When you buy through links on our site , we may realise an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it ferment .
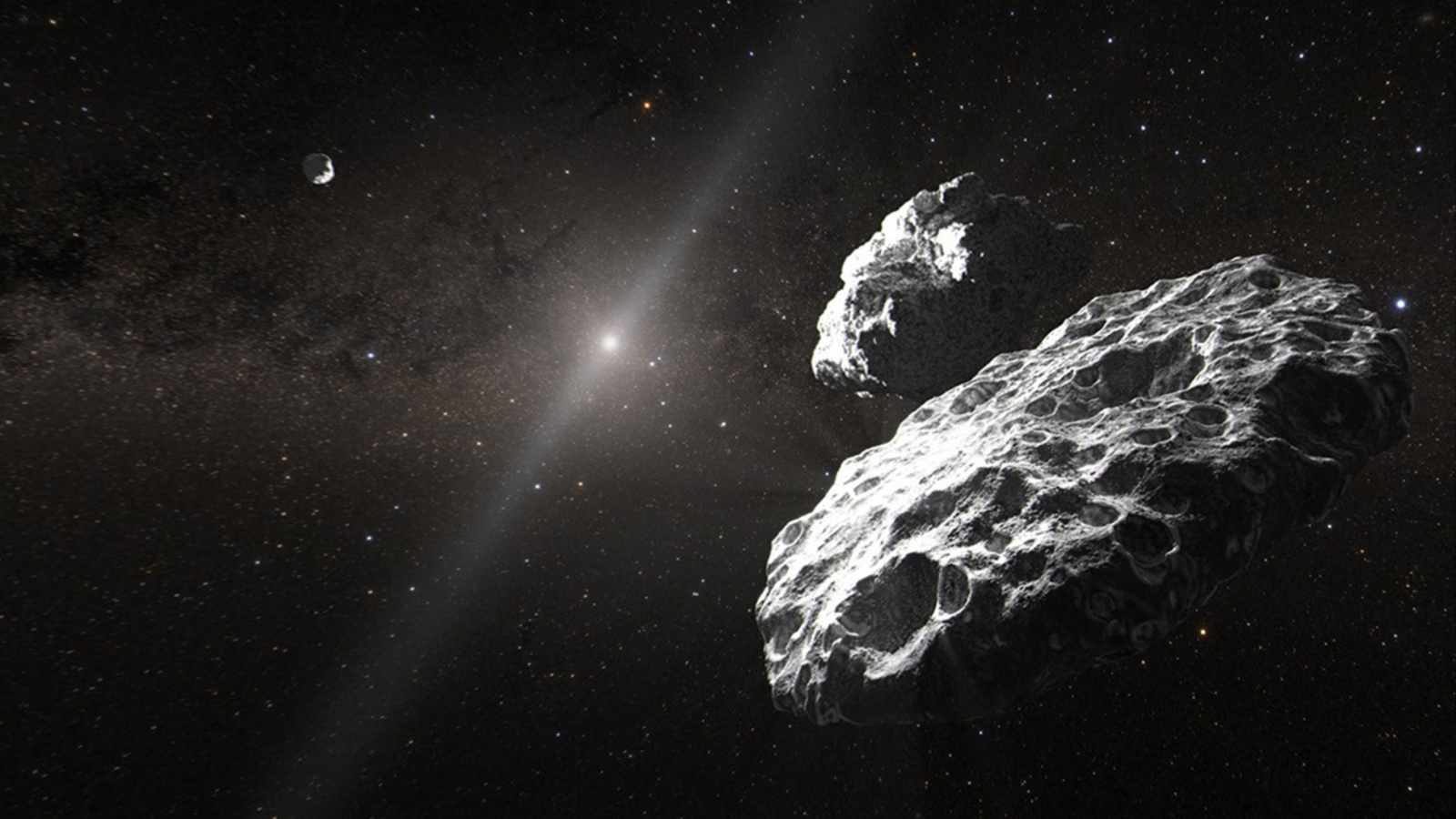
inscrutable pairs of " rogue , " Jupiter - size objects may have arisen from embryonic stars , a new study suggests . The theory could explain some characteristics of theseJupiter - masses binary objects(JuMBOs ) , such as why member of each pair are so wide separated , but more data is needed to confirm the theme .
