When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
El Niño is a climate cycle in the Pacific Ocean which impacts atmospheric condition patterns around the world .
The cycle begins when ardent water in the western tropic Pacific Ocean shifts eastward along the equator toward the coast of South America . commonly , this quick urine pool near Indonesia and the Philippines . During an El Niño , the Pacific ’s warmest airfoil waters sit offshore of northwestern South America .
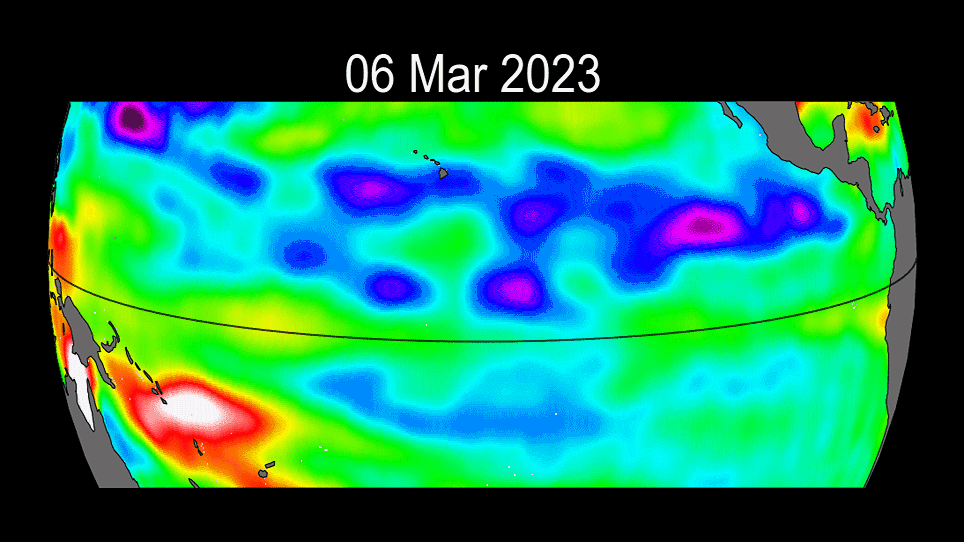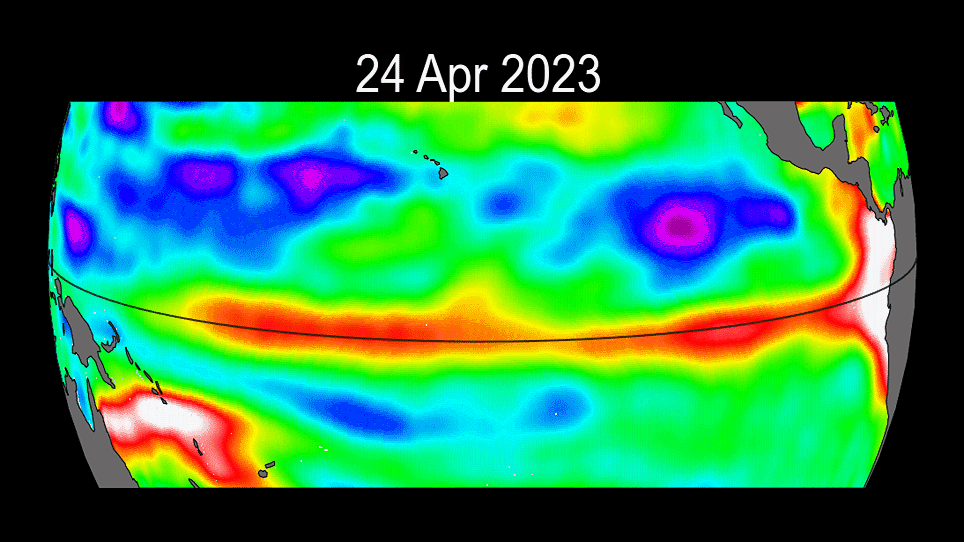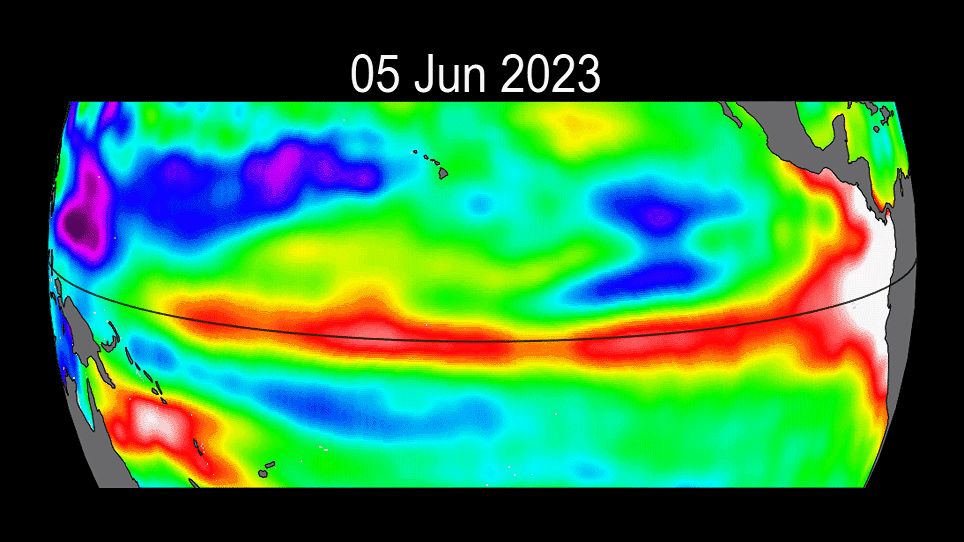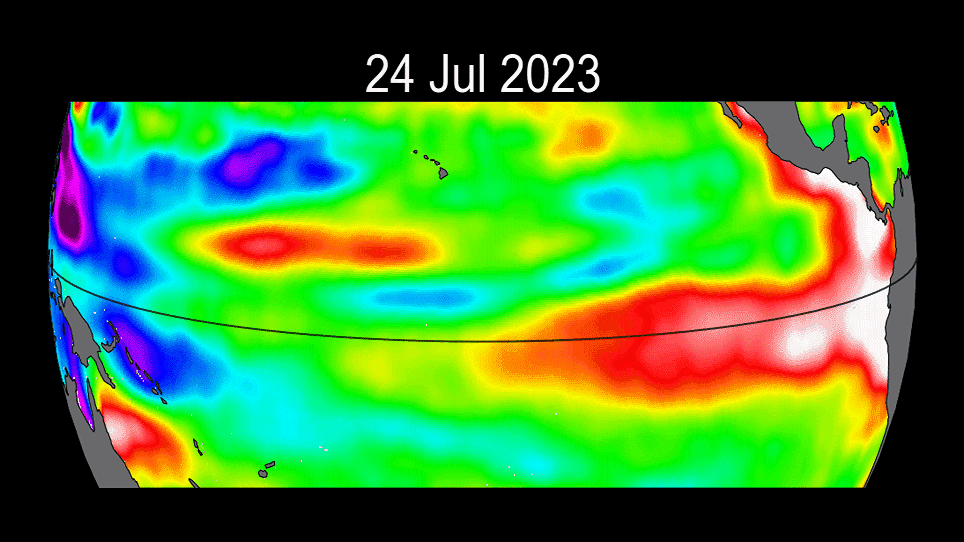
The ongoing progress of the 2023 El Niño event.
The location of tropic storm shifts eastwards during an El Niño because atmospheric moisture is fuel for thunderstorms , and the greatest amount of vapor have position above the sea ’s warmest water .
The opposite of El Niño is La Niña , which is when the waters of the tropic eastern Pacific are cold than normal and patronage flatus blow more strongly than usual .
Collectively , El Niño and La Niña are role of an cycle in the sea - atmosphere system hollo the El Niño - Southern Oscillation , or ENSO cycle , which also has a indifferent stage .
