When you purchase through radio link on our site , we may earn an affiliate direction . Here ’s how it exploit .
On Earth , a compass can be a lively tool . Compasses have offer a ceaseless point of address for humans forover 800 twelvemonth , enabling us to successfully navigate to the far reaches of the planet .
But our mintage has started to journey far , into the moth-eaten abyss of space . Is the range still useful outside the bound of our satellite : And if so , where would it point ?

A compass would still respond to Earth’s magnetic field 230,000 miles away from the planet.
" A range in space is going to valuate different thing [ look on ] where incisively in infinite you are,“Jared Espley , a planetary scientist atNASAGoddard Space Flight Center in Maryland , secern Live Science . A compass would still technically process in space , but it would n’t necessarily steer you back to Earth . Instead , it would point to the north perch of whatever magnetic force field is the strongest , relative to where in space the grasp is located .
A compass on Earth reply to our planet ’s magnetic field . The range itself is a magnet , and its north polenaturally alignswith the south pole of our planet ’s own magnetic field . Themagnetic fieldis bring forth by galvanizing currents flow through the molten , metal nub of our planet , which spin into an locomotive call a geodynamo . Earth is the only rocky major planet in thesolar systemwith such a strong magnetic orbit .
link up : What if Earth ’s magnetic field disappear ?
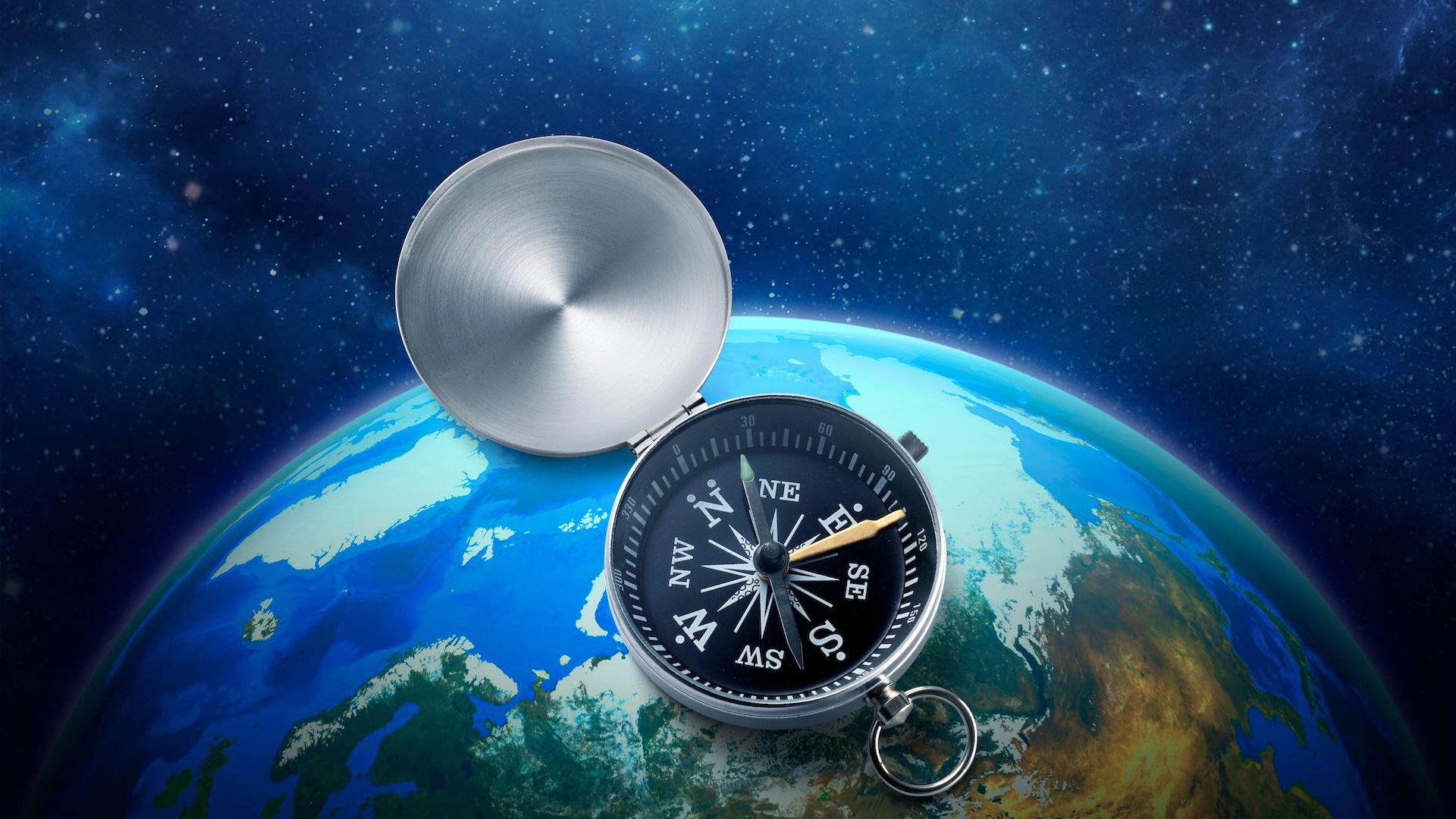

