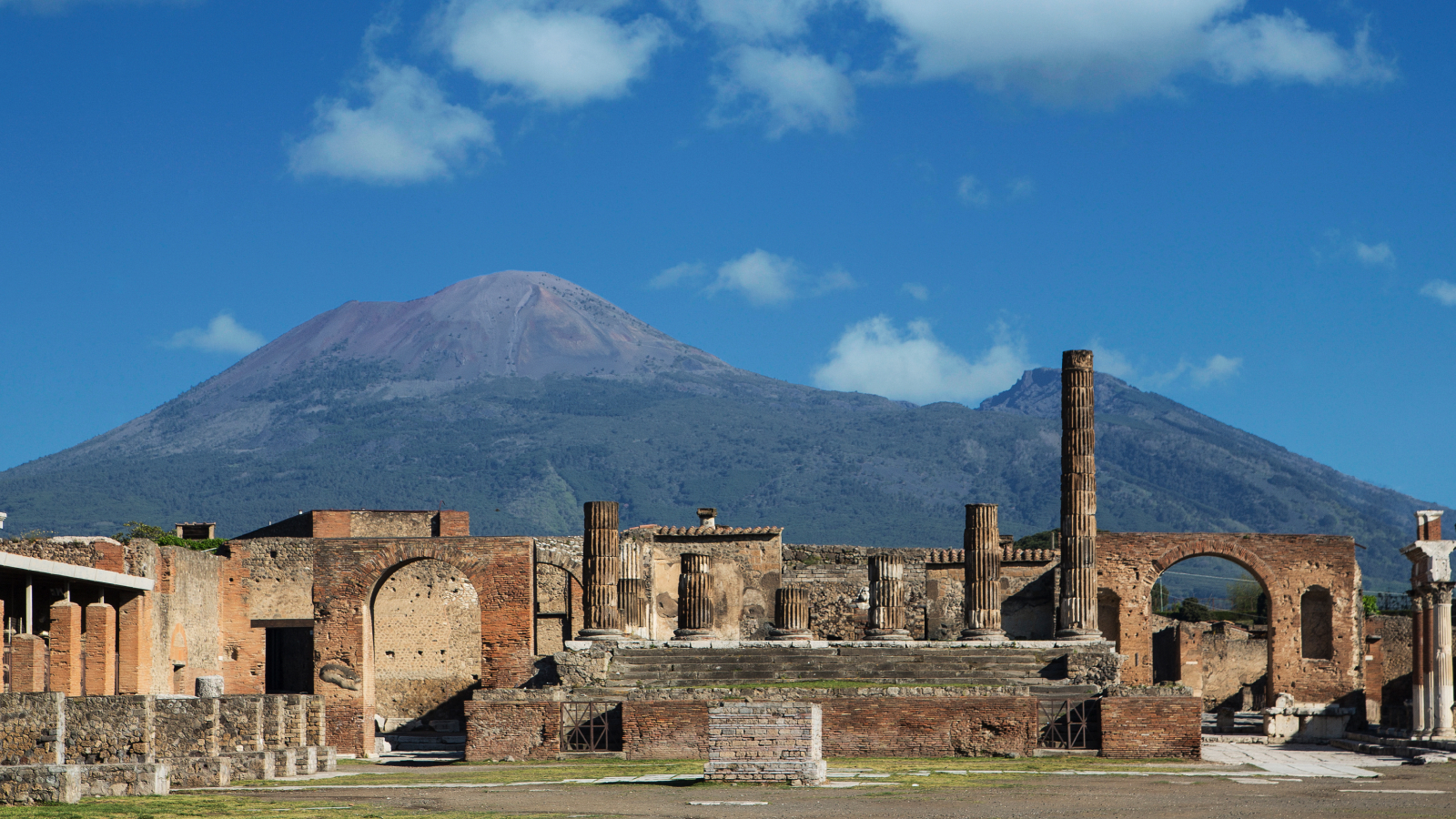
Alexander the Great conquer a monolithic empire that stretched from the Balkans to modernistic - daylight Pakistan . But if the Macedonian king had turned his attention westwards , it ’s possible he would have conquered Rome , too , feasibly smiting theRoman Empirebefore it had a hazard to arise .