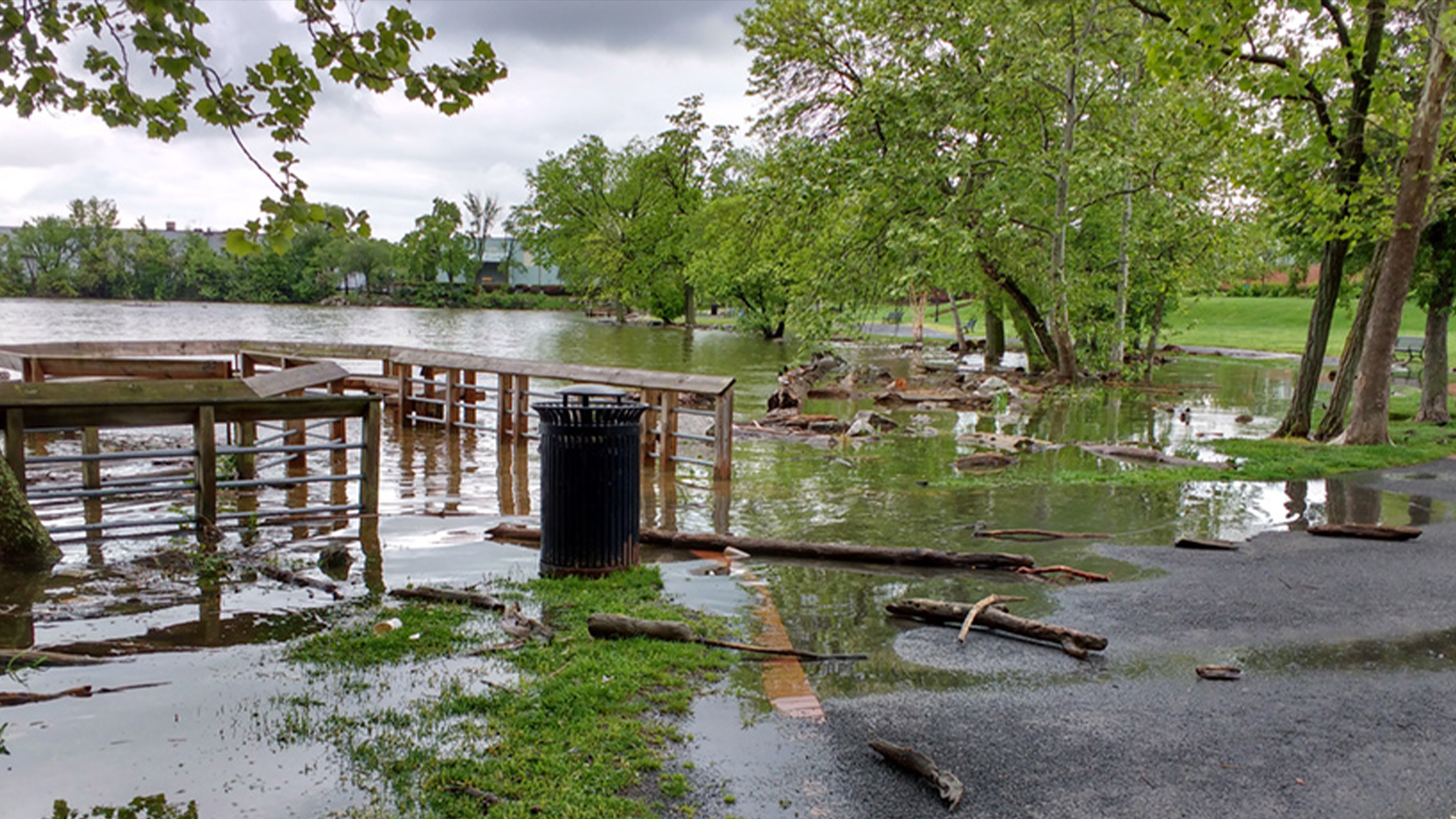

Nuisance flooding in the U.S. due to 2015 El Niño.
How long will El Niño last?
El Niños pass off everythree to five yearsbut may descend as ofttimes as every two years or as rarely as every seven years . Typically , El Niños come more frequently than La Niñas . Each effect usually lasts nine to 12 months . They often set about to mold in spring , reach peak durability between December and January , and then decay by May of the following twelvemonth .
Climate scientists at NOAA say there is a more than 95 % chance that the current El Niño event will persist into 2024 . They expectwarmer - than - averageconditions that will gradually strengthen into the Northern Hemisphere ’s pin and winter .
What causes El Niño?
Scientists do not yet understand in item what spark off an El Niño cycle . Not all El Niños are the same , nor do the atmosphere and sea always follow the same practice from one El Niño to another .
To portend an El Niño , scientists supervise several regions across the Pacific .
