When you buy through links on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it sour .
The origin of our specie , Homo sapiens , has puzzled paleoanthropologists for generations — and finding the answer has only gotten more complicated with the find of far - flung fossils and the advent of genetic analysis . So where and when did our antecedent first look ?
presently , the answer is still up for debate : research worker have so far unearthed300,000 - twelvemonth - older fossils attribute to our species , while some scientist trace modernistic humans ' extraction to 1 million years ago . One of the ground for the lack of clarity is the definition of species itself : what do we mean byHomo sapiens ?

A series of morphing skulls, includingAustralopithecus afarensis,Australopithecus boisei(also known asParanthropus boisei),Homo erectus, Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) and modern humans (Homo sapiens).
What is a species?
The biological species concept is the most well - know — penis of a universe that can interbreed are considered one mintage . Thanks to DNA depth psychology , in2010 , scientists discovered thatNeanderthalsand mankind had hybridise in Europe and the Middle East , with more recent research suggest they paired up as far back as250,000 years ago . Another close relative , theDenisovansfrom Asia , also interbred with humankind at least 50,000 years ago . Some anthropologist now consider Neanderthals and Denisovans to be the same biological species as we are — man sapiens — but others maintain each is a disjoined mintage within theHomogenus .
But since scientists have not been able to take out DNA from older specimens in Africa , where DNA does not preserve well past about 20,000 years , paleoanthropologists apply an additional concept to endeavor to sympathise the evolution of our species . In the phylogenetic , or fellowship - tree diagram specie construct , a particular group of forcible trait — such as a rounded braincase , a high forehead and a prominent mentum for human race — is used to place members of a metal money . This is the independent manner that paleoanthropologists sort and understand the fossil of our hominin ascendent . Additional grounds , such as the Edward Durell Stone tool type set up with the fogy , can suggest which species an individual belonged to .
