When you buy through link on our land site , we may realise an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it work .
Many people first study aboutmRNAvaccines during thecoronavirus pandemic , when the companies Pfizer - BioNTech and Moderna put out theirCOVID-19 vaccines . The Pfizer - BioNTech shot was the first COVID-19 vaccinum to earn emergency authority in the United States , and later , it would become thefirst mRNA vaccinum of any kind to be fully approvedby the U.S. Food and Drug Administration ( FDA ) .
But even though these get-go took place during thepandemic , template RNA vaccine had been in ontogeny for many years before COVID-19 emerged as a threat .

mRNA technology was thrust into the limelight during the COVID-19 pandemic, but had been in development for decades prior.
Looking forward , they ’ll likely stay to playact a big persona in preventing — and even treating — other diseases in the future .
So what , exactly , are mRNA vaccines , and how do they mould ?
How do mRNA vaccines work?
mRNA vaccinum learn the immune system to aim specific protein , often proteins constitute on a pathogen , like a virus . To do this , they use instructions carried in a genetic molecule call messengerRNA(mRNA ) .
Although they ’re unequalled in that they use mRNA , these vaccines still utilize very exchangeable strategy as traditional vaccines — such as the approve shots formeasles , tetanusorthe flu — to protect against infective diseases .
" All vaccine work by teach yourimmune systemto recognize specific immune signals call antigens,“Dr . Vinod Balanchandran , director of the Olayan Center for Cancer Vaccines at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center , told Live Science in an email . " Antigens are proteins , or even pieces of proteins , that the physical structure recognizes as ' extraneous . ' "
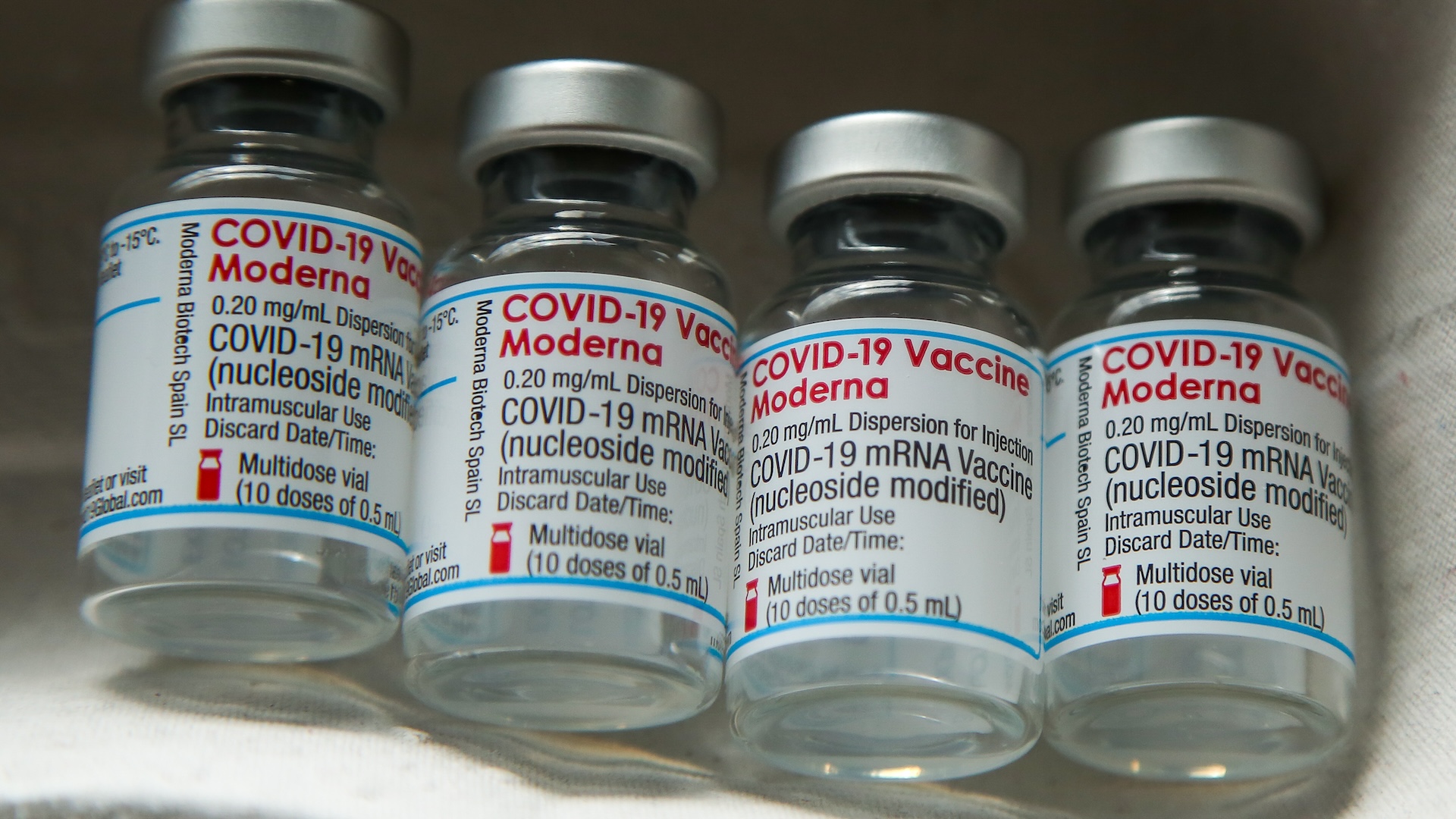
The Moderna COVID-19 mRNA vaccine made history as one of the first mRNA vaccines to enter widespread use.
Traditional vaccines teach the resistant system to recognise antigens from viruses or bacterium by directly exposing the body to antigens from that microbe . A pass on vaccine might contain the whole seed , but a version that ’s been weakened or killed so it ca n’t make disease . instead , a blastoff may convey only a piece of the germ that contains the antigen of pursuit .
When theimmune systemdetects a new antigen , it learns to recognize it as a potentially grave invader . After this training , if the resistant system sees that antigen again in the context of a real infection , it can speedily recruit the trunk ’s defenses and fend off the seed before it takes clench and do serious illness . The most effective vaccines can prevent even mild typesetter’s case of infection .
Rather than carrying any antigen , mRNA vaccinum curb only the inherited instructions for the antigen of interest . These hereditary book of instructions are encoded in mRNA , a corpuscle found in all human cells . mRNA often act as an intermediary corpuscle , carrying the blueprint for building protein from the cell ’s nucleus to a protein - making factory , call a ribosome .

