When you purchase through connection on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Vampirebatsrely on blood - descend aminic Zen to fire their activity , scientists have discovered after making the animal work out on tiny treadmills .
Most mammals , include human , trust on carbohydrates and fats from their complex dietsto fuel physical activity . However , vampire bat exclusively go through blood , which is very low in carbohydrates and avoirdupois but mellow in protein . This raises the question of whether vampire squash racket rather obtain most of their energy from the protein they consume — similar to bloodsucking worm .
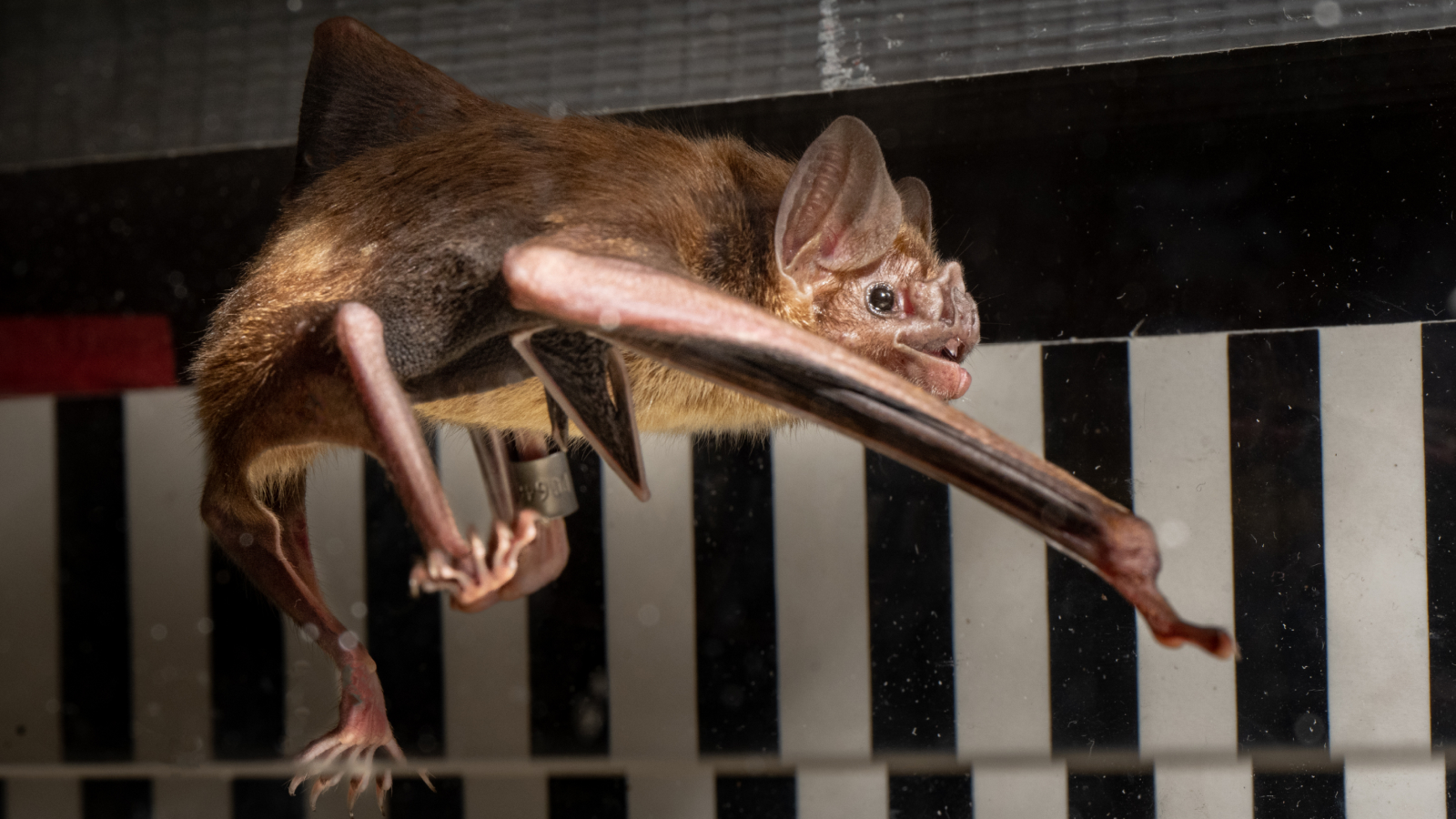

