When you purchase through links on our land site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Since ancient times , humankind have looked to the genius for answer to liveliness ’s big questions . Now , raw image from theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) reveal a bizarre cosmic object that seems to be throw a question of its own justly back at us .
fleck by JWST ’s Near - Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph instrument , the target in question is a distich of distant galaxies being warped , magnify and multiplied into the shape of a cosmic interrogative sentence mark . Inquisitive aliens are ( likely ) not responsible for — rather , it ’s make by a rare form of a common cosmogenic phenomenon called gravitative lensing , NASAresearchers revealed in astatement .
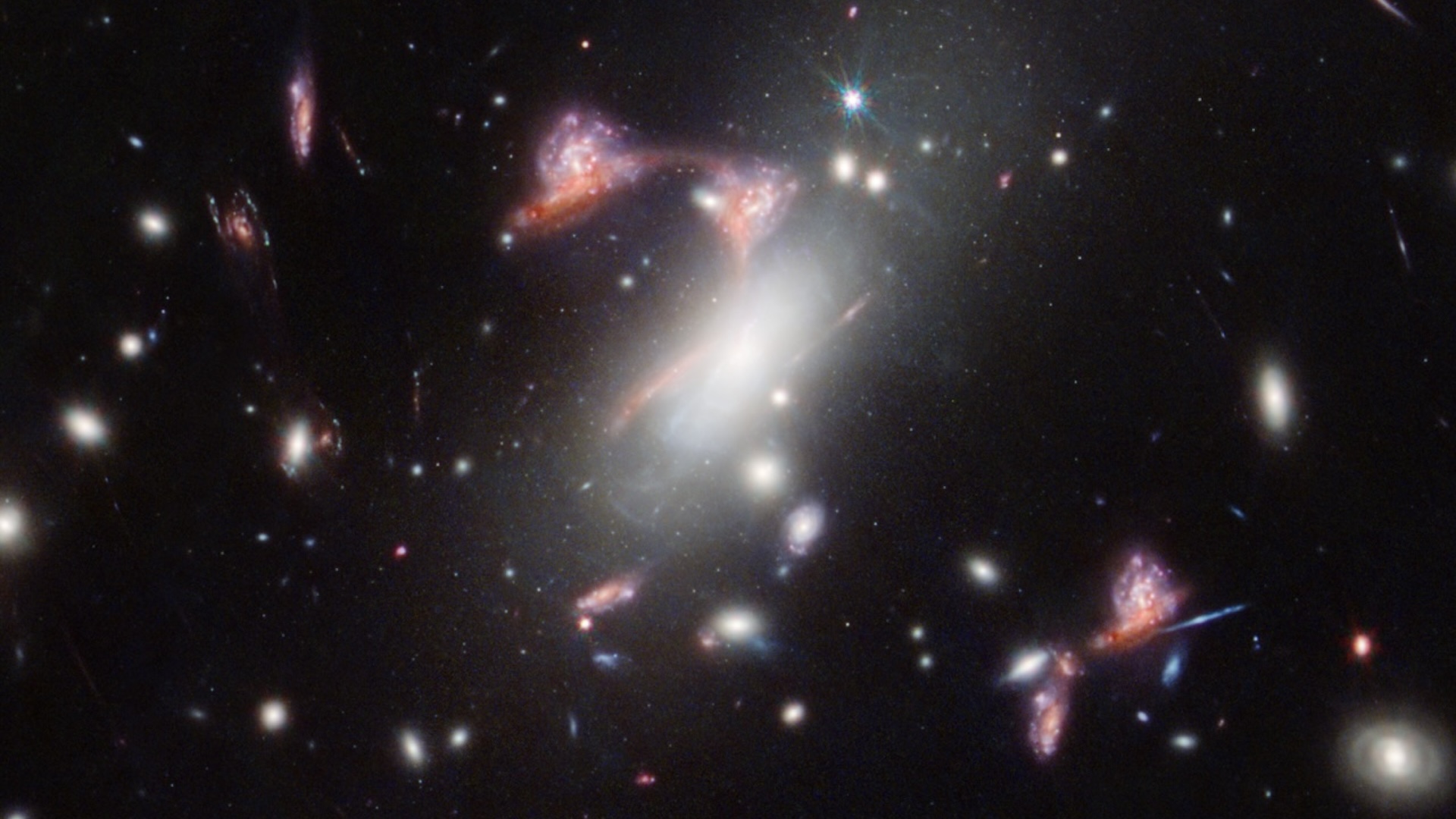