Once an mRNA vaccine is administered , our cellular machinery follows the genetic teaching it arrest to bring out copy of an antigen . This then enables the immune system to familiarise itself with the antigen , as it would with any other type of vaccine .
Related : New template RNA ' genus Cancer vaccinum ' trial launches in UK
What ingredients are in mRNA vaccines?
In add-on to the mRNA itself , mRNA vaccines contain a few other ingredients , which vary somewhat by the vaccinum and maker but accrue into a brace of common categories .
These include lipids , or fats , which assist shape a protective coating around the informational RNA that prevent it safe in the body and enables it to well steal into cells . dissimilar types of sugars , salt , acids and chemical stabilizers also may be admit in a chip in vaccine to facilitate equilibrise the acidulousness of the formula and keep its temperature stable .
These ingredients assist ensure that the vaccinum has fourth dimension to complete its chore before the drug is broken down by the body .
How many mRNA vaccines have been approved?
So far , the only mRNA vaccine to be approved by the FDA are the coronavirus vaccine produce by Pfizer - BioNTech and Moderna .
Other informational RNA vaccines are in various microscope stage of development , admit shot to preventinfluenza , Ebola , Zika virusandHIV , as well as shots aimed at handle and preventingcancer .
Were mRNA vaccines made “too quickly”?
To some mass , it may seem like mRNA vaccinum came out of nowhere , but the engineering science has in reality been in development for over 30 years .
mRNA molecules werediscovered in 1961 , and by 1978 , scientists were experimenting with ways of delivering the moleculesinto mouseandhuman cellular phone . Scientists first testedmRNA injections on living mice in 1990 , and the first human clinical visitation for anmRNA - ground rabies vaccinebegan in 2013 .
It make a long time for scientists to figure out an effective way to deliver mRNA molecules into the body without the ticklish corpuscle degrading . So , although the development of the coronavirus informational RNA vaccines seemed quick , it was actually introduce by decades of research .