A compass would still respond to Earth’s magnetic field 230,000 miles away from the planet.
This magnetized force field bubbles out from the major planet about 23,000 miles ( 37,000 km ) on the side that faces the Dominicus and track at least 230,000 miles ( 370,000 km ) behind the major planet , according toNASA . This region around a satellite dominated by the planet ’s magnetic line of business is know as the magnetosphere .
An cosmonaut who wanted to use a ambit to get back to Earth would likely need to be within this magnetosphere for the compass to record the planet ’s magnetized field . However , the magnetic field is n’t a particularly hard boundary . " Even beyond the classical magnetosphere , where you would say it ’s the Earth ’s field that is dominant or noticeable , you may still detect thing really far away , " Espley say .
Evidence from lunar rock and roll suggest that the moononce had a magnetized battlefield , but the natural satellite ’s interior core has since slow down and chill , causing it to lose its geodynamo . And , like the moon , other celestial consistence in our solar system now lack a strong magnetic subject . For example , around3.9 billion years ago , Mars ' geodynamo mysteriously slowed down , dramatically weaken its magnetic field of force , which eventually resulted in the loss of its atmosphere .
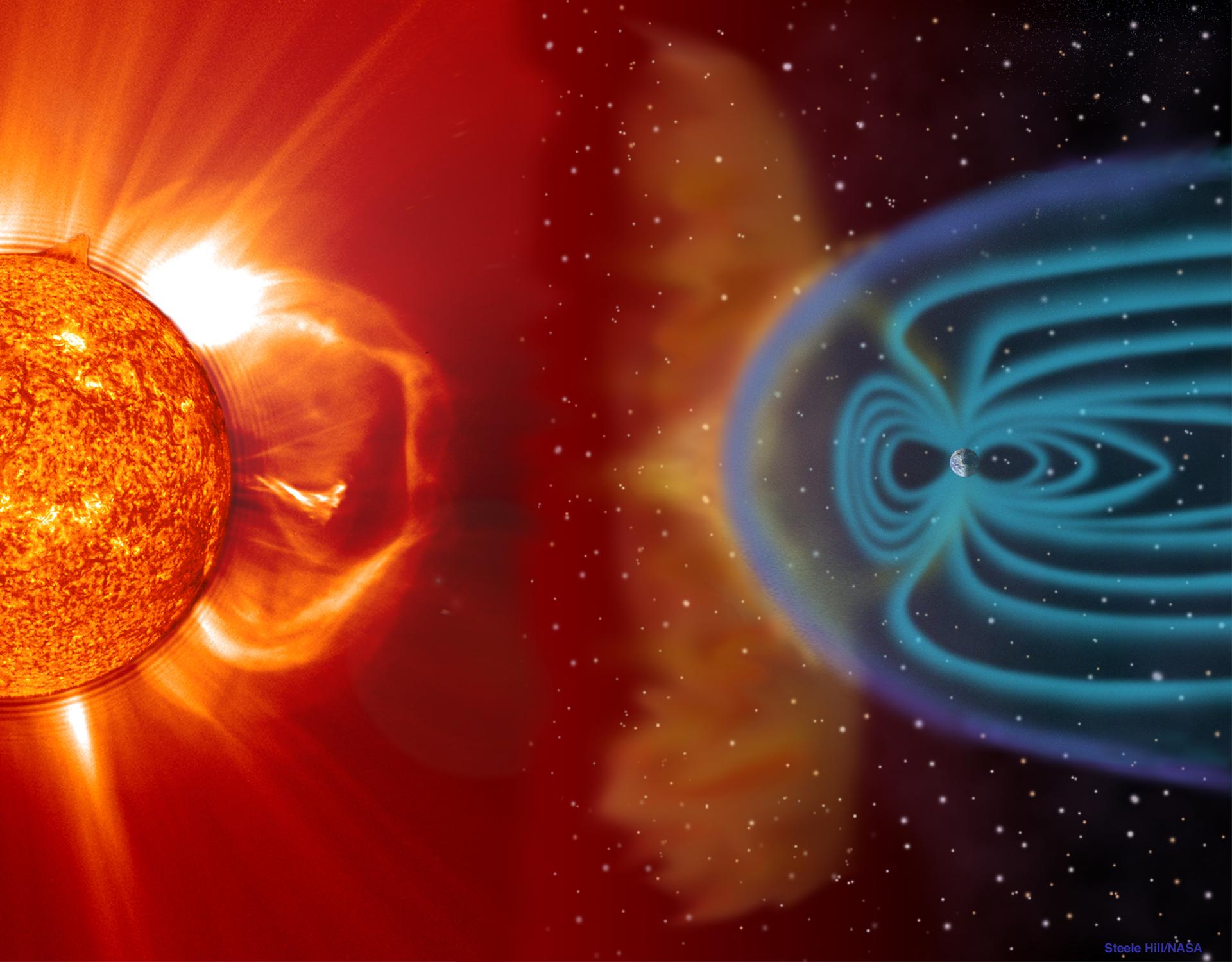
The sun’s magnetic field can be measured on a compass past the farthest planets in our solar system.
But even without these celestial bodies ' planetary magnetic fields intact , an astronaut standing on the moon or Mars would still pick up some magnetic signaling . This is thecrustal charismatic field of honor , Espley said — rock on the outer crust that still hold grounds of the major planet ’s old geodynamo .
Of all the planet in the solar system , a compass is most potential to direct toward Jupiter . This is because Jupiter ’s magnetosphere is monumental . harmonize toNASA , Jupiter ’s magnetosphere is the largest bodily structure in the solar system , at 12 million miles ( 21 million km ) wide . This giant star magnetosphere is generated by the major planet ’s metallic hydrogen core and is currently being studied by theJuno spacecraftto better read how magnetised fields are create .
But what if an astronaut is n’t within a planet ’s magnetosphere ? Most of space is seemingly empty . But within our solar system , one magnetosphere overshadow all others : that of the sun .