" You have to think of each region as an ocean splash around , " said Neville Sweijd , director of the Alliance for Collaboration on Climate and Earth Systems Science ( ACCESS ) in South Africa . " Sometimes it splosh to one side , and sometimes it sloshes to the other . That ’s El Niño and La Niña . "
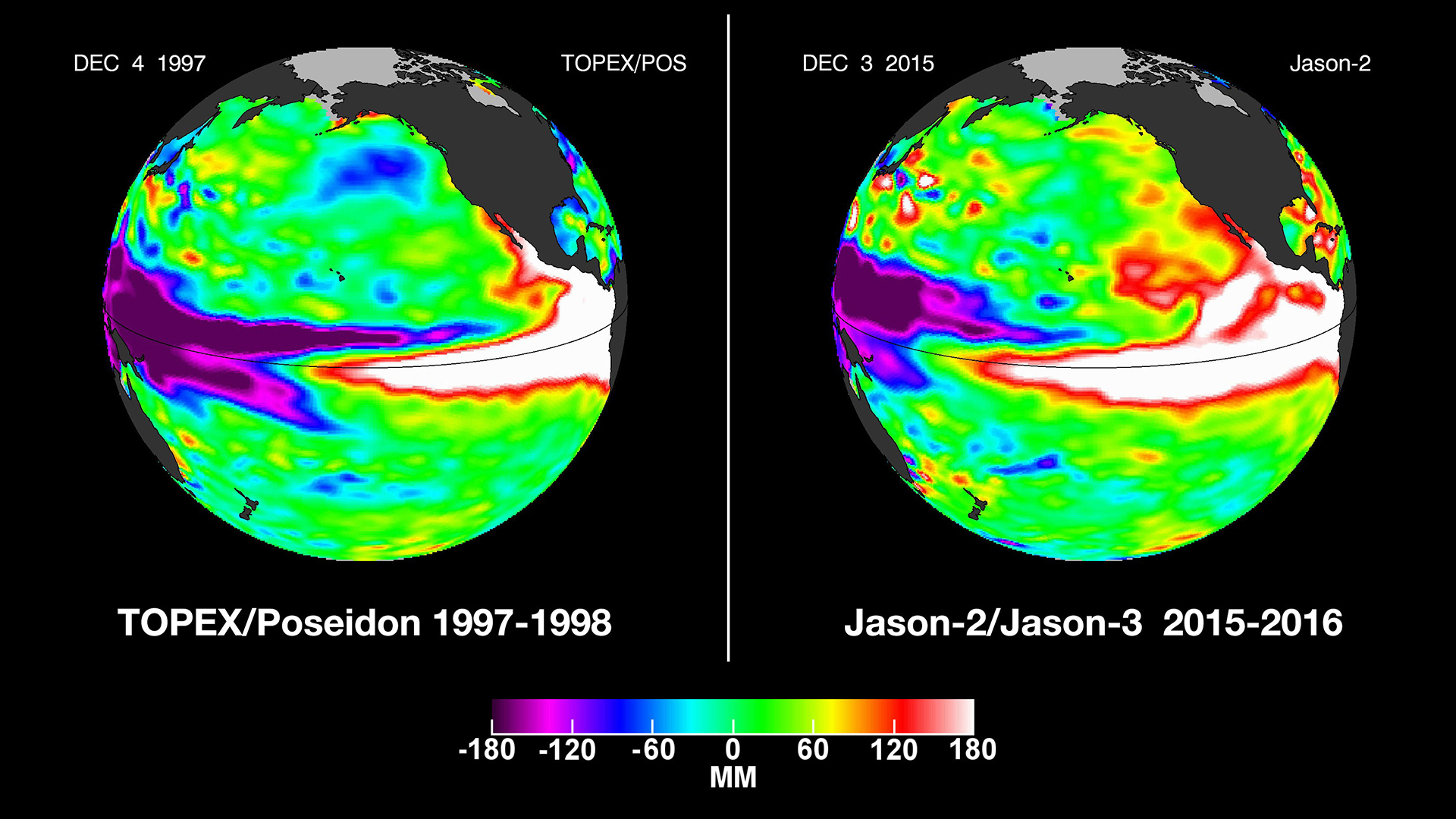
El Niño events of December, 1997 compared to December, 2015.
expert " monitor the fair sea - aerofoil temperature in each region and practice that to form a model , " he told Live Science . " The models will then predict the likelihood of the manifestation . "
In normal , non - El Niño conditions , business deal idle words blow toward the west across the tropic Pacific , aside from South America . These winds pile up warm aerofoil pee in the western Pacific so that the ocean aerofoil is about1.5 feet ( 0.5 meter ) higher offshore Indonesiathan it is offshore Ecuador . Higher ocean - surface temperature cause piddle floor toexpand and go up , and alsoshifts rainfall from commonwealth to ocean .
