When you buy through link on our site , we may gain an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
In Virgin Valley , Nevada , it ’s potential to spend an afternoon dig for rare black fervidness opals , while visitors to Coalinga , California , can scour the dirt for slice of the res publica ’s official gemstone , benitoite . At Arkansas ' Crater of Diamonds State Park , aspiring gemhounds give just $ 10 to run for the existence ’s most essay - after stones .
Each of these jaunt requires little more than helping hand tools , yet most stone start between3 to 25 miles ( 5 to 40 kilometers ) belowground , and some prolong far deeper .

Diamonds form deep in Earth’s mantle over billions of years before making their way to the surface.
But which gemstones are find the deep , and how do they make their way to the surface ?
According toLee Groat , a mineralogist at the University of British Columbia , the deepest known gemstonesare diamonds , sought for their beauty , use in diligence and the scientific datum they contain .
How diamonds human body still is n’t only understood , but laboratory experiments show that the gemstones sort out only under uttermost pressure level . Most naturally occurring stoneshave been traced to the upper mantel , at depths between 93 and 186 miles ( 150 to 300 km ) , where pressures can reach beyond 20,000 atmospheres .

Diamonds form deep in Earth’s mantle over billions of years before making their way to the surface.
Related : What is the rare mineral on Earth ?
For a tenacious time , this put ball field in challenger with a treasure forebode peridot for the title of deepest - occurring gem . Peridot is the gem shape of a mineral called olivine that makes up more than one-half of the upper mantlepiece , which protract from the Qaeda of the crust down to 255 statute mile ( 410 km ) . But in 2016 , scientist described a collection of superdeep diamondssourced from around 410 miles ( 660 km ) , and another plenty in 2021 wasdetermined to come from a astuteness of 466 miles ( 750 km ) .
" It ’d been hard to tell whether diamond or peridot were the deepest , but that pretty much settled the debate , " Groat said .
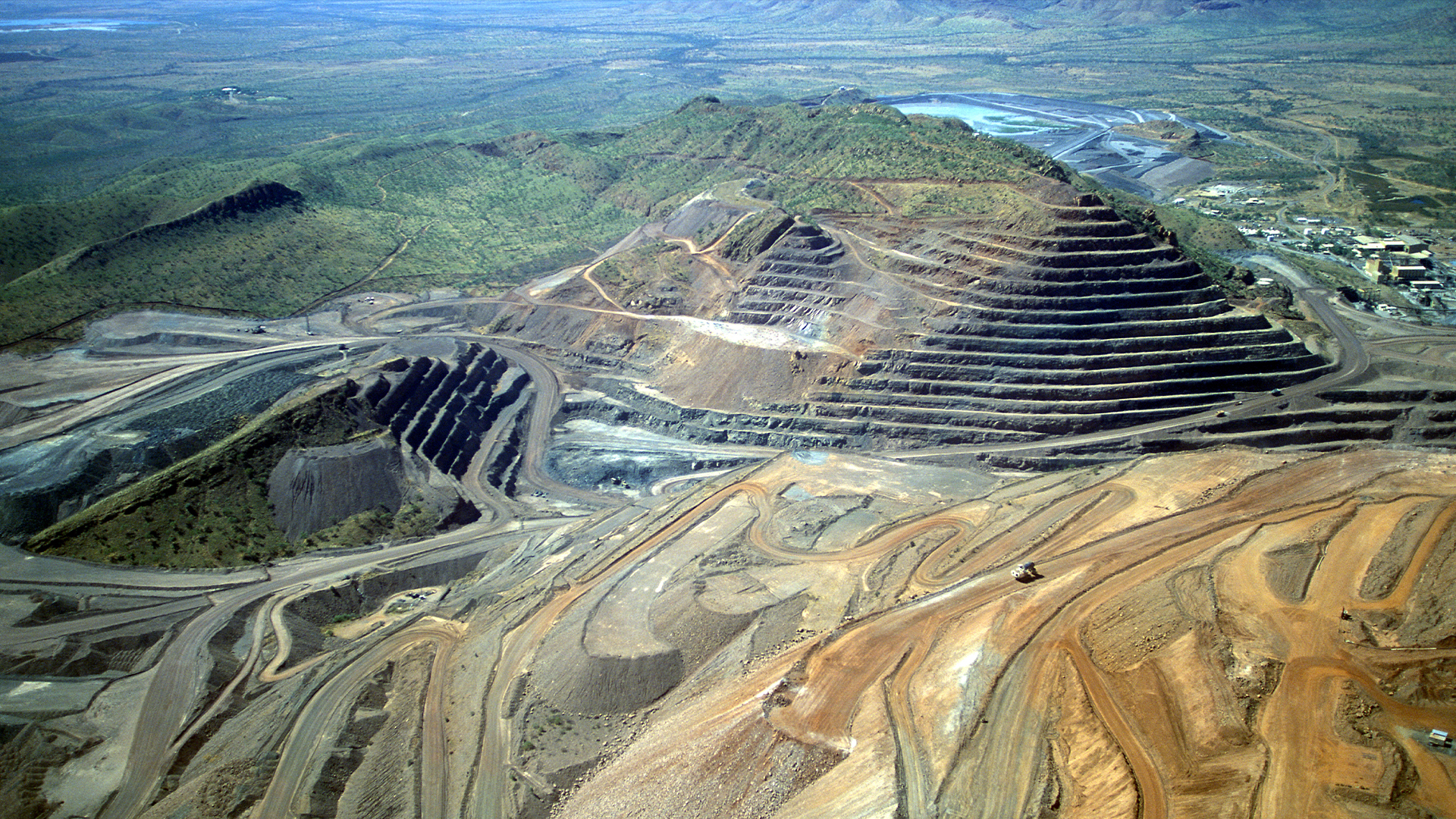

