When you purchase through links on our land site , we may make an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it put to work .
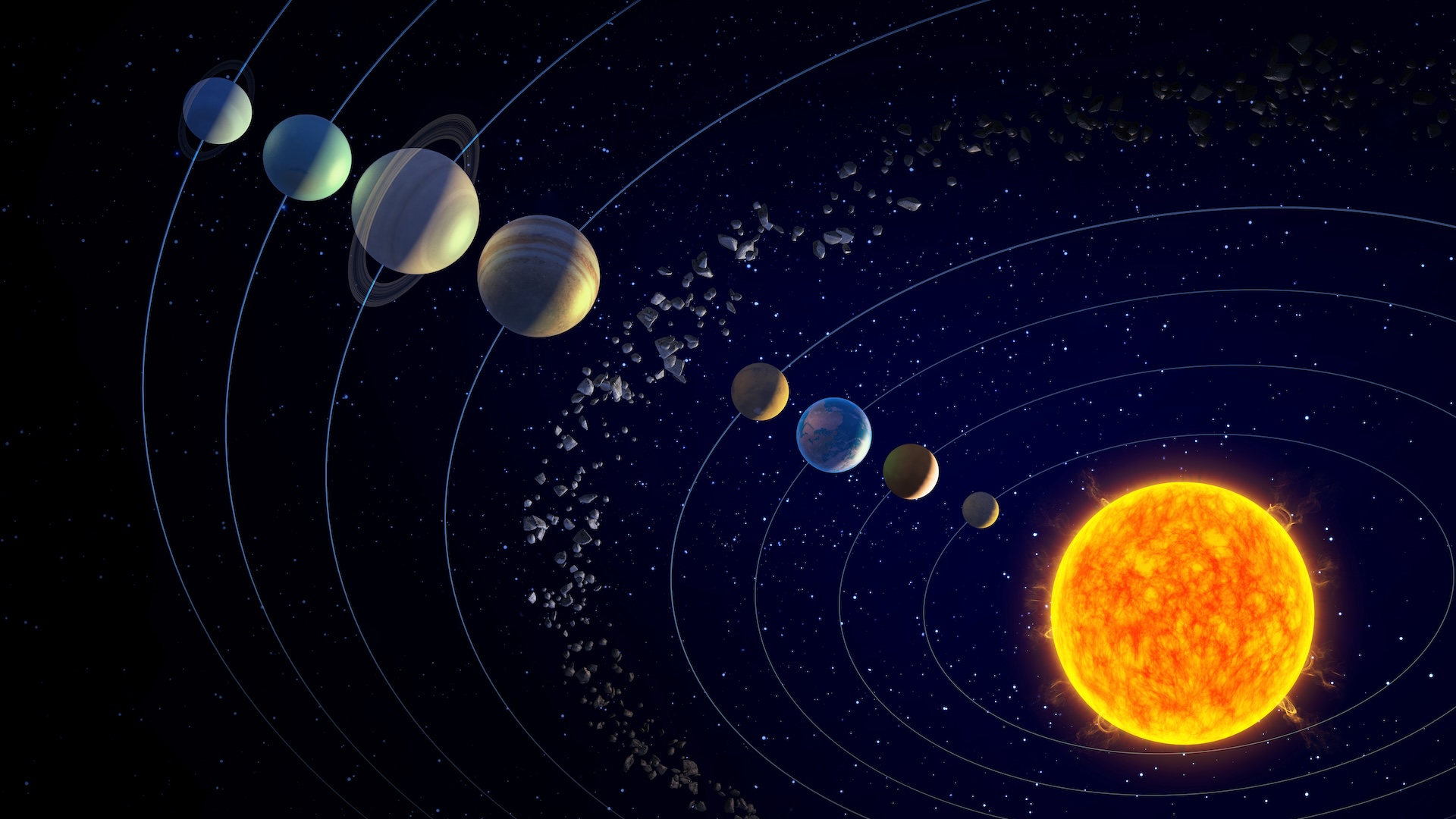
Many maps of thesolar systemmake it look as though everything in space moves in perfect , concentrical circles . planet orbit the Sunday , and Moon orbit the planets . So that must be the case for everything in outer space , good ?
Not quite . Orbits form all sort of shapes . " Planets and other body rarely go around in perfect circles,“Paul Wiegert , an astronomer at the University of Western Ontario , evidence Live Science . Cometshave so - called hyperbolic domain , meaning they slingshot from one degree and back again . Asteroidscan travel in complicated loops around planets . Even the moonlight ’s orbit is wobbling , tardily inflate twelvemonth after class as ittwirls around the Earth .

Saturn’s 146 moons orbit the ringed planet. But do all celestial bodies orbit in a circular path, or do they have stranger routes?
So how do these diverse paths shape ?
First , it ’s authoritative to understand the physics behind motion in quad . When it comes to orbits , there are two main strength at work . The first is impulse : When an object is in motion , it has momentum that propels it in a specific instruction . The second is gravity , an attractive force , saidRenu Malhotra , a prof at the University of Arizona who analyse orbital dynamics . Objects , particularly large ones like planet , have potent forces of gravity and so can pull moving objects toward them . Together , the pushing of momentum and the pull of gravity soma orbits .
relate : How many satellites orbit Earth ?