The James Webb Space Telescope’s image of the galaxy cluster MACS-J0417.5-1154 reveals a cosmic question mark.
" We know of only three or four happening of like gravitational lens configuration in the observable universe,“Guillaume Desprez , an astronomer at Saint Mary ’s University in Nova Scotia and a extremity of the team behind the newfangled icon , allege in the argument . The scarceness of other object like this one " makes this find oneself exciting , " Desprez bestow , and it speaks to JWST ’s index to see what prior space telescopes could not .
gravitative lensing come about when the gravity of a massive foreground object — such as an enormous galaxy or a cluster of galaxies — turn the igniter of objects place behind it , relative to our view from Earth . The result creates a kind of cosmic spyglass , which can not only magnify our view of background signal target but also distort and multiply them .
Related:35 jaw - dropping James Webb Space Telescope project
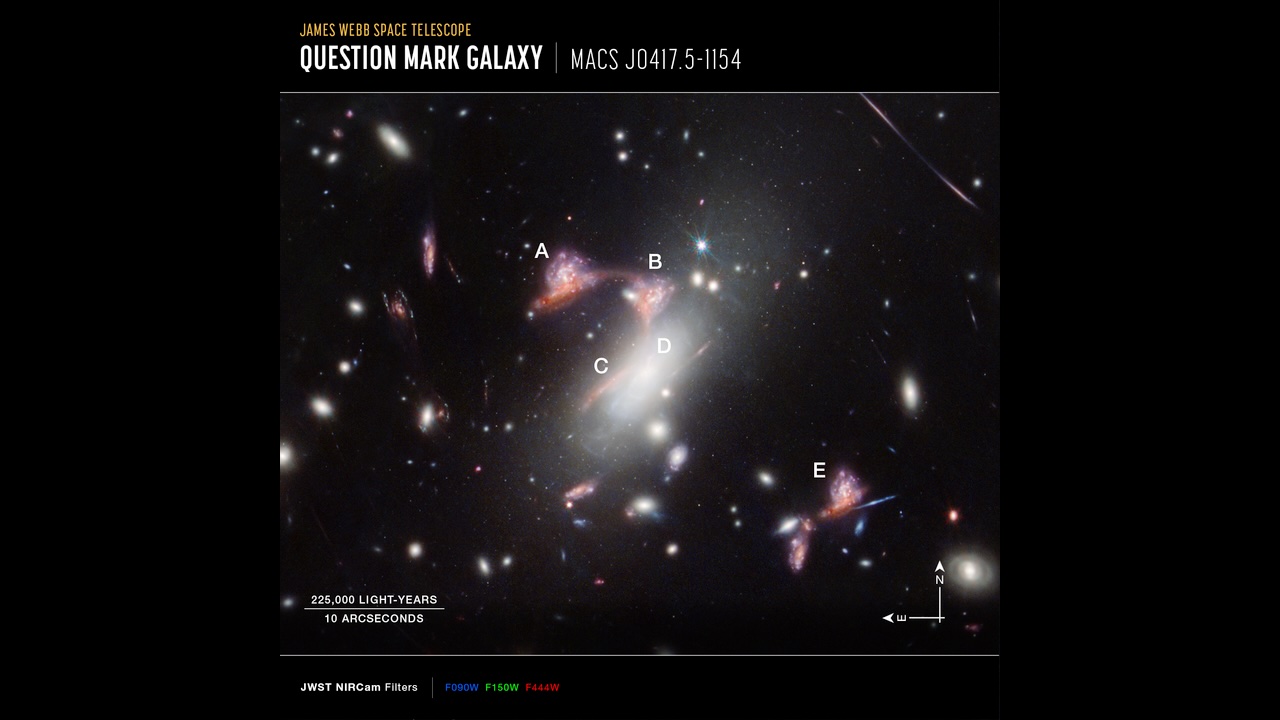
A pair of distant “teenage” galaxies is multiplied five times thanks to a rare form of gravitational lensing.
In this case , a gargantuan galaxy clump called MACS - J0417.5 - 1154 is warp and enlarging a pair of tight - knit galaxies located far behind it . The range of the two galaxies is multiplied five time ; four copies of the astronomical duo are visible in the wiggly body of the question mark , while the fifth drifts off to the lower right side , as noted in the label picture below . ( An unrelated galaxy forms the interrogation gull ’s lower dot . ) This particular organisation is known as a " hyperbolic umbilic gravitative lens , " according to the investigator .
turn up rough 7 billion light - years from Earth , the lensed galaxies escort to when the universe was roughly half its current age , according to NASA . This was a fourth dimension of speedy star formation , and many wandflower — including our own — were start to bulk up and take shape . Seeing them allows astronomer to study what theMilky Waymay have looked like aeon ago , during its own starring ontogeny spurt .
— Star - packed Triangulum Galaxy beam in new Hubble Telescope image

— The James Webb scope find out century of ' small reddish Lucy in the sky with diamonds ' in the ancient universe . We still do n’t know what they are .
— infinite photo of the workweek : The first image of an alien planet
" These beetleweed , see billions of years ago when headliner formation was at its peak , are similar to the batch that theMilky Waygalaxy would have been at that time,“Marcin Sawicki , also an astronomer at Saint Mary ’s University , said in the argument . " Webb is allowing us to analyse what the teenage geezerhood of our own galaxy would have been like . "

This discovery punctuates what has been a officious summer for the ever - inquisitive JWST . Scientists using the scope ’s data have answered many pressing questions — include " What does that alien satellite smell like ? " and " How big were the earliest galaxies in the universe ? " — while raise infinite new conundrums . The most vexing of these questions — " Is our understanding of the universe really broken ? " — may want a turn more pondering to resolve .