So why didn’tAlexander the Greattry to conquer Italy ? The answer may be that he give way before he got the chance .

Alexander the Great conquered one of the largest empires the ancient world had ever seen. So why didn’t he set his sights on Rome?
The king of Macedonia ruled from 336 B.C. to 323 B.C. , when hedied of an unsung illnessin Babylon at age 32 . Alexander ’s empire go down apart soon after his death . Had he not give-up the ghost , however , it ’s possible that Alexander would have targeted Rome and , with his substantial forces , overcome the Eternal City .
Some ancient texts suggest that Alexander the Great was planning a military campaign in the West that involved conquering parts of Italy , among other localisation along the Mediterranean . The R.C. historiographer Quintus Curtius Rufus , who live in the first century A.D. , claimed that Alexander the Great had plan a serial of conquests that , if successful , would have expand his conglomerate all the way to what is now the Strait of Gibraltar . Alexander planned to construct 700 ships to support this intrusion , Rufus observe . Other ancient writers made similar claim .
" The Romans were convert that Alexander would have attempted the seduction of Rome , but for modern historians , it is impossible to say,“Nikolaus Overtoom , an associate professor of history at Washington State University , told Live Science in an e-mail .
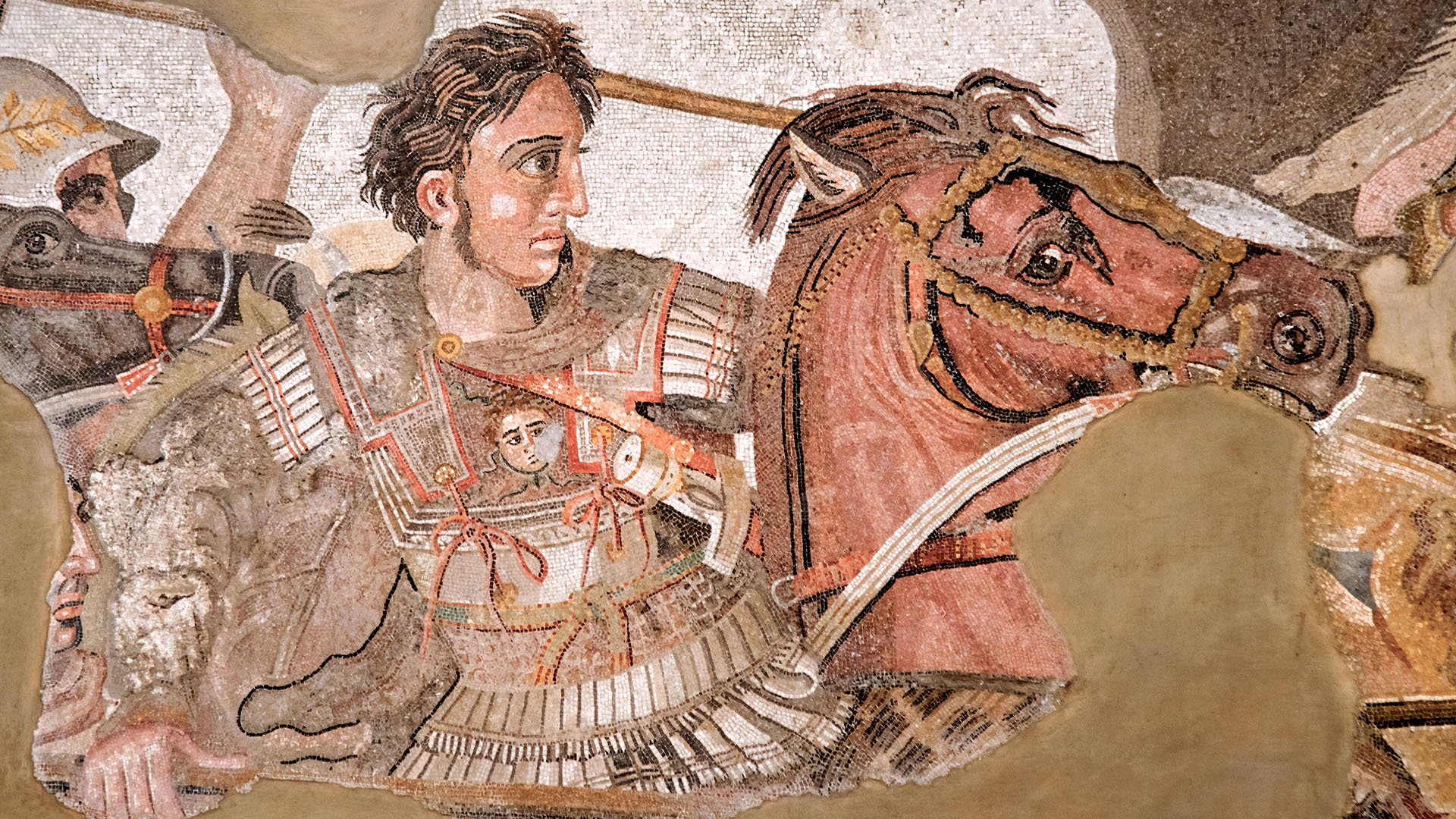

Alexander the Great conquered one of the largest empires the ancient world had ever seen. So why didn’t he set his sights on Rome?
associate : Where is Alexander the Great ’s grave ?
Some ancient writers claimed that after Alexander snuff it , his secretary , Eumenes , gave one of Alexander ’s elderly generals , Perdiccas , plan that included the conquest of part of Italy , Robin Waterfield , an sovereign scholar with a background in classic , enjoin Live Science in an e-mail .
" Now , some scholars believe that the [ plans ] are not genuine — perhaps a forgery by Eumenes , or perhaps the whole story arose yr , even decades later on , " Waterfield said . However , " I think the balance of grounds is that they ’re genuine . "
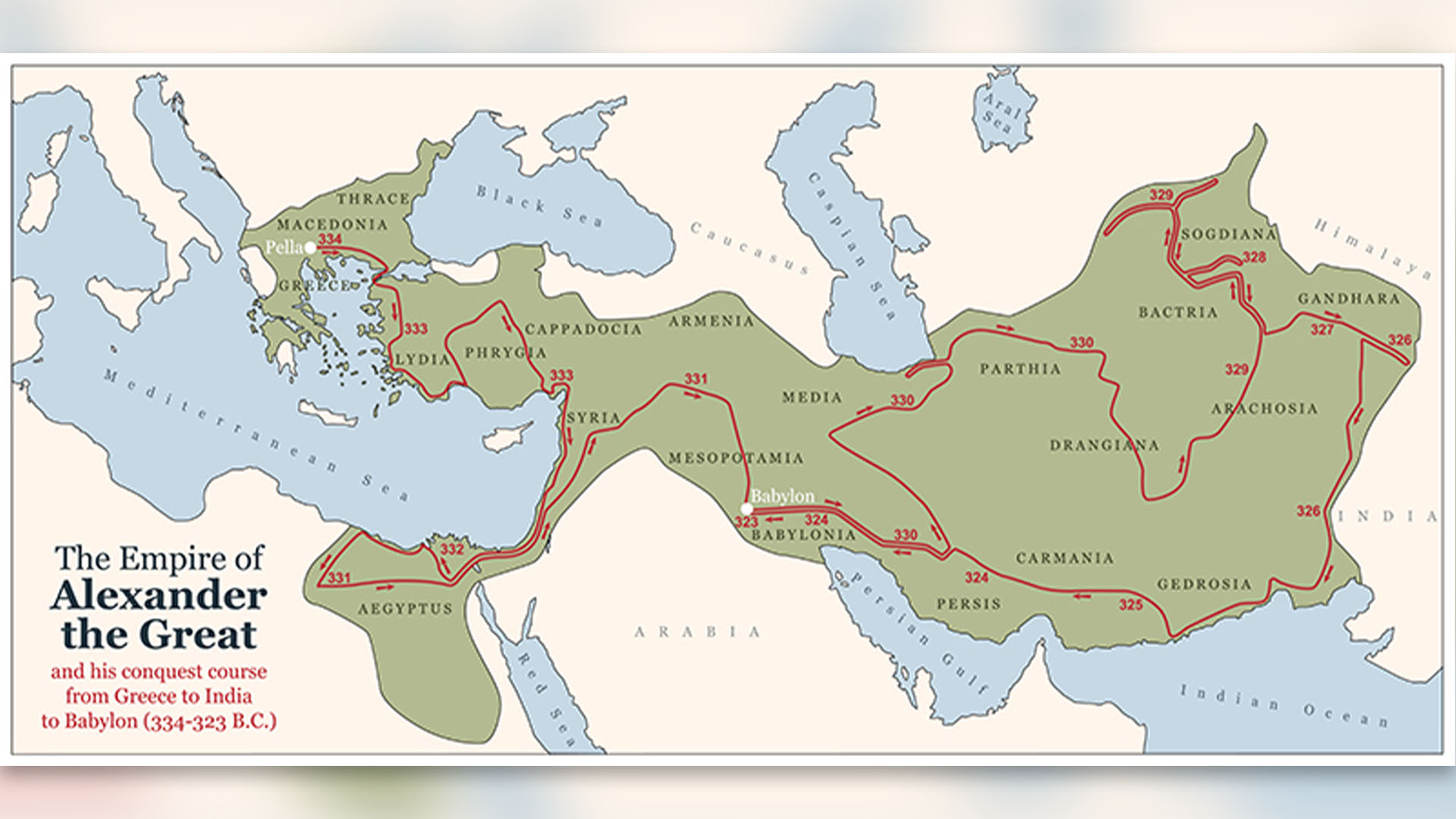
The route Alexander the Great and his forces took while conquering his vast empire from 334 B.C. until his death in 323 B.C.
How would the invasion have gone?
It ’s ultimately unclear what would have happened if Alexander the Great had attempt to invade Italy . The Romans were so strongly positive that Alexander would have attempted the invasion that the historian Livy ( lived circa 59 B.C. to A.D. 17 ) wrote a textual matter hypothecate how the encroachment would have ended , with Livy predicting that the Romans would have get the better of Alexander . Livy note that Alexander ’s uncle , Alexander I of Epirus , who ruled a land of the same name , tried to conquer part of Italy but was kill in struggle in 331 B.C.
Waterfield note that descriptions of Alexander ’s plan indicate he would have invade other locations in the Mediterranean before landing on the Italian mainland . This evoke that Alexander ’s forces would have been overwhelming , even if the Romans had any allies in their fight against him .
" By the time he hand Italy and faced theRoman Republiche would have had the resource of the entire Mediterranean at his mastery — a vast moneymaking regular army , and he ’d have command all the supply routes , " Waterfield say . The " only matter that could have hold on him was internal rising or mutiny by his Macedonian troop . "

— Did Alexander the Great have any children ?
— Who really wore togas ?
— Did all roads run to Rome ?

Philip Freeman , a humanities prof at Pepperdine University in California , say that if Alexander had invade Italy , he in all probability would have succeeded , noting that there were a number of Greek colonies in Italy that might have supported Alexander ’s rule .
" The Romans were tough and would have resisted , but they were not yet the powerful force of later C , " Freeman told Live Science in an electronic mail . " If Alexander had invaded , I opine there would have been no Roman Empire since Roman power would have been nipped in the bud , so to speak . "