Saturn’s 146 moons orbit the ringed planet. But do all celestial bodies orbit in a circular path, or do they have stranger routes?
When gravity and momentum are balance , orbit theoretically work an oval , or oval . This was announce by Johannes Kepler , a 17th - century German scientist who constructed numerical models to figure out how to explicate the movements of planets . Before Kepler , scientist thought planets move in perfect circles . But in picky , Mars ' scope , the most elliptic out of all the planet in our solar system , did n’t correspond that model . Kepler figured out that an oval was the answer to Mars ' path , and explain the track of other planets as well — shaping a law that forms the basis of how we see orbits today .
But the elliptical orbits that Kepler theorized are only approximations of what planet , asteroids and other bodies are actually doing , Malhotra tell Live Science . In reality , the forces of momentum and sombreness on an aim are ever - change . If the momentum is too secure , or if gravity is too weak , dissimilar patterns can forge . comet , for example , are attract by the gravity of the sun , but they have extremely eminent momentum . This allows them to travel rapidly through the galaxy from one point to the next , shape a long ellipse cranial orbit .
The vast measure of object in the universe can also elaborate the kinetics of eye socket , Malhotra enjoin . More objects add more sources of gravity , which can make the question of a planetary body turn of events and turn into more complicated paths .
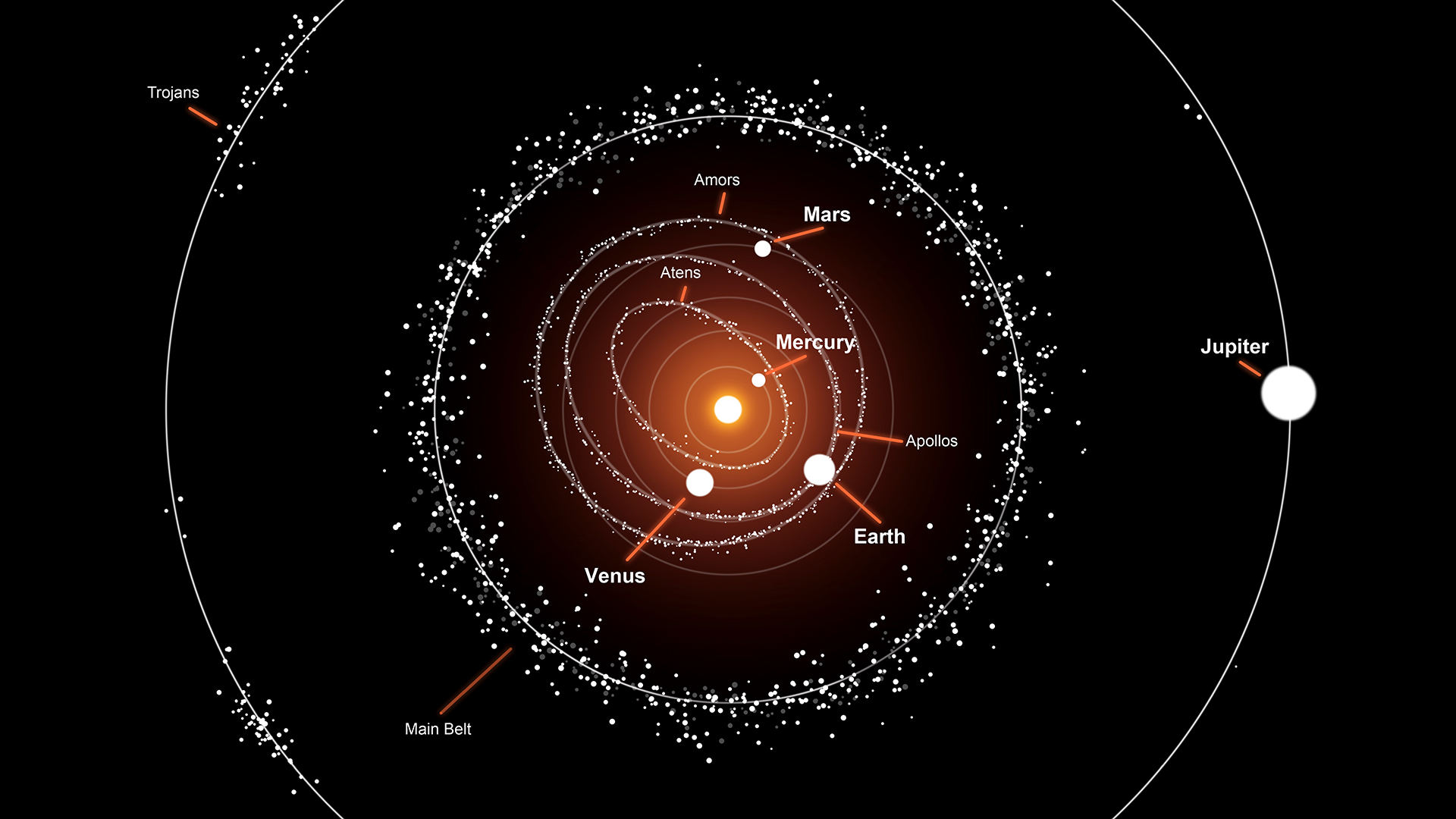
An illustration showing asteroids that orbit the sun. Scientists think the asteroid belt is a planet that failed to form because of the gravitational influence of Jupiter.
