When you purchase through links on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it works .
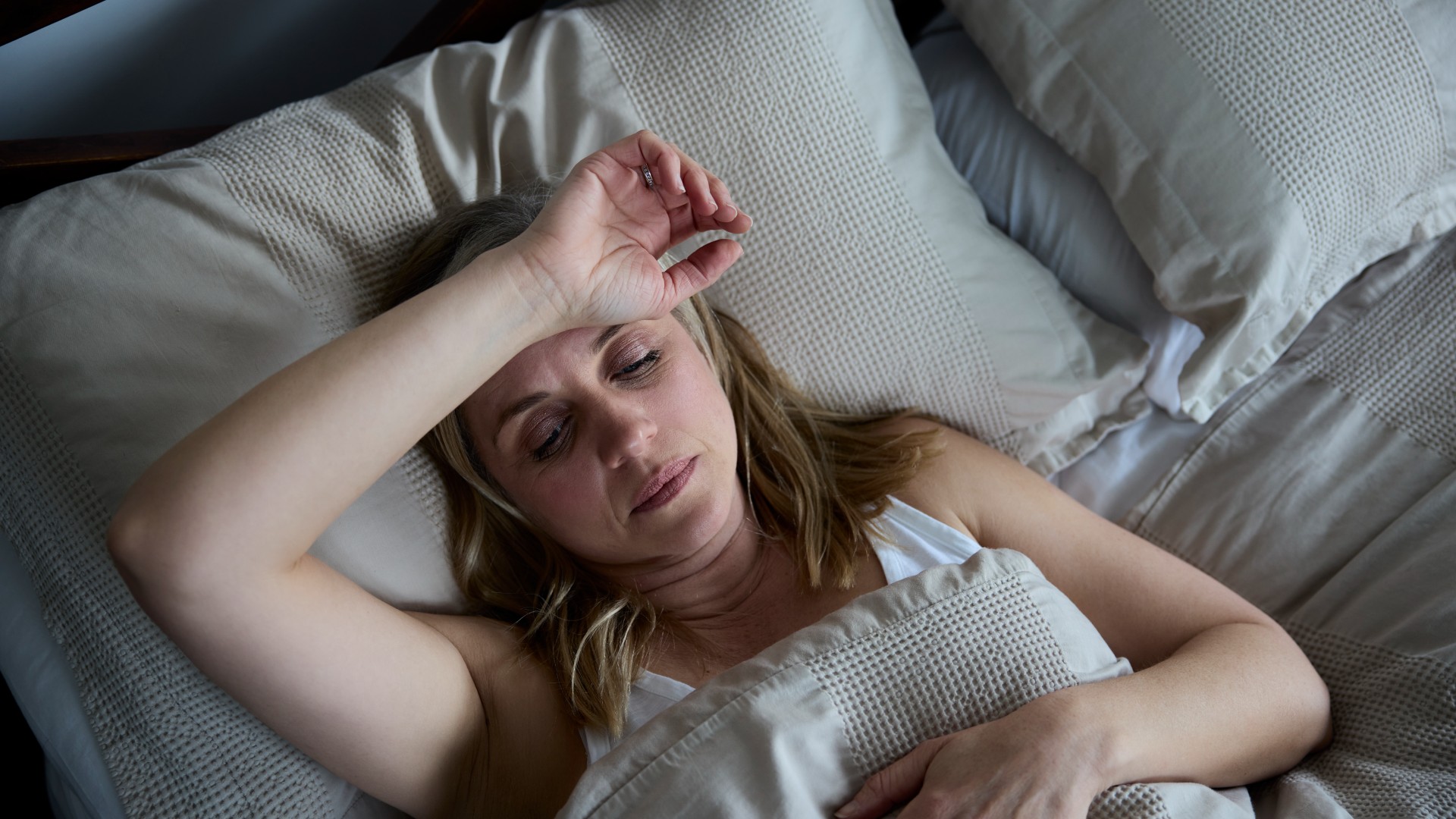
You awaken up in the middle of the dark , shivering . You ’re know afever — a irregular ear in eubstance temperature .
fever can develop as the consistence ’s defence system fight back off an contagion , but they can also be activate by other thing , includingautoimmune diseasessuch asrheumatoid arthritis , or occur as aside gist of sure drugs .

