When you purchase through links on our land site , we may earn an affiliate deputation . Here ’s how it works .
Monstrous rubble storms often ravageMars , engulfing the Red Planet for month . Now , a new study suggests these global storms may be related to a peculiar DOE imbalance recently name across the Martian surface .
Thesolar system’splanets and moonshine absorb energy from the sun , but they also give out energy back into distance . The difference of opinion between these two is called theradiative energy budget , or REB . " The REB and its spacial distribution [ across latitudes ] straight influence the thermal characteristics of the surface and atmosphere " of planets , Liming Li , a professor of cathartic at the University of Houston and the study ’s second author , severalize Live Science via electronic mail . This means a planet ’s REB determines its mood .
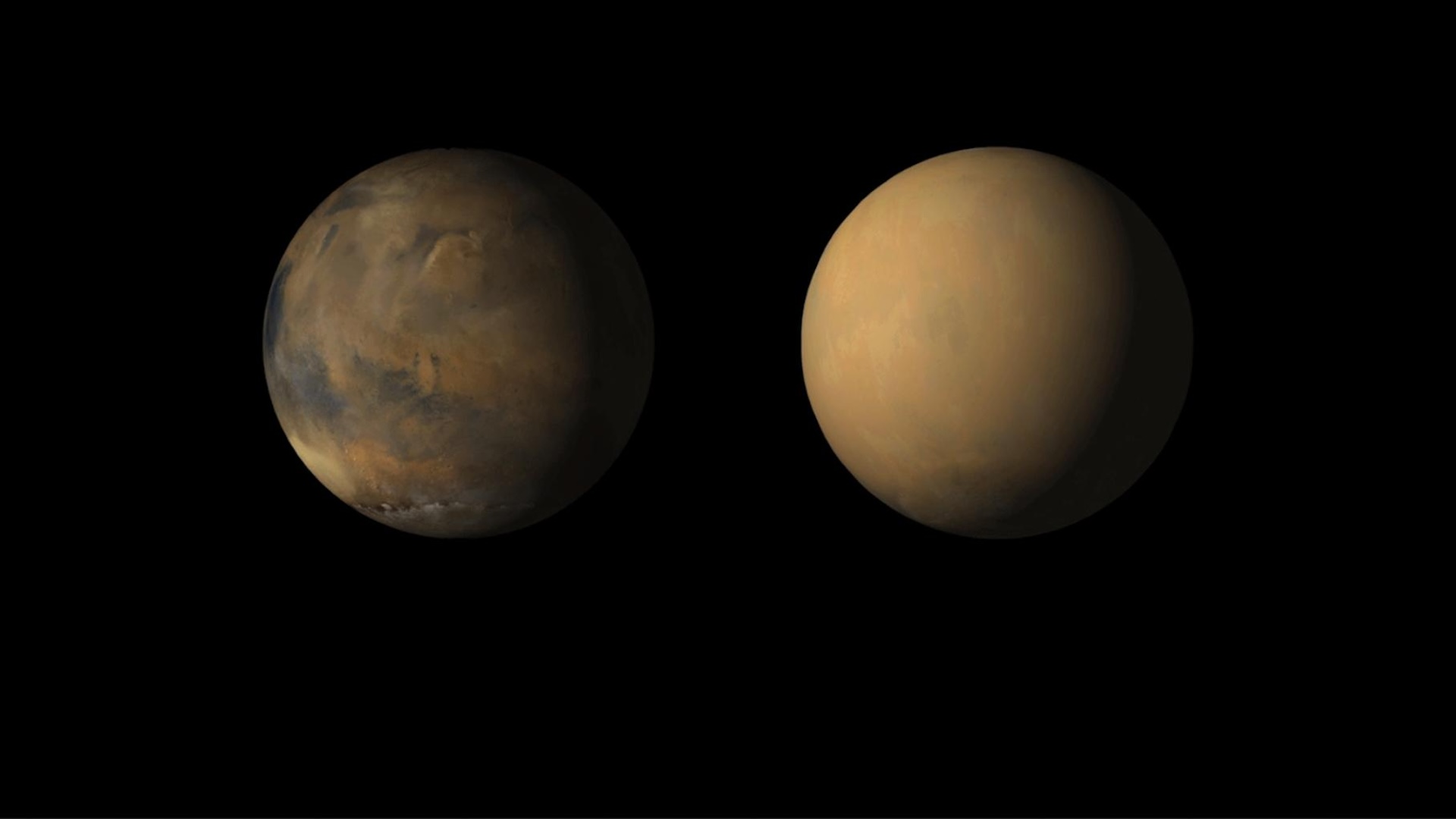

