When you purchase through link on our website , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it operate .
For the first clip , researchers have capture nanoscale video footage of hydrogen and oxygen atoms conflate into piddle out of " slight air " — thanks to a rare metallic element catalyst . The super - efficient response , which could one day serve astronauts make piddle in space , also produced the small bubble of H2O ever seen , researchers say .
The video was part of a new study , publish Sept. 27 in the journalPNAS , in which researcher test how Pd catalyzes a reaction between hydrogen and oxygen gas to create water in standard lab conditions . The squad studied this chemical reaction with a new type of monitor apparatus that captured the summons in extraordinary detail .
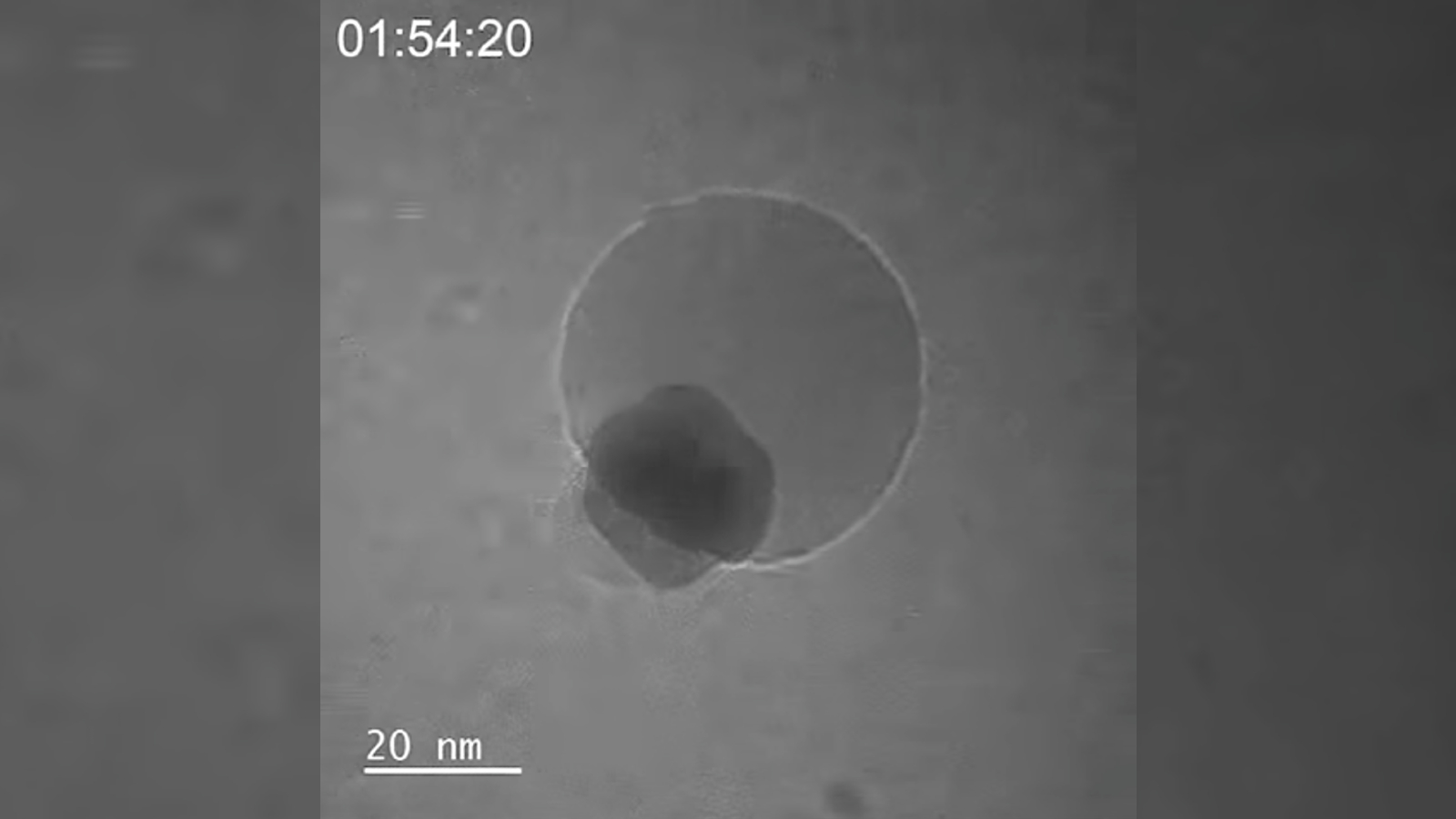

Researchers believe that they have captured footage of the smallest water bubble ever seen by humans. It measured roughly 50 nanometers (0.000002 inch) across.
" We think it might be the smallest bubble ever work that has been viewed directly , " study lead authorYukun Liu , a materials scientist at Northwestern University in Illinois , said in astatement . " fortuitously , we were recording it , so we could leaven to other citizenry that we were n’t crazy . "
The team make the reaction using a special ultra - fragile glassy membrane that take for gas molecules within honeycomb - shape " nanoreactor " chambers . This intend the tests can be view in substantial time using electron microscopes , activate the researchers to learn more about how the reaction works .
investigator from the Northwestern University Atomic and Nanoscale Characterization Experimental Center ( NUANCE ) open up this novel technique in astudy issue in January .