TheJames Webb Space Telescopespotted these JuMBOs in the trapezoid zone of the Orion Nebula . Each JuMBO pair represent two gas giant , each between 0.7 and 30 time the mass of Jupiter . These " rogue " planet mate have been found orbit each other — but not a parent star topology — at a distance of about 25 to 400 galactic units , or 25 to 400 times the average distance between Earth and the sunlight .
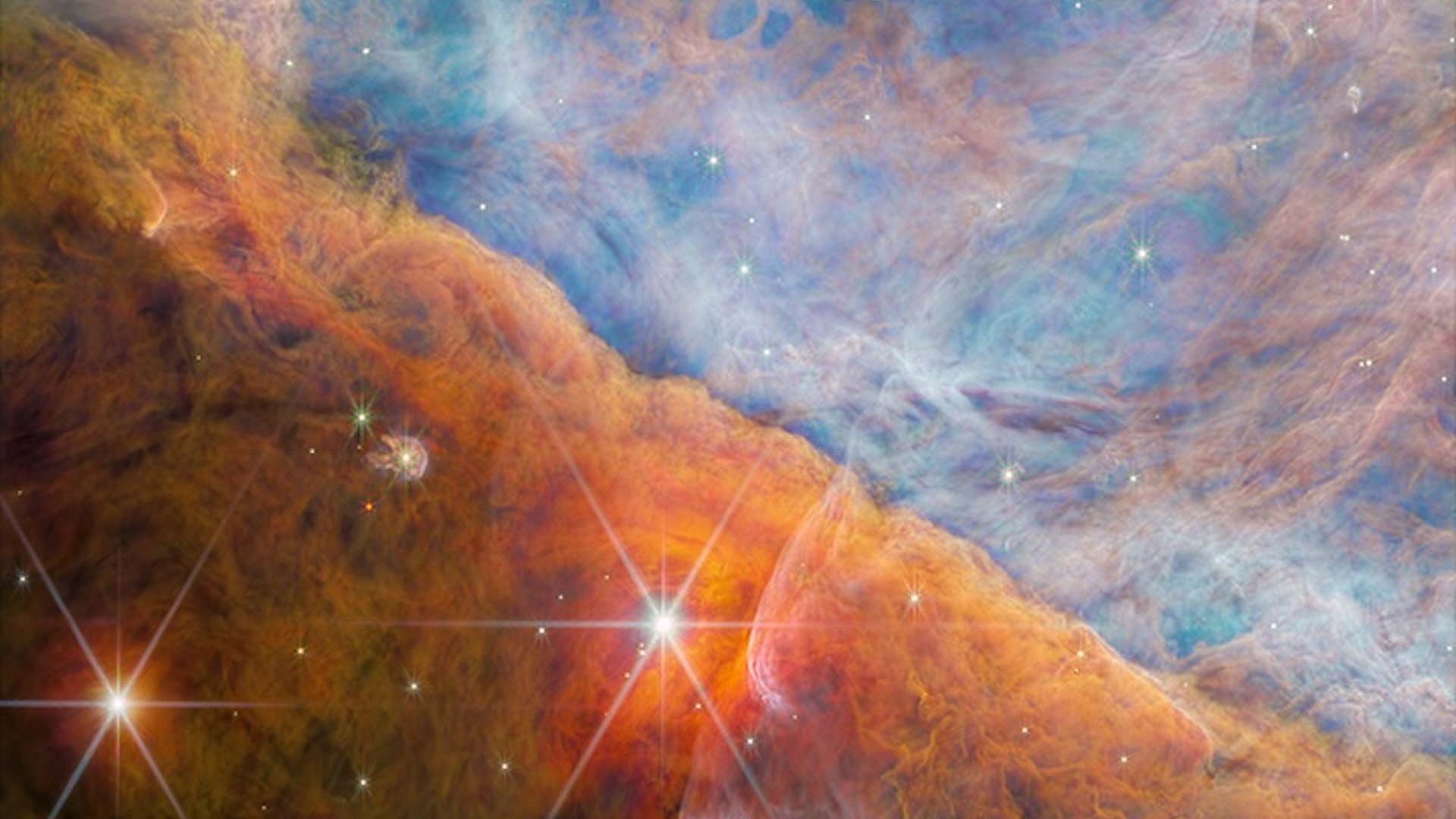

The Orion Nebula, seen in this JWST image, is home to dozens of mysterious paired Jupiter-size planets, zooming around untethered to any star.