We don’t need to probe hundreds of miles below the surface to reach diamonds because natural geological processes bring them to the surface. Even still, diamond mines can be massive operations.
To fare up with those estimates , researchers contemplate the diamonds ' crystallisation convention as well as their inclusions — spot of mineral or fluid entombed in the gem from when they were form . Inclusions of a mineral call bridgmanite and smoothing iron - Ni - carbon - S melt told scientist that these superdeep diamonds likely formed in the lower mantle , which is made up of about 75 % bridgmanite , and that theygrew from liquid metalsurrounded by methane . At these depths , pressures can surpass 235,000 atmospheres .
Diamonds are also thought to be extremely old . Some estimation intimate that diamonds on the Earth’s surface today may have form up to3.5 billion years ago , although many are much younger . Their longevity is attribute to the strength of their chemical substance bonds , Groat said . adamant are made ofcarbon , and because they organise under pressure , " it withdraw a great force to break their bonds apart . " inflame a diamondabove 1,652 degree Fahrenheit(900 degree Celsius ) will cause it to degrade into graphite .
Gemologists did n’t necessitate to tunnel into the Earth to instruct this ; the deepest we ’ve ever penetrated into the planet ’s DoI , at theKola Superdeep Boreholein Russia , scarcely scratched the control surface , at just 7.8 miles ( 12.6 km ) recondite .

Instead , diamonds are take to the surface by a unique character of magma call kimberlite . Kimberlite magma lean to be fickle , erupting at speedsof more than 100 metrical foot per 2nd ( 30 meters per second ) and pulling diamonds from the surrounding rocks as they go . In this way , stone that form over one thousand million of years jettison to the surface in calendar month or even hours .
Beyond their esthetic value and their born hardness , which makes them attractive to industries interested in blades , drill snatch and polish powders , diamonds check invaluable scientific selective information , saidAnanya Mallik , an experimental petrologist at the University of Arizona . In many guinea pig , " adamant are the only sources that researcher have for sympathise the makeup of the satellite ’s interior and the processes get place there , " she differentiate Live Science .
— Can diamond combust ?
— Is anything concentrated than a adamant ?
— How many architectonic plates does Earth have ?
By canvass these gemstones , scientists have check that betimes Earthwasn’t as tectonically combat-ready as it is today . Other analytic thinking have revealed carbon signature reproducible withphotosynthesis , demonstrate that thecarbon cycles/second reaches deep into the planet ’s interior . More of late , scientists study rarefied diamonds found grounds of waterdeeper in the mantle than antecedently expected , and even discoveredentirely new mineral .

" Diamonds have their own time value because of their beauty , but in addition to that , their scientific importance shit them even more valuable , " Mallik tell .