touch : fresh reactor could more than triple the yield of one of the cosmos ’s most worthful chemicals
research worker have known since the 1900s that palladium , a silver-tongued - white uncommon alloy alike in appearance to platinum , can catalyze a ironic reaction between H and atomic number 8 , researchers wrote . However , until now , it was unclear incisively how the reaction worked .
The fresh survey discover that the gaseousatomsfirst squeeze between the palladium particle , which are arranged in a substantial grille . This expands the lattice and enable body of water droplet to form on the accelerator ’s surface . The team also find that the process can be sped up by adding hydrogen atom to the atomic number 46 first , because they are small than oxygen atoms . This enables the palladium lattice to expand before the oxygen is added , creating heavy gaps for the expectant atoms to fit more promptly deep down .
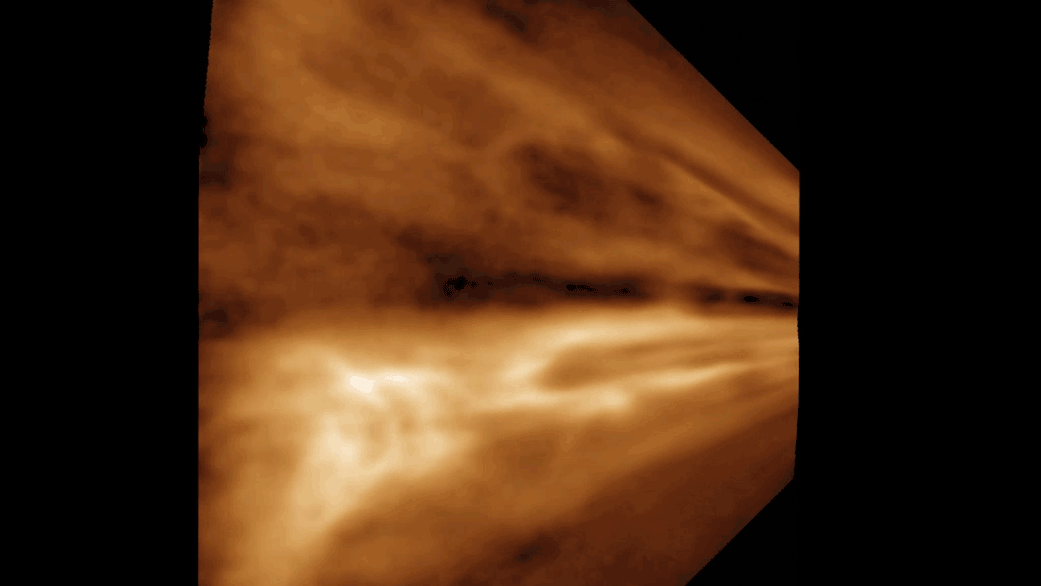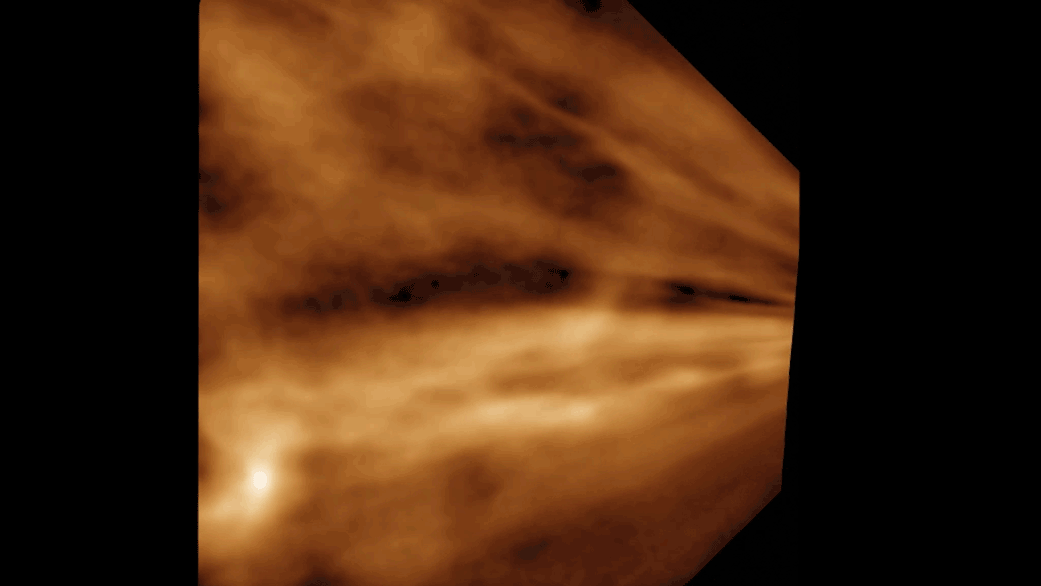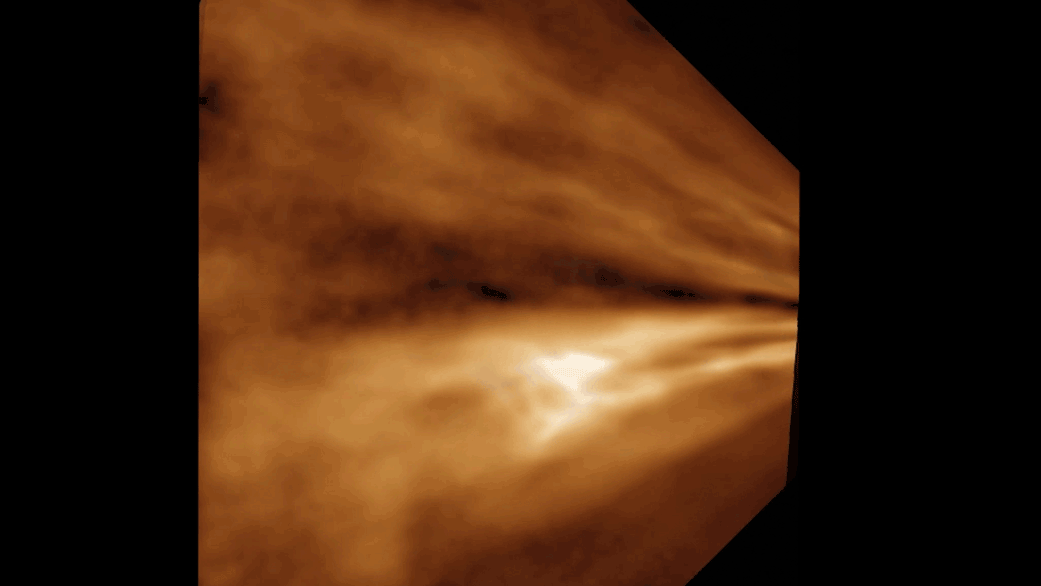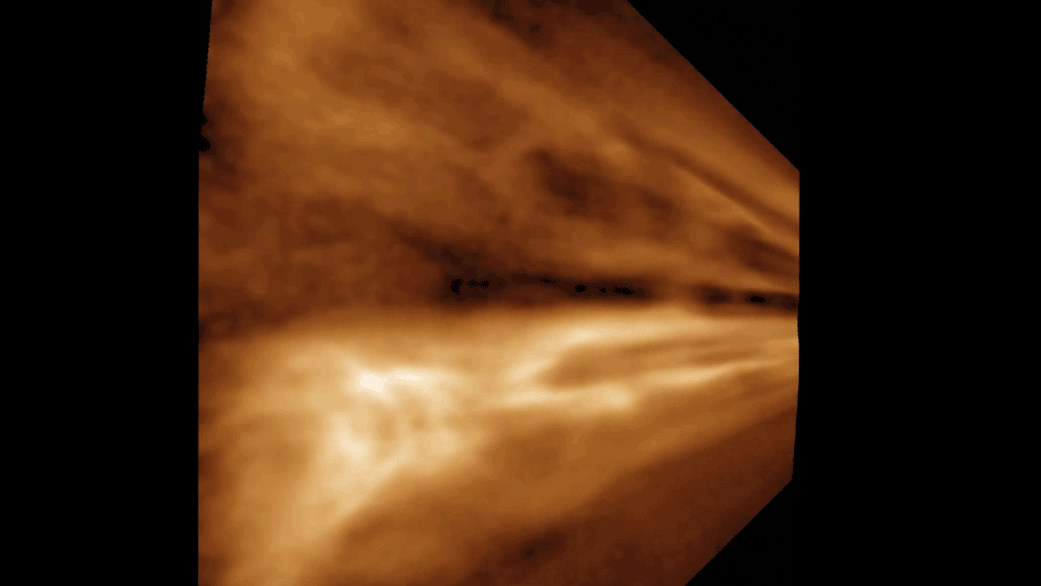
The squad trust that a scaled - up version of the chemical reaction could be used to create water for astronauts in space or in dependency on otherplanets . The researcher compare it to a scenery from the sci - fi film " The Martian " starring Matt Damon , in which a stranded cosmonaut makes pee on Mars by burning arugula fuel and combining it with oxygen from his suit .
" Our process is analogous , except we bypass the need for attack and other extreme conditions , " report atomic number 27 - authorVinayak Dravid , theatre director of the NUANCE Center , said in the instruction . " We just mix palladium and gases together . "
— Scientists grow diamonds from scratch in 15 minutes thanks to groundbreaking new procedure

— World ’s thin gold leafage , dubbed ' goldene , ' is just 1 atom thick
— Chinese scientist have find a direction to make battery more efficient — by using H2O
Pd is an expensive and rare material , costingupwards of $ 1,000 per apothecaries' ounce . This is largely because it can catalyse many other chemical substance reactions and is used in a wide range of technologies . As a upshot , creating a water - engender equipment for astronauts could be super high-priced .

However , the researchers argued that it would be worth the expense in the long run .
" Palladium might seem expensive , but it ’s reclaimable , " Liu say . " Our procedure does n’t devour it . The only thing wipe out is accelerator , and hydrogen is the most abundant gas in the world . "