When you buy through nexus on our site , we may earn an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it run .
mark fall in all shape , sizing and coloring material and are the result of the skin’snatural healing outgrowth after equipment casualty , whether it ’s because of operating theatre , infection , trauma or rapid body increment .
Scars attend to an of import role : They activate the dead body to replace lost or disfigured tissue . But what are scars made of ? And why are they permanent ?
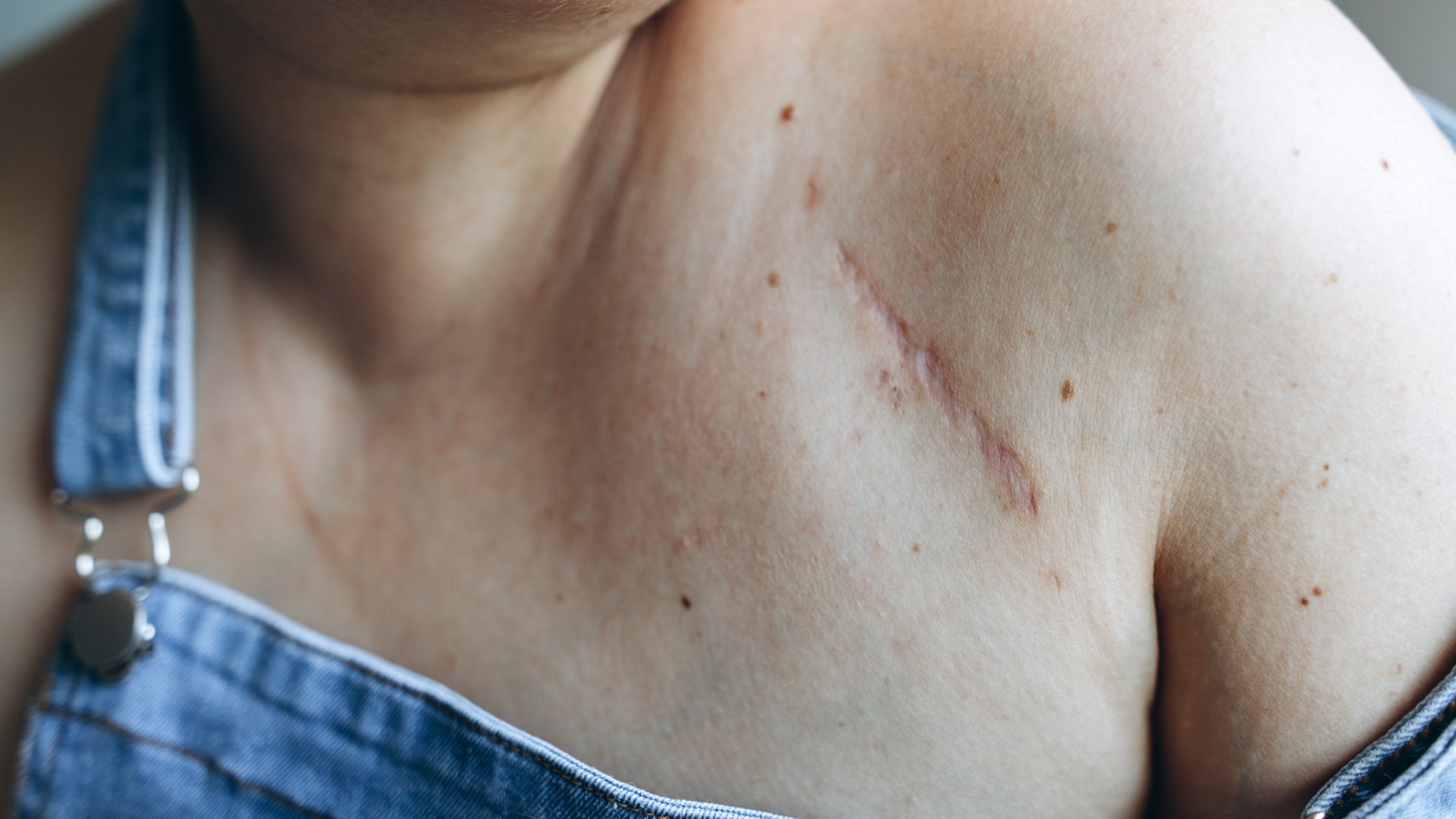
Scars are made of disordered bundles of fibrous protein known as collagen, which are laid down in the skin as the body attempts to heal itself after injury.
To answer these question , first it ’s necessary to clarify what a scar is .
The skin is made ofthree main layers . The outmost level of skin , lie with as the epidermis , is the thinnest layer . It ’s composed of layers of flattened cells , called epithelial cells , which collectivelyact as armour , protecting the body from the outside world .
refer : Self - healing ' living skin ' can make robots more humanlike — and it look just as creepy as you ’d expect
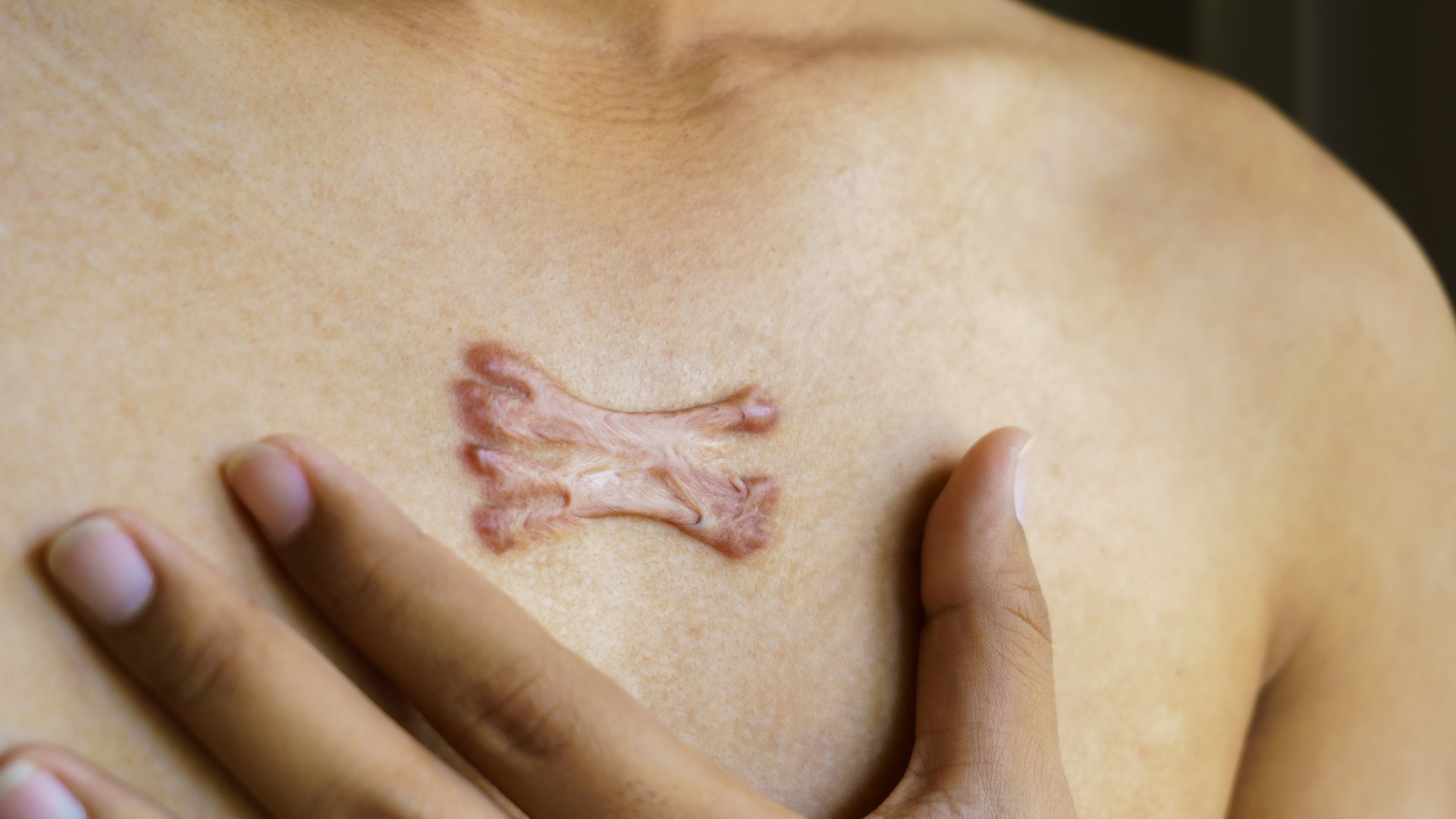
Keloid scars are thicker and more raised than regular scars and are larger than the original wound.
Underneath the cuticle is the dermis , the thickest layer of skin that containsnerves , stemma vessel , fuzz follicles and sweat and crude oil secretor . Within the derma , there is also a gravid , stringy net of proteins hollo collagen and elastin that , severally , support the structure and elasticity of the tegument . Finally , the hypodermis is the cryptical layer of the skin . It contains fat tissue paper for isolate the body , cushioning interior organ and shielding tissues from injury .
If you damage only the epidermis — such as in most cases of suntan — this outer bed of skinwill just peel off , leaving the deeper layer of skin intact . But if an injury infiltrate deep into the derma , the body then has to touch on this damaged tissue . A scab formsto varnish the injury , and then inflammationinitiates healing . Then , the hide begins to recast the tissue within that injury , and the haphazard way it does this is what make a scar to spring .
In normal cutis , the dermis ’s internet of collagen fibre is like a piece of fabric that is carefully woven in a overnice , smooth pattern , Dr. Damon Cooney , an associate professor of credit card and reconstructive operating room at Johns Hopkins Medicine , told Live Science . If an trauma shoot down this fabric , the body makes new collagen fibers to fill in any break .