Now that the basic technology for mRNA vaccinum live , a groovy advantage of the shots over traditional ones is that they can be farm quickly in response to new pathogen . And they can be apace update for pathogen that evolve speedily , picking up fresh mutations and give rise to novel variants .
As an example , the yearly influenza vaccine ismanufactured primarily using virusescultivated in chicken eggs — a process that takessix monthsto make all of the necessitate doses . By equivalence , " template RNA vaccine can be developed and cook up at a faster pace than other kinds of vaccine , which may be crucial when a Modern computer virus emerges or evolves quickly like we have understand with SARS - CoV-2 , " the computer virus that induce COVID-19 , Melissa Dibble , a former spokesperson for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC ) , told Live Science in an electronic mail .
Related:‘Any protein you’re able to imagine , it can deliver ' : AI will help discover the next find in RNA , says Nobel Prize succeeder Dr. Drew Weissman
Can mRNA vaccines affect your DNA?
mRNA vaccinum do not affectDNA .
" The genetical stuff delivered by mRNA vaccinum never enters the nucleus of your cells , which is where your DNA is keep , so the vaccinum does not alter your DNA , " Dibble said .
moreover , " after the consistency produces an immune response , it get rid of all the vaccinum ingredients just as it would get free of any information that cells no longer ask , " she said .

Typically , an mRNA vaccine takesa few days to be fully broken downby the soundbox .
What are possible side effects of mRNA vaccines?
The COVID-19 informational RNA vaccines have been shew to be safe , with most reported side effects beingmild and temporary . These side gist , which are also seen in people given traditional vaccines , include annoyance or tumefy at the injection site , headache , weariness , muscle or joint pain , nausea , chills and febricity .
Serious side event are very rare . For model , anaphylaxis , a stark supersensitized reaction that can potentially hap after any case of inoculation , occur in about 5 out of every 1,000,000 COVID-19 mRNA vaccinum superman .
Myocarditis and pericarditis — which respectively involve dangerous kindling in or around the heart — can happen very seldom in answer to mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 , but these conditions typically respond well to discussion . It ’s also important to note that both myocarditis and pericarditis arepotential complications of a COVID-19 infectionitself , and that the peril of prepare heart complications from aninfectionis about ten times greater than the risk of infection from thevaccine .

Based on these data and data from clinical trials , expert have concluded that the welfare of mRNA vaccinum far preponderate any potential risk .
What is “frameshifting,” and should I be concerned?
A2023 report published in the diary Naturesuggested that the body can sometimes accidentally make a diminished amount of the wrong proteins base on the genetic instructions from an mRNA vaccinum . The subject area was conducted in lab mouse and a radical of 20 human participants .
The effect was due to a knock - on resistant reaction , the investigator reported , and it happened due to a phenomenon called " frameshifting , " in which a cubicle ’s protein - making machinery starts reading an mRNA mote at the incorrect point of its episode .
Most of the time , the cell detects that the frameshifted teaching are frill , and it stop making the protein . But every now and then , a cell may acquire a belittled quantity of the wrong protein . However , the Nature study launch that these frameshifted proteins were n’t harmful and that none of the survey participant who experienced this reception had any vaccine side effects . And notably , prison cell do n’t proceed to make the frameshifted protein after the mRNA has break down , so this is a temporary effect .

Frameshifting is not uniquely associate with mRNA vaccinum — it also occurs during actual viral transmission . computer virus double inside the soundbox by hijacking cellular machinery to re-create their viral DNA , and frameshifting can often happen during this mental process , too . In fact , the investigator of the Nature subject area suggest that exposure to frameshifted protein might help the soundbox modernize broad immunity to a computer virus .
The authors of the field emphasized thatneither the frameshifting or knock - on immune responses they keep compromise the safety of mRNA vaccinum . However , they indicate that succeeding mRNA vaccines be designed with molecules that prevent protein - making machinery from " slipping " around the informational RNA strand . This would aid cells read the mRNA more accurately , without frameshifts , and make new vaccines even more accurate .
The future of mRNA vaccines
Although mRNA vaccines rise to prominence during the coronavirus pandemic , their applications stretch far beyond infectious diseases .
— New mRNA therapy shows promise in process ' ultrarare ' inherit disease
— Could we ever eradicate the flu ?

— 2 - in-1 shot for flu and COVID shows promise in advanced visitation
Today , many cut - edge research groups are exploring the electric potential of mRNA technologies to treat conditions such asCeliac disease , lung damage , preeclampsia , brain cancerandpancreatic malignant neoplastic disease .
" We are very excited about the diligence of mRNA vaccine to treat cancer , " Balachandran said . " In our body of work oncancer vaccine , we apply mRNA technology because it is amenable to rapid and conciliatory yield , allow us to customise a vaccinum for every patient . " Cancer vaccines in general work like a kind of immunotherapy , prime the resistant system to go after tumor cells that can otherwise shroud from its attacks .

This article is for informational intent only and is not meant to offer medical advice .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to figure your display name .