In a non El Niño year , the sea - open temperature is also about 14 degrees Fahrenheit ( 8 degrees Celsius ) warmer in the westerly Pacific . Cooler ocean temperature command offshore northwest South America , due to an upwelling of frigid water from deeper levels .
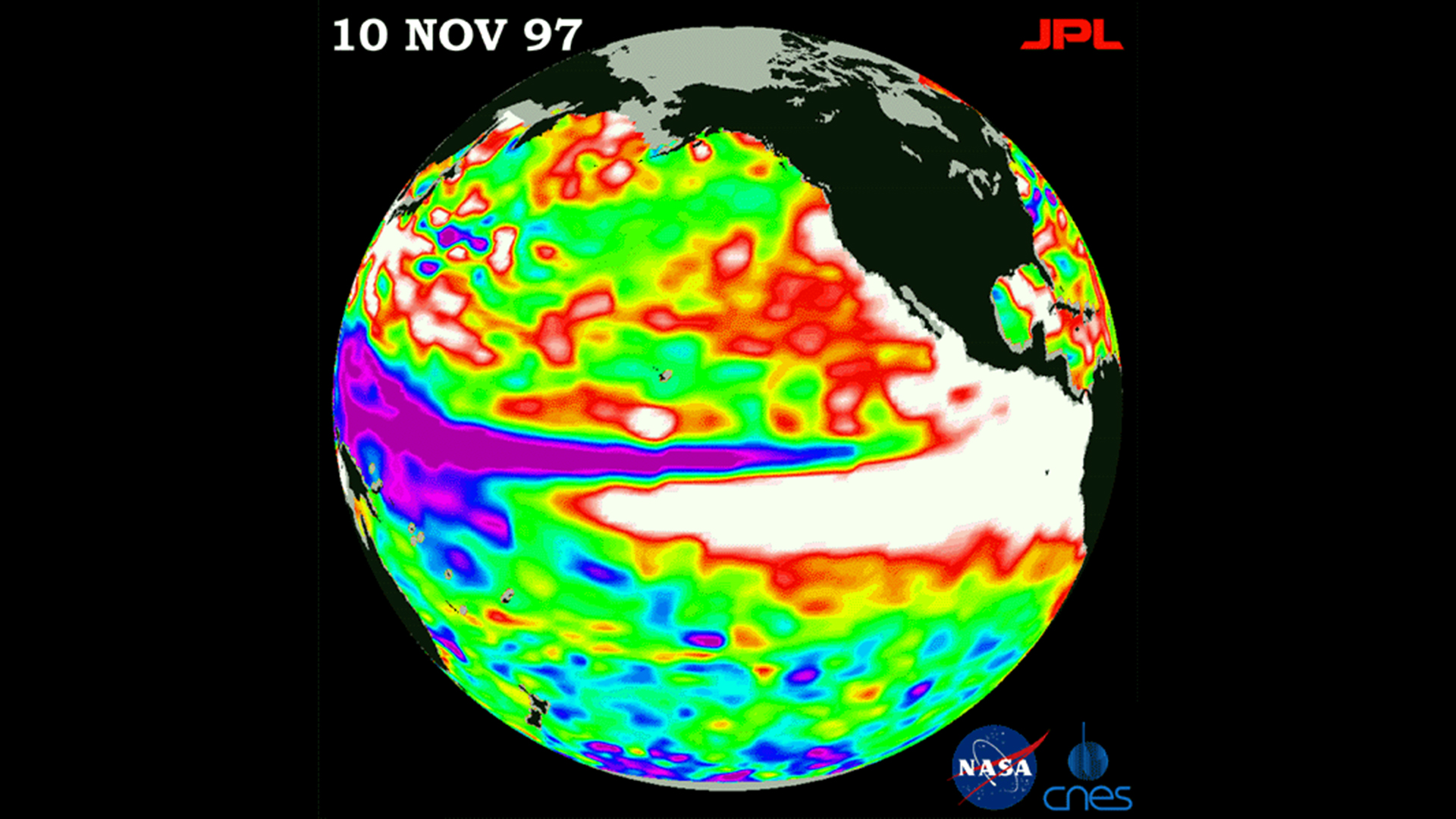
Satellite image of sea surface height relative to normal ocean conditions in the Pacific Ocean on Nov. 10, 1997.