However , instead of nicely weave the new fiber back together across the injury , the body dump them all together in a jumbled galvanic pile , Cooney said . This disorganised buildup of collagen makes up most scar tissue paper , making it look different from — andmove less flexiblythan — normal skin .
Scar tissue paper also differs from unscarred tegument in that itdoesn’t turn back any hair follicles or sweat glands . In people with light tegument , a scar may first appear pink or red , but over time , this coloration will evanesce and the scar will becomeslightly clear or darkerthan their normal tegument color . The scars of people with darker skin will often look like drear spots .
Sometimes , the body continue to lay down collagen within scar tissue paper for longer than it commonly would , do what ’s known as a cheloid or a hypertrophic cicatrix to form . These are boneheaded , raised scars that can be red , pink or violet , or just subtly sullen than a individual ’s normal skin tone . Keloid scars arelarger than the original injury , while hypertrophic mark are the same size .

teen and fraught cleaning lady aremore likely to develop hypertrophic scarsthan other groups , possibly because ofhormonal modification that boost inflammationin the body . Keloid cicatrice are more vernacular in citizenry with gloomy skin tones , in all likelihood due to genetic hazard constituent .
Related : Why do wrinkles form ?
Scars can fade over time as the disorderly collagen character within them start to flatten and smooth out out , Cooney say . This operation can take aroundsix to 18 months . How much a scar fades bet on itssize , emplacement and character . However , scrape never in full vanish , because the jumbled tissue persist basically unlike from the skin around it .

In theory , there could be a way to trigger scar - free healing in humans . Some animals , like salamanders , cancompletely regenerate hurt skin , leave no scrape behind . humanity can also do this , but only as fetus , during the first two trimesters of gestation . Beyond that point , we lose the power to renew injury tissue , and scientist do n’t really bed why .
Animal studieshave shown that pelt transfer from an adult to a fetus will still pock . This suggest grownup cutis cell are programmed in a room that causes them to scar , rather than regenerate , after injury . Differences in thenumber and placement of bow cellswithin skin may also explain why only fetal wounds regenerate . However , this research is still in its babyhood .
The " Proto-Indo European in the sky " goal would be to develop a therapy that allow the torso to exchange from scar to positive feedback , Cooney say .

— Skin cells made 30 age younger with new ' greening ' technique
— Is collagen beneficial for hide ?
— Viruses unleashed into a woman ’s wound to slay superbug in her leg

In the meantime , some treatments can reduce the appearance of scars . For instance , laser therapycan change the color and height of a cicatrice , while rub down a scratch , peculiarly withsilicone gel sheets , can avail smooth and flatten out it , Cooney said .
Other treatment options includescar revision , whereby doctors surgically remove a scrape and create a new one that is more uniform in appearance . Steroid injectant can alsoreduce the sizeof hypertrophic and keloid scars . These injection helpdisband the collagen fibersin these scars and reduce the inflammation that can do the tissue within it to swell .
Ever question whysome people make brawn more easy than othersorwhy freckle come out in the sun ? broadcast us your questions about how the human body work tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject production line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answer on the website !

star at the March 29 solar eclipse can cause eye damage in seconds — and you wo n’t even feel it happen
New cells discovered in oculus could help oneself restore vision , scientist say
See the reconstructed place of ' polar dinosaurs ' that thrived in the Antarctic 120 million years ago