In response to infection, the hypothalamus in the brain can induce a temporary spike in body temperature — a fever — in a variety of ways.
But what materialise in the eubstance during a febrility ?
Human eubstance temperaturevaries slightly from daytime to day and from person to someone , but it ’s normally maintained at around 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit ( 37 point Celsius ) . This create the unadulterated surroundings for our cellsto work efficiently . Part of thebraincalled thehypothalamusacts like a thermostat , constantly monitoring the body ’s temperature and turning home dial to rein it back to some 98.6 F.
Related : Why do coughs linger after a cold ?
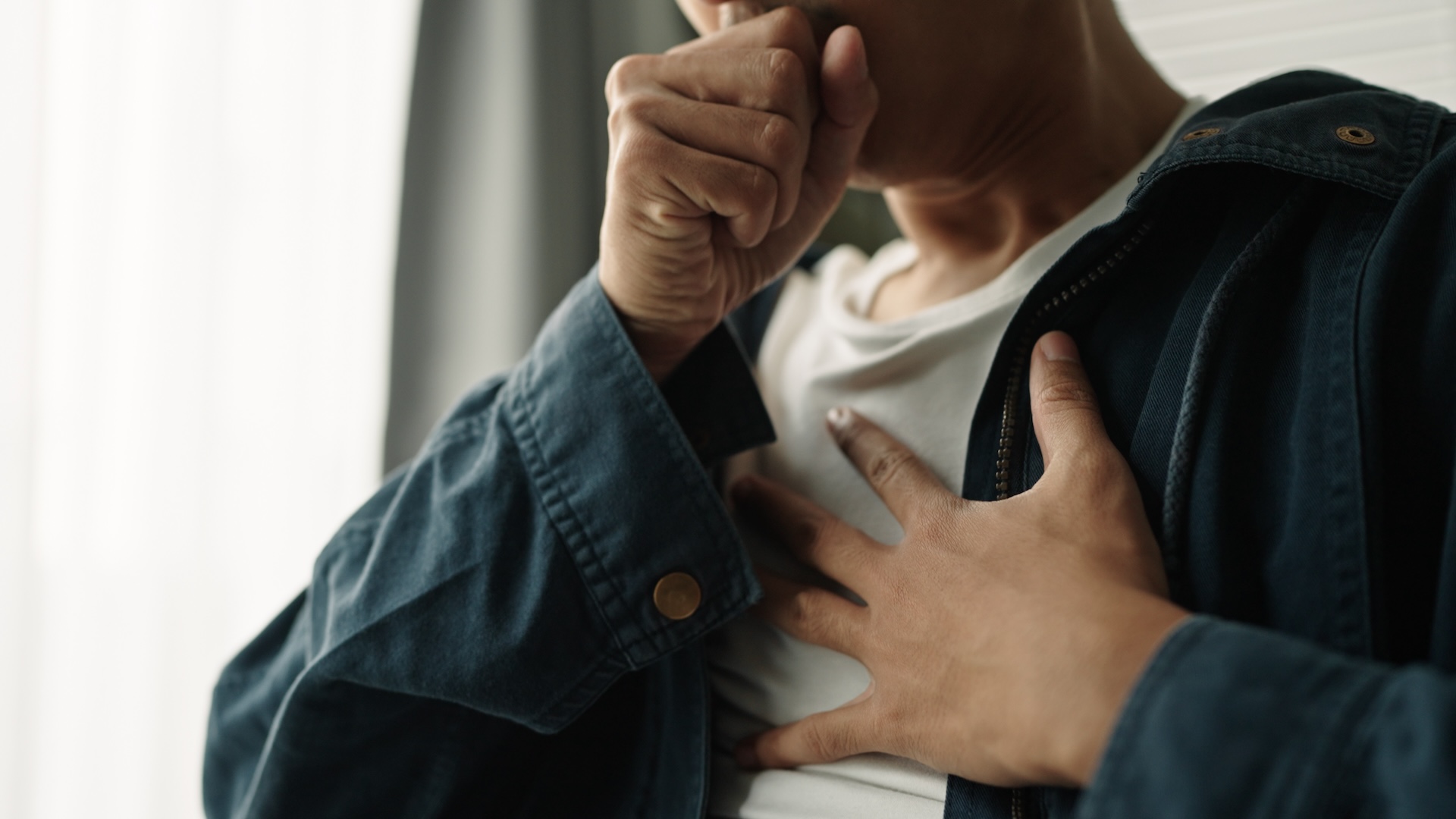