Forecasters declare an officialEl Niñowhen they see both ocean temperature and rainfall from storms veer to the eastward . Experts who supervise El Niño also face for prevailing craft winds to de-escalate . These changes set up a feedback loop between the atmosphere and the ocean that boost El Niño term .
What is the El Niño forecast for the 2023-2024 winter?
Aftermonths of warning , on June 8 , scientists at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration ( NOAA)confirmed the arrivalof the latest El Niño issue .
El Niño for the 2023 - 2024 winter is calculate to be very solid , which means normal sea - aerofoil temperatures in the Pacific Ocean are expect to deviate dramatically from their normal average . However , their strength does not directly correspond to the severity of their impacts , as this relationship can vary considerably between cycles .
" Their effects vary look on the intensity , length , time of yr when it develop , and the fundamental interaction with other style of climate variability , " said Álvaro Silva , a climate expert at the World Meteorological Organization . " Not all region of the world are affected , and even within a region , the impacts can be different . "

The current El Niño effect is expected to push orbicular temperatures into uncharted district and kick in to global warming crossing the critical2.7 F(1.5 one C ) threshold within the next five year . It will most likely intensify uttermost weather events assort with climate variety — such as heat wave , drouth and fleshy rain — in certain areas .
" El Niño is a strong contributing factor to some of the extreme we have experienced in the past and that we are potential to experience in the next month , " Silva told Live Science . " It is very potential that this yr or next year we will see the warmest year on record . "
Does El Niño cause more rain, or drought?
During an El Niño , thetrade wind instrument weakenin the central and westerly Pacific . Surface weewee off South America warm up up because there is less upwelling of the cold water from below to cool the surface . The cloud and rainstorm associated with warm sea waters also shift eastward . The tender piddle release so much energy into the atmosphere that weather changes all over the major planet .
An El Niño make substantial wind shear and more stable air travel over the Atlantic , which pass water itharder for hurricane to formthere . However , the warm - than - median sea temperatures boost easterly Pacific hurricane , contributing to more active tropic violent storm seasons .
Strong El Niños are also tie in with above - fair precipitation in the southern United States . The cloudier weather condition typically get below - average winter temperatures in that part of the area , while temperature tilt fond than modal in the northern U.S. Rainfall is often below norm in the Ohio and Tennessee valleys and the Pacific Northwest during an El Niño , according to NOAA .

track record rain often strikes Peru , Chile and Ecuador during an El Niño twelvemonth . Fish catch offshore South America are typically downcast than normal because themarine life transmigrate to the northand south , following colder water .
El Niño also touch hurry in other areas , including Indonesia and northeastern South America , which run toward drier - than - normal conditions . Temperatures in Australia and Southeast Asia run hotter than average . El Niño - make drouth can be widespread , affecting southerly Africa , India , Southeast Asia , Australia , the Pacific Islands and the Canadian prairies .
Unlike El Niño , La Niña events are characterized by a free burning cooling result around the equator and eastern tropic Pacific . This often results instronger and more frequent hurricanesacross North America and can lead to heavy implosion therapy in many Pacific Island country , as well as drouth along the west coast of South America .

What were past El Niño years like?
— El Niño is officially here , scientists say
— Will El Niño end the Southwest ’s megadrought ?
— Odds of ' substantial ' El Niño now over 95 % , with sea temperatures to ' well outmatch ' last large warming issue

The last El Niño issue pass off between February and August 2019 , but its impacts were comparatively frail . One of the strongest in recent decades was the El Niño that developed in the winter of 1997 to 1998 . It ensue inthousands of death and injuriesfrom severe storms , heatwaves , flowage , fires and drouth . Inthe US , devastating storm in the south damaged substructure and crops , while the north experience above - normal temperature and very small pelting and snow .
Between July 2020 and March 2023 , arare triple - dipLa Niña upended weather condition patterns around the worldly concern . Thethree - twelvemonth eventwas partly responsible for record - breaking rainfall and grievous flooding in Australia , a record - breaking Atlantic hurricane season in 2020 and the third most fighting hurricane time of year in 2021 .