When you purchase through connection on our web site , we may earn an affiliate committal . Here ’s how it works .
Sea levels are rise as climate change rapidly melts glaciers and ice-skating rink rag and thewater within the oceans expandsin a thawing world . But have ocean levels ever been higher than they are today ? And when were they the highest ?
In brusk , sea levels have easily been higher than they are today . But it ’s still unclear exactly when they were at their highest , although scientist have a few idea .

Researchers have two main ideas for when Earth’s sea levels were highest.
Within the past half - billion years , ocean levels likely peaked 117 million years ago , during the Aptian age . At this prison term , which was part of theCretaceous period(145 million to 66 million years ago ) , ocean levels were around 700 infantry ( 200 meters ) higher than they are today , according to a 2022 report in the journalGondwana Research .
" Over the retiring 540 million age , the high sea storey were in the Cretaceous , at the time when the dinosaurs were walking the Earth,“Douwe van der Meer , the study ’s lead author , an exploration geoscientist in the oil and accelerator pedal industry and a guest researcher at Utrecht University in the Netherlands , tell Live Science . " Beyond that , it ’s essentially speculation,“Jun Korenaga , a prof of Earth and planetary sciences at Yale University , secern Live Science .
Korenaga’sresearch suggeststhat ocean levels were high-pitched much earlier inEarth ’s roughly 4.5 billion - year - oldhistory , when the first Continent were still forming and Earth ’s surface was most barren of dry land .

Researchers have two main ideas for when Earth’s sea levels were highest.
In the shortsighted term , sea point is a routine of unthaw trash . For instance , when Antarctica ’s " Doomsday " Thwaites Glacier melts , the entire West Antarctic Ice Sheet may break down , increase the mean global sea levels by around 11 feet(3.4 m ) . In the long condition , shifting continents and a stretch out seafloor also come into play . And then there ’s the curveball : Korenaga believes the former oceans held more water than they do today . Since the planet ’s genesis , sea may have been lento draining into the Earth ’s mantle .
Related : How will sea levels transfer with clime change ?
The last prison term sea were above their current height was around 120,000 days ago , during the Last Interglacial point ( 130,000 to 115,000 year ago ) , when mod man still shared the planet with ourNeanderthalandDenisovancousins . At this time , a warmer climate caused Antarctic ice to melt , causing sea level to peak about 20 ft ( 6 metre ) above their current norm .
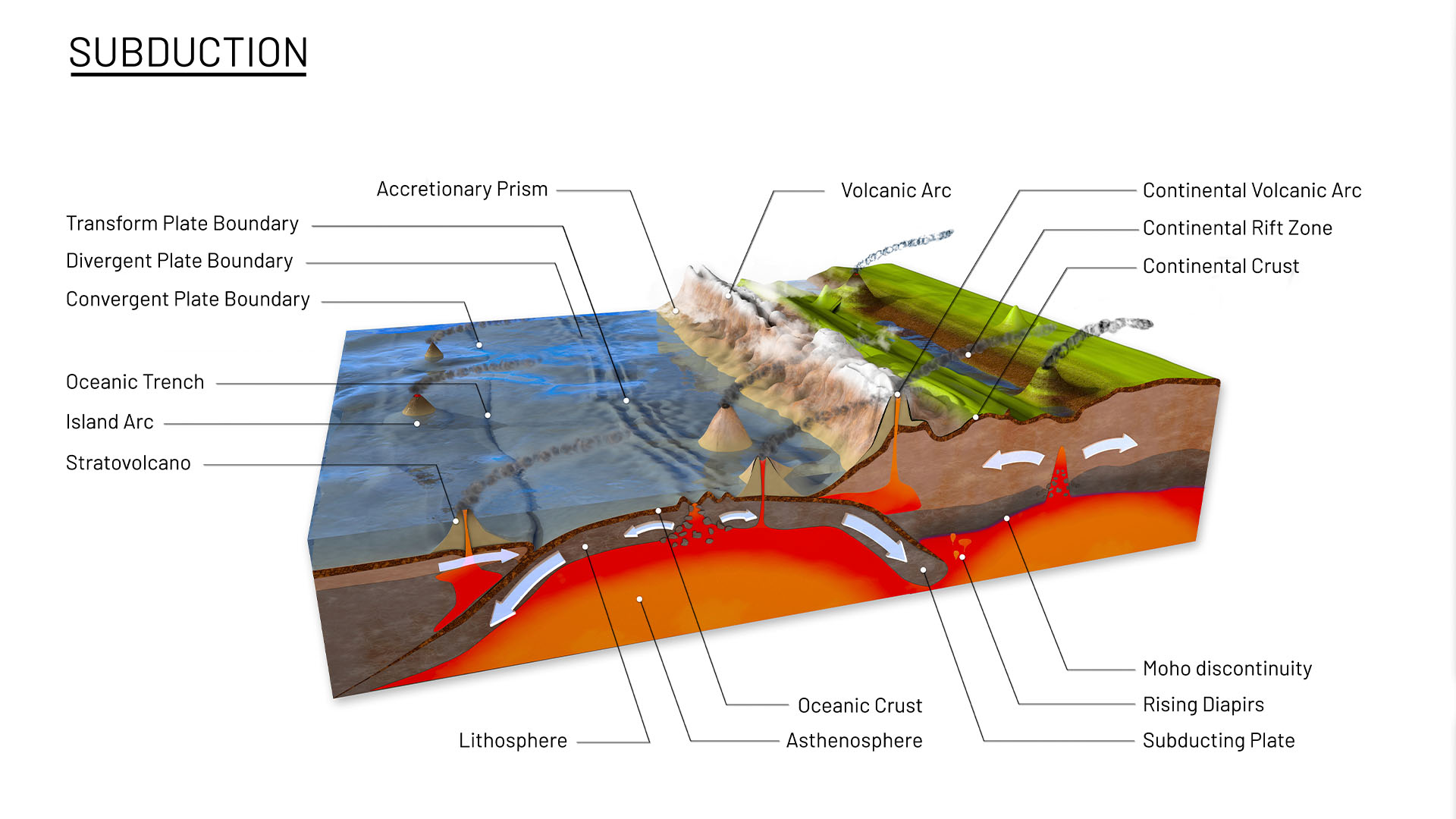
As new magma comes to the surface at tectonic plate boundaries, older, heavier magma is pushed down under overriding plates.
Back then , the climate was warm due to predictable changes in the Earth ’s orbit . In modern times , ice is fade because human being are burn dodo fuels , quickly increase the amount of major planet - warm carbon dioxide and othergreenhouse gasesin the atmosphere . Either way , unthaw Methedrine mean higher sea . Throughout both menstruation , however , Earth has been in along methamphetamine age , during which the satellite has had polar ice caps . Between major ice ages , Earth can lose its polar ice .
When Earth is completely ( or even virtually ) ice - free , sea levels can reach 10 times that of the Last Interglacial period . " If you go back by about 50 million eld ago , there ’s no chicken feed onGreenland ; there ’s no water ice onAntarctica , " van der Meer said . " You had a ocean level rise of about 70 meter [ 230 foot ] . "
And while ocean levels are highest when methamphetamine levels are depleted , that does n’t full explain the high sea during the Cretaceous , when 30 % of today ’s ironical land was underwater , van der Meer said . At that time , home plate tectonicsalso dally a role . Specifically , van der Meer estimate that ocean levels were highest around the time South America was propel away from Africa , from around 200 million to 100 million year ago .