The current challenge in palaeoanthropology is in figuring out how fossils , archaeology and DNA grounds can be bring together to understand where we came from .
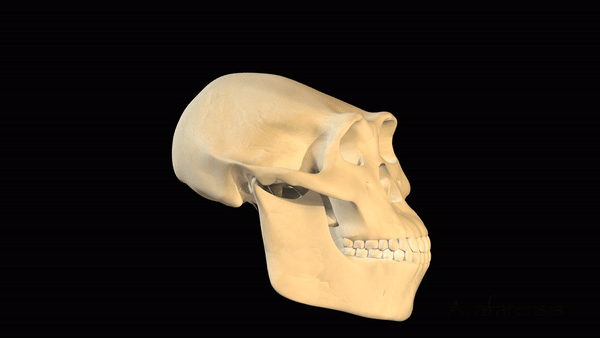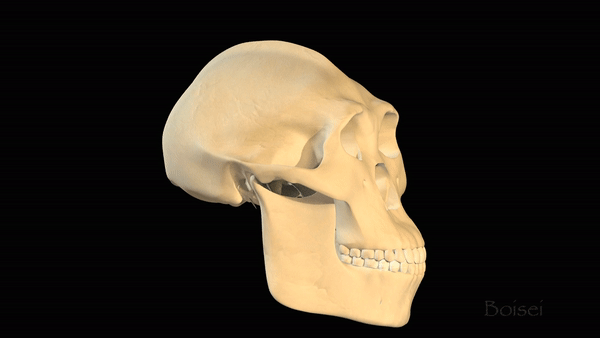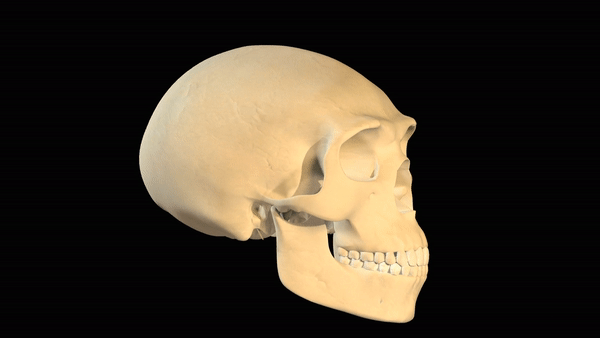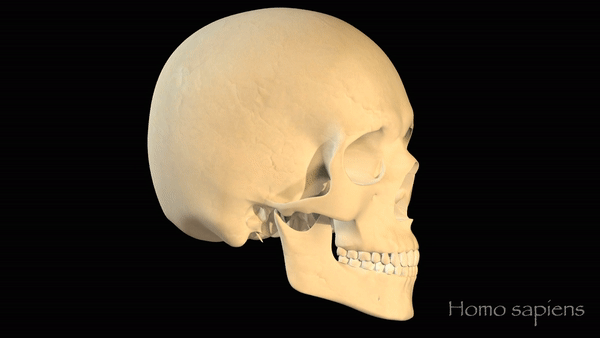
A series of morphing skulls, includingAustralopithecus afarensis,Australopithecus boisei(also known asParanthropus boisei),Homo erectus, Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) and modern humans (Homo sapiens).
bear on : What did the last common ascendent between man and ape look like ?
New fossils push back dates
So what is the oldest - know fossil belong to to a modern human?Chris Stringer , research leader in human evolution at the Natural History Museum in the U.K. , told Live Science in an email that " in my view , the oldest acknowledge fossil showing a morphologic pattern similar to extantH. sapiensis the Omo Kibish 1 skeleton from Ethiopia , [ which is ] about 230,000 days erstwhile . " This fogey skull has a tall , world - shape head and a man - like Kuki , which has ledresearchers to call itthe oldest knownHomo sapiensfrom East Africa .
But Stringer also pointed out that many researchers accept a fogey from South Africa calledFlorisbad , date to 260,000 years ago , and fossil from Morocco as examples of earlyHomo sapiens .
" The honest-to-goodness forms ascribe to our species are the fossils from Jebel Irhoud in Morocco , see to around 300,000 years ago,“Jean - Jacques Hublin , a paleoanthropologist at the Collège de France whodated the fossils , told Live Science in an email . fossil from the site includedseveral skullswith long braincases and hard brow ridges — features of our older ancestors — but with faces , jaws and teeth that are standardized toHomo sapiens .
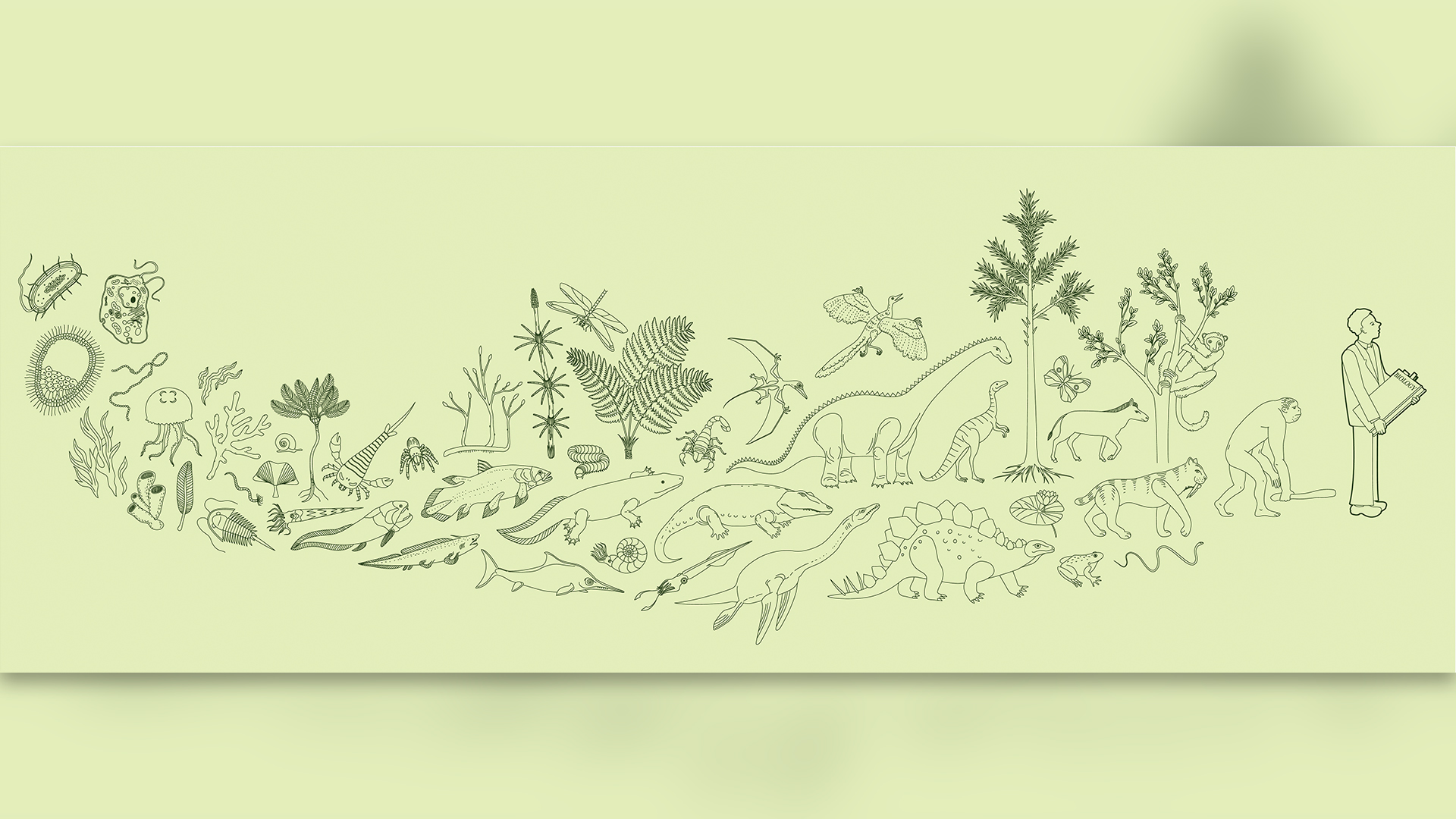