During an transmission , when our resistant cellular telephone detect foreign invaders such asbacteriaorviruses , they release fever - inducing chemical substance calledpyrogens . These chemicals travel to the brain , where they roleplay ontemperature - sensitive neuronsin the hypothalamus , fundamentally telling it that it ’s time to raise the temperature in the menage , Dr. Paul O’Rourke , an assistant prof of medicine at Johns Hopkins University , told Live Science .
As a result , these neurons free hormone - like meaning calledprostaglandins — specifically , one called PGE2 — to twist the dial on the dead body ’s thermostat and originate a fever .
" We typically regard a fever when you ’re reaching temperature keen than 38 degrees Celsius [ 100.4 fluorine ] , " O’Rourke said .

The hypothalamus can levy body temperature in several way . For instance , it directsblood vessels to constrict , which reduces the amount of heat energy that dispel through the control surface of the skin . It also inducesshiveringto render as much rut as potential .
These physiological mental process conjointly form part of the body ’s first line of descent of denial against contagion , known as acuteinflammation . The principal aim being to impart infection under control condition and stop it from spreading .
Paradoxically , people may have tingle alongside a feverishness , even though their body temperature is rising . This is because the hypothalamus has temporarily increased the torso ’s internal thermoregulator to ahigher " normal " level . As your dead body tries to contact this young baseline , you feel relatively moth-eaten .

So why does the body ask the heating system ?
One potential reason is to make it harder for bacterium or computer virus to duplicate and infect our cells , O’Rourke said . A higher body temperature may also turn the resistant scheme into a skillful " scrap machine , " he said . For example , when our body temperature rise up , cells produceheat jolt proteins(HSPs ) , which touch off resistant pathway to agitate off contagion . HSPs are normallyupregulated by cells during inflammation , as the body strive to protect itself against foreign encroacher .
" For your modal older child or grownup , you may experience a degree of febricity for a few day , certainly two or three days , without needfully necessitate to get a lot of aesculapian attention,“Dr . Kitty O’Hare , a consulting associate in the Department of Medicine at Duke University , tell Live Science .

But if you are concerned about your symptoms or they do n’t seem to be improving , you should contact your healthcare provider , she say .
Sometimes when children get a high fever , for instance , they can know convulsions calledfebrile seizure . Although these may be dreaded , they generally last only a few minutes and are commonly harmless . Nevertheless , parents should call their healthcare supplier anytime their tike has a gaining control , even if it is during a fever , O’Hare said .
The degree of fever also matters , O’Hare say . " It ’s good to get advice from your own health care supplier based on your health history on how much of a fever would be problematic for you , " she said .

— What induce this military man ’s sudden , monthly sweating episodes ?
— What are the unlike types of headaches ?
— Why do we shiver when we ’re cold ?
Depending on your age , an over - the - counter medication such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate the symptoms of febrility . dispatch a layer of clothing , hold a cold bath and drinking coolheaded liquids can also serve the febrility to improve , she said .
increase your physical structure temperature during a feverishness shoot a portion of effort — for every 1.8 F [ 1 C ] increase in body temperature , you use an additional10 % more energythan you would normally employ to uphold your temperature . So it is important to stay well catch one’s breath , O’Rourke enunciate .
This article is for informational purposes only and is not intend to offer medical advice .

Ever wonder whysome people build brawn more well than othersorwhy lentigo come out in the sun ? Send us your questions about how the human body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answered on the website !