For instance , if an asteroid is travel through the solar system , it ends up being pulled by not only the Sunday but also any nearby planet — what Wiegert called " a dynamical relationship . " These bodies are often called quasi - satellite , or quasi - lunation .
The Trojan asteroids , for case , have a dynamical human relationship with Jupiter and the Sunday . They technically trip around the sun , sharingJupiter’sorbit by hover either just ahead or behind the planet . But Jupiter ’s sobriety also pulls the asteroids into a warped ellipse trajectory around the satellite . These eye socket can resemble a polliwog or even horseshoe , seesawing from one point to the next .
— Why are asteroids and comets such weird shape ?
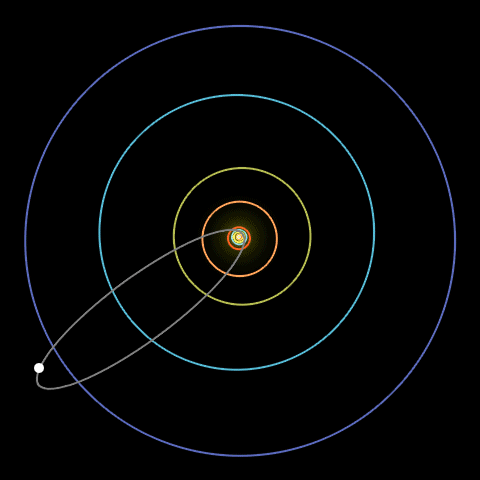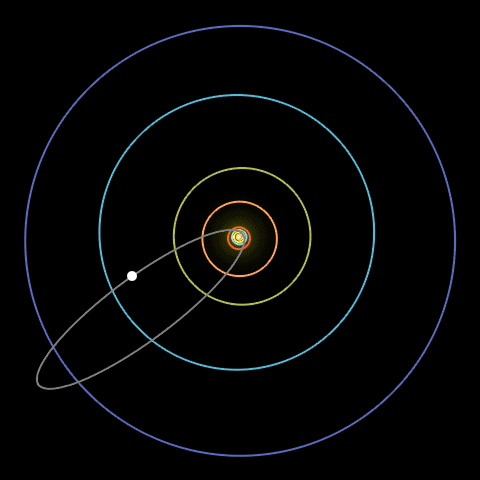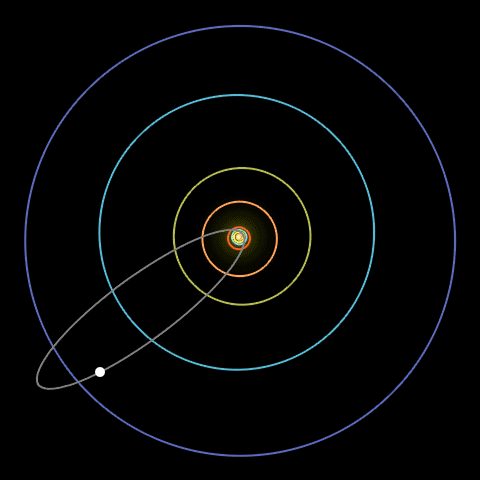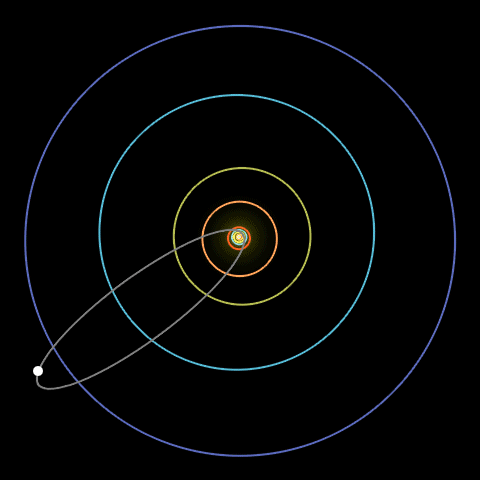
An animation of Halley’s Comet traveling in a long loop across the solar system.
— What are the gravid shock crater on Earth ?
— What ’s the maximal number of major planet that could orbit the sun ?
Another example is Kamo’oalewa , a recently discovered quasi - satellite near Earth that ’s hypothesized to bea chip off the moon . " It ’s actually orbiting the sun , but it ’s orbit close enough that the Earth ’s sobriety modifies its orbit a lot , " read Malhotra , who , along with colleagues , publisheda number ofpaperson this quasi - orbiter .

An animation of 2010 TK7, a near-Earth asteroid, showing its orbit from A.D. 1600 to 2500.
These " strange orbit are quite unstable , " she pronounce . But what ’s interesting about Kamo’oalewa is that it has been hanging around Earth for centuries . It ’s found a recess amid all of the dynamic force at work in orbits , she said .