The oldest evidence of life is from 3.95 billion-year-old rocks. Humans evolved much later in Earth’s history, possibly around 1 million to 700,000 years ago, although the earliest fossil evidence dates to around 300,000 years ago.
" It should be stress , " Hublin say , " that these humans were substantially dissimilar from present - day world . Evolutionhas never barricade . "
" The Jebel Irhoud fossil is widely — though not by everyone — consider to be an case of a very earlyHomo sapiens , " saidEleanor Scerri , leader of the Pan African Evolution Research Group at the Max Planck Institute of Geoanthropology in Germany . But it is very unmanageable to determine what early members of our species should look like , Scerri order Live Science in an e-mail , because different features likely go up at different time in unlike grouping , and then eventually coalesced through gene flowing .
As there are archaeologic examples of modern cognition , such as tools and art , that seem around the same clip as Jebel Irhoud , " it ’s significant to look at different sources of information here , not just fossils " when classifying ancient hominins into specie , Scerri read .

Do modern African genetics suggest an earlier origin?
Even if we take the earliest fossil evidence and earliest behavioural evidence at nerve value , the appointment of roughly 300,000 age ago for the origin of our specie might still be too recent .
" For me , Homo sapiensevolved between 1 million and 700,000 years ago in Africa,“John Hawks , a paleoanthropologist at the University of Wisconsin – Madison , told Live Science in an email . " We make love the genetic discrepancy of African from Neandertal - Denisovan ancestors was around 700,000 days ago , " Hawks pronounce , and there is additional genetic research suggesting specialisation of ancestral African groups around 1 million years ago .
That 2023 inquiry , which was release inNature , worked back from the genes of almost 300 modern people from Africa , modeling a scenario of evolution and uninterrupted factor flux around the continent . In gist , their " universe fragmentation - and - coalescency model " hint there was an patrimonial human population around 1 million year ago in Africa that split up into South , West , and East Africa groups , all the whilemaintaining their genic link to one another .

If this deep genetic model is right , our antecedent might not have start in one specific space and time but develop slowly throughout Africa over 1 million age .
An incomplete answer
The question of when our specie acquire is unbelievable to have a absolved answer anytime soon .
" Every single part of that question is being questioned , " paleoanthropologistSang - Hee Leeof the University of California at Riverside tell Live Science in an electronic mail , including " the definition ofHomo sapiens , the definition of a ' first ' , and the definition of ' appearance . ' These are exciting time . "
— What ’s the oldest known face of cancer in human race ?

— When did humans discover how to use fire ?
— What did people use before toilet paper was make up ?
Scerri noted that more fossils , archeology and ancient DNA from different regions are necessary to " sympathise which region in Africa act a role in our origins , what the role was , if dissimilar regions work a great office than others , whether they were all roughly equal , which ecosystems were involved , and even if there were areas that were plainly pass on out of the story . "

Stringer match . " We involve much more , and good quality , grounds " for crowd ahead on doubtfulness about the origin of our metal money , Stringer said . " Even Africa has honorable fossil evidence from less than 10 % of its area . "
' If it was a man , we would say that ’s a warrior ’s grave ' : Weapon - filled burials are shaking up what we know about womanhood ’s part in Viking society
' It was designedly hidden ' : Gold hoard of well-nigh 600 coin rule in Czech Republic may date to World War II

The unvarying surveillance of modern life could exacerbate our brain function in ways we do n’t fully realise , disturb studies suggest