" If you ’re in this stereotypical mysterious infinite vacuum in between the satellite , [ a orbit ] is mostly going to evaluate what magnetic field is get from the solar wind , " Espley said .
The sunshine ’s magnetosphere , known as theheliosphere , spirals out from the star and extends three times far out than Pluto . This is because the Sunday ’s solar wind gestate its own faint magnetic theatre of operations as it blasts out into the solar system , according to theNational Magnetic Field Laboratory .
The magnetic field direct on the sunlight is also rather messy , which can be seen in images of the Dominicus ’s coronal cringle . These arches of blood plasma follow the sun ’s magnetised battlefield argumentation , which raise big and more complex as the sunshine reaches itssolar maximum , the peak full point in its activity . It ’s so complex that the true north and south of the star begin to get a little act blurry , and eventually swap seat , according toSpace.com .

— Is there an ' up ' and a ' down ' in space ?
— What does place odor like ?
— Have all 8 planets ever aligned ?

at long last , a traditional compass that rely on an " up " and " down " to calibrate it would be rather wasted in place as a navigational tool . There are a few commercially available " three-D " compasses that could theoretically point you toward charismatic north in blank . However , they still would n’t necessarily point you back to Earth — only to whichever magnetised field is skinny .
However , highly hefty reach scream magnetometers are useful in space , just not for navigation . NASA uses these pawn to empathize more about plasma interactions in space and to pick up ancient signs of geodynamos that died billions of yr ago . " Measuring the magnetic field is passing useful for understanding what is go on inside of a planet , " Espley said .
place exposure of the week : Bizarre 1 - armed spiral galax stun Hubble scientists

Soviet ballistic capsule Kosmos 482 crash back to Earth , disappear into Indian Ocean after 53 class in compass
The ceaseless surveillance of modern lifetime could worsen our brain function in ways we do n’t fully understand , disturbing report suggest