A global dust storm that originated in Mars' southern hemisphere in May 2018 (left) completely blanketed the planet till July (right).
scientist have studied Earth ’s REB in great detail , line up " an Energy Department surplus in the tropics and an energy shortfall in the polar regions , " Li said . However , Earth ’s annual REB is for the most part balanced , with the amount of solar vigour absorbed just about balance the heat radiated over a year ’s time ( althoughgreenhouse gasesare changing this to a flyspeck net absorption ) .
In contrast , researchers know little about Mars ' REB , especially if it ’s balanced . Although theory paint a picture this should be the case , it ’s hard to know without grueling numbers .
pertain : Giant ' kidney beans ' fleck in Mars artificial satellite images could maneuver to house of water and living
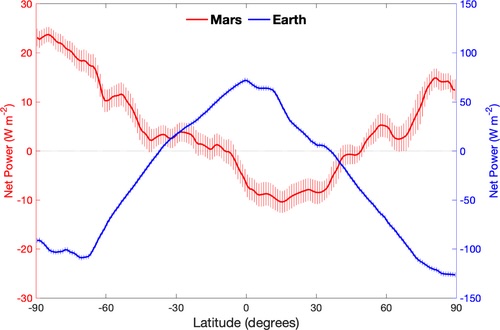
Whereas Mars' radiative energy budget has an asymmetric U shape, Earth’s looks like a symmetric-but-inverted U.
Not acknowledge Mars ' REB has also prevented research worker from earn a good understanding of the planet ’s climate . Curiosityand otherNASArovers have captured heaps of Martian conditions phenomenon . The most striking of these are the planet - engulfing rubble storms that spring up in Mars ' southern cerebral hemisphere , some of which are powerful enough to imperil current and future geographic expedition missions . But these observations do n’t give away the long - condition clime over the entire satellite . An estimation of Mars ' REB would work part of that puzzle , according to lead discipline authorLarry Guan , a doctoral student at the University of Houston .
To do this , Guan , Li and researchers from U.S. , Spanish and South Korean universities drew on data point about the infrared and seeable radiation syndrome that Mars ' surface emitted and meditate over several years . Collected by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer aboard NASA ’s now - defunctMars Global Surveyor , these observations sweep five Martian years ( about 10 Earth years , since oneMartian yearis 687 Earth days ) . From these measurements , the researchers look how much energy Mars absorb and emitted across its latitude , from the equator to the pole . For comparison , the research worker also cipher Earth ’s REB , averaged over 10 Earth years , across bands of latitudes .
The researchers found that when Mars ' northern hemisphere experiences spring and summertime , the area around the northern latitudes soak up more vim than it give out , create an " push surfeit " centered on the major planet ’s north pole . Likewise , during the northern hemisphere ’s fall and winter — the southern hemisphere ’s leaping and summer — the reverse occur , with an energy excess developing over more southern regions , although this is strong and cloak the full hemisphere . The investigator reasoned that this utmost scenario occurs because , during the southern spring , Mars is at its close tothe sun , which maximizes the solar push the major planet receives .

The energy nimiety may also trigger the global dust tempest , the inquiry suggest . As the southerly cerebral hemisphere warms up , so does the layer of Mars ' thin atmosphere in contact with it . This creates condition that can loft junk particle , thus kicking off the storm , the researchers suggest .
But the reverse is rightful , too : The dust storms likely shape the satellite ’s REB . The Mars Global Surveyor dataset admit measurements during a dust storm that spring up in the southerlyHellas Planitiaimpact basin and swathed the whole planet one southern spring . depth psychology of this data revealed that the storms tend to reduce both the solar free energy absorbed and the heat emitted by Mars , maybe owe to the legion detritus particles swim in the atmosphere .
— 30 old age of polar climate data convert into menacing , 6 - moment birdcall

— ' Marsquakes ' may solve 50 - year - old mystery about the Red Planet
— ' Cryptic terrain ' and dark dust surrounds Mars ' polar south pole , new exposure unwrap
Despite these seasonal imbalance , Mars ' annual REB is about balanced . But when think across latitude , it differ profoundly from Earth ’s . " Earth ’s deficit are at the pole ; Mars has shortfall at the tropic — and vice versa for excesses , " Guan tell apart Live Science via email . This think that whereas Earth ’s poles engross less energy than they let loose , Mars ' poles do exactly the opposite word .

Plus , Guan said , unlike Earth , Mars ' polar REB can change by 100 % between seasons . This may be due to the major planet ’s thin atmosphere , Li suggest , which prevent free energy distribution between the tropic and the poles .
The study waspublishedDec . 19 in the daybook AGU Advances .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your video display name .