Those continents were pushed apart as the South Atlantic Ocean was form between them . According to van der Meer , young oceans be given to be shallow than the ocean they replace . Above a layer of blistering , semiliquid rock ‘n’ roll called magma lies Earth ’s insolence , which is split up into big collection plate that slide around . Magma that do to the surface can solidify into new crust . When it does , it can push the boundary of an old plateful back down to make space .
Old pelagic incrustation is dumb ; it compact down on the magma at a lower place , ensue in deep oceans , van der Meer say . new Earth’s crust has had less time to solidify ; it ’s more floaty , so newer sea are shallower . That impacts ocean point . " It ’s a bit like a bathing tub , " van der Meer said : A shallow bathing tub holds less pee , so ocean levels go up .
The Cretaceous commingle a lack of diametric frappe with shallow sea for the high-pitched ocean grade in the past half - billion years . That time span , the Phanerozoic aeon ( 541 million days ago to present ) , is our best study , as it is when complex life — and fossil — became common . Some of those fossil release into fossil oil and gas reserves , and fossil fuel troupe have long studied past sea level to know where to find them , Korenaga said .

Scientists ' data collection and the geologic phonograph record itself both get sparse further back . Korenaga studies the murky Hadean and archaean eons , the earliest parts of Earth ’s history .
gamy levels of radioactive compounds in early rocks suggest that early continent were hotter , weaker and not yet strong enough to control their shape , Korenaga said . Until Continent solidified , volcanic islands may have been the only juiceless demesne .
— Could we ever pull in enough carbon out of the atm to break off climate modification ?

— Has the Earth ever been this hot before ?
— What countries and cities will disappear due to uprise ocean level ?
In a paper in the journalPhilosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A , Korenaga and colleague approximate that Earth ’s surface ab initio have twice as much water as it does today . Like the oceanic plates themselves , H2O can bicycle in and out of the magma beneath Earth ’s impudence . Korenaga ’s mathematics suggests a net loss of water supply from Earth’s surface ocean over 1000000000 of years .

If that ’s honest , then while the seas will continue to prove , their high days are likely in the past . Earth ’s other seas were the gamy , because there was simply more body of water to go around .