Astronomers have purpose several ideas for how these mysterious duos form . One theoryis that they were flung at the same time from their home systems by a decease star , althoughsome scientistsbelieve this is very unlikely . Anotherideais that JuMBOs emerged around a lead but their somberness tug them toward each other and out of orbit during close skirmish .
However , all of these theories assume that JuMBOs originate from planet that have already shape . In contrast , the new bailiwick proposes a radically different idea : that the Orion Nebula ’s JuMBOs are n’t preexist pairs of planets but rather the hearts of embryologic superstar .
A star form from a monumental and impenetrable swarm of gas and debris call a pre - stellar substance . As a nitty-gritty grows , it collapses under its own exercising weight , forming a baby whizz call a protostar ; if the core fragment , it could form twinned or even ternion headliner .
Related : James Webb Space Telescope smash its own record book to find the earliest galaxies that ever existed
But such greenhouse are n’t serene places . They could be surrounded by massive stars — just as the Orion Nebula is — which produce improbably high - energy radiation . Twenty long time ago , the astronomers Anthony Whitworth and Hans Zinnecker had theoretically shown that these brawny photons could pummel pre - stellar cores , strip aside their outer layers . At almost the same prison term , a compression wave would bear on against the core ’s center , compress it into a smaller - tidy sum object . The final result was that the star itself transform into a satellite or abrown nanus , which is sometimes call a " failed star " because it ’s not monumental enough to fuse hydrogen to He .
The unexampled cogitation ’s authors knew of Whitworth and Zinnecker ’s study and wondered whether the same mechanism could create JuMBOs , too . They " noticed that the JuMBOs [ ' ] separations were similar to those ofstellar binary systemswith two stars of interchangeable or higher sight to the Sun,“Richard Parker , a senior lector in astrophysics at the University of Sheffield in the U.K. and elderly author of the unexampled study , distinguish Live Science in an electronic mail .

That makes them unlike most brown dwarf twins elsewhere in theMilky Way , which are divide by only a few Earth - sun distances , Parker said , so a dissimilar mechanism must be regard . " We supposed that the core was already fragment to create a stellar binary program , but then the radiation from the monolithic star removed a batch of the mass , " he added .
To test this idea , Parker and Jessica Diamond , a graduate student at the University of Sheffield and lead source of the study , turned to hypothesis . First , they make a bunch of virtual pre - astral cores , each with a mass within the range of mountains spotted in nature . They also assumed the core would split into two , and selected a value for the spatial arrangement between the siblings — again , from economic value observed among star duo . Then , they practice Whitworth and Zinnecker ’s computation to the virtual cores . This fundamentally pound them with in high spirits - vigour radiation sickness from a nearby massive star , fret the core ’s cloak and compressed its center field .
— Physics - breaking ' rogue ' objects spot by James Webb telescope are let loose radio signals that scientists ca n’t excuse

— hundred of inscrutable ' scallywag ' planets key out by James Webb telescope may in conclusion have an account
— James Webb telescope reveals long - study infant star is actually ' Gemini ' — and they ’re throwing identical conniption
Diamond and Parker found that the resulting match object had masses and detachment distances very similar to the JuMBOs ' . The findings suggest that , with a strong push of radiotherapy from neighbouring whiz , developing binary stars could become pairs of rogue planets , providing an account for how the JuMBO couple form . The results of theirstudywere published Nov. 5 in The Astrophysical Journal .

More data , such as grounds of JuMBOs in other star - forming complexes with monolithic stars , would help to affirm the hypothesis , Parker tell . In his opinion , one exemplar of such a plaza is the Scorpius - Centaurus association , a conglobation of thousands of champion that make up parts of the constellations Scorpius and Centaurus .
In any case , Parker does n’t govern out JuMBO organisation through other path . " I always have a hard clock time in thinking there is only one means to take shape aim like these , " Parker aver . " We hump so little about them that it ’s feasible they may make from a variety show of slipway . "