Unlike most mammals, vampire bats rely on amino acids to fuel their activity.
" Whereas most mammals , like us , rely on carbohydrates and lipide to fire our natural process , these fuels are not abundant in the vampire squash racket dieting , suggesting they might not rely on those fuels like us , " study lead authorKenneth Welch , an associate prof of biology at the University of Toronto , told Live Science in an email .
There are three vampire cricket bat species : the common lamia at-bat ( Desmodus rotundus ) , the haired - legged vampire bat ( Diphylla ecaudata ) and the white - wing vampire squash racket ( Diaemus youngi).All are found in strong regions of the Americas , include Mexico , South America and Trinidad , according to theSan Diego Zoo . They live in colony of20 to 100individuals and are the only mammalian that are obligate blood birdfeeder .
Related : Scientists unlock the secrets to squash racquet ' fleshy - alloy growling
Vampire bats are obligate blood-feeders.
The unwashed vampire bat is theonly vampire bat metal money that ’s open of running ; it uses a unequalled bounding pace to move promptly on the ground . Much like gorilla , they use their front limbs to propel themselves in short burst so they canmove quickly toward their prey .
In the new study , published Nov. 6 in the journalBiology Letters , scientists capture 24 adult usual vampire chiropteran along known flight of steps paths in the tropical forest of Belize . The bats were held for up to 18 hour to check that their last meal was in full support . The vampire bats were course with cow ’s blood enriched with one of two labeled amino group acids — glycine or leucine . Each cricket bat was then send into a treadwheel sleeping room so scientist could measure the ratio of O to carbon dioxide ( CO2 ) and forecast the pace of metabolic activity at different running speeds .
To determine if the amino acids were being used for energy , the researcher used a specialised car with infrared lasers to detect the presence of sure C isotopes in the exhaled carbon dioxide .
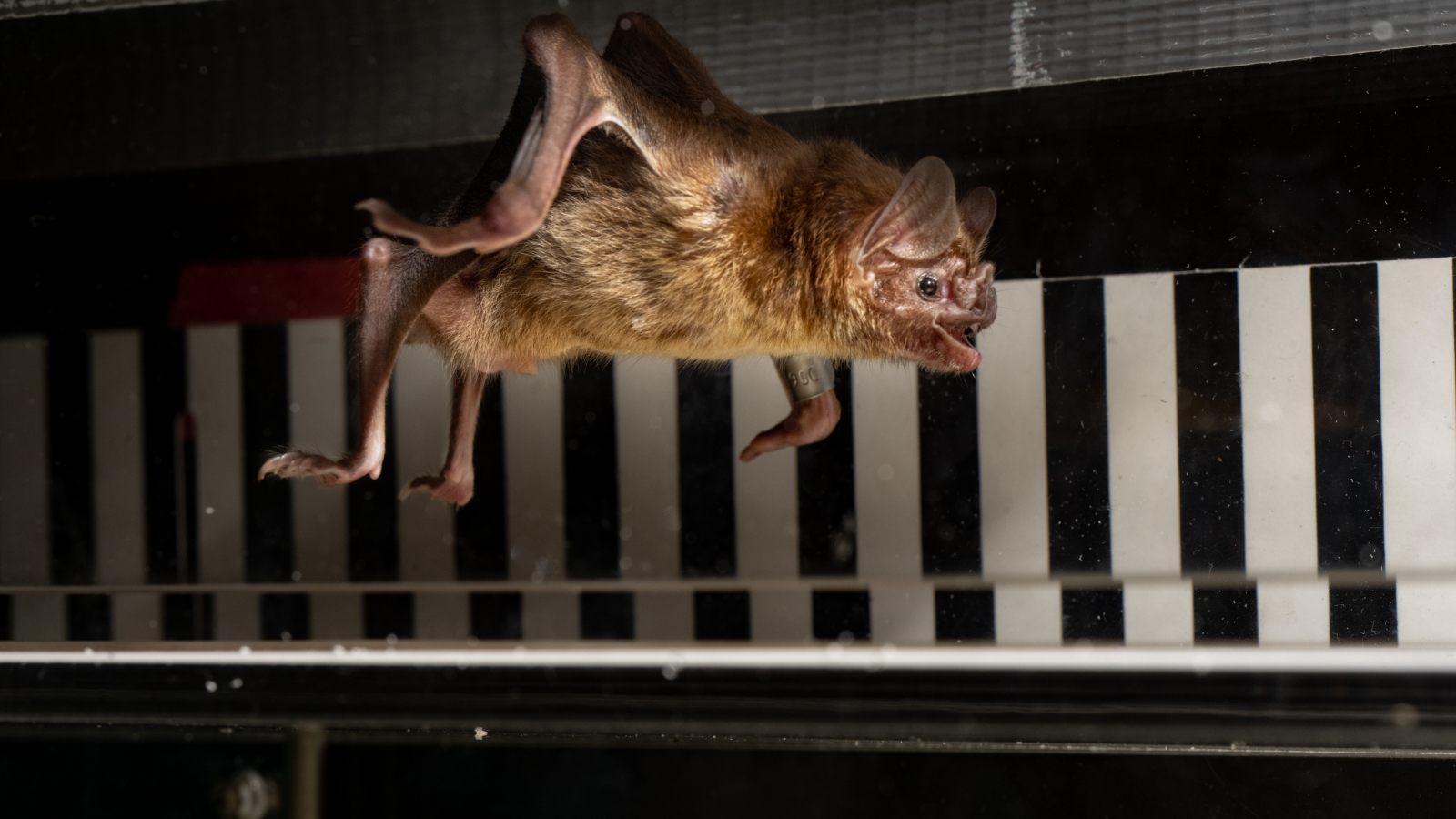

The common vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus) uses a gorilla-like movement to run.
The solvent revealed that the ratio of O to C dioxide remain uniform across all tread-wheel speeds . This indicated that the vampire at-bat were using aminic acids as their basal fuel source , the researchers say . In other mammalian , the ratio increase with the strength of exercise , mirroring the shift from burning lipide to burning carbohydrates .
The scientists also found that the vampire bat rapidly absorbed the free amino acids within just 10 proceedings of consuming their meal .
— pound - channelize bat : The African fruit bat that looks like a gargoyle and concord honking pageants

— bat with weirdly giant member have sexual urge for up to 12 hours in a way never seen in mammals before
— 52 million - class - previous bat skeleton is the oldest ever found and belongs to a never - before - see species
" What was telling was how quickly that judge CO2 showed up , and how abundant it was from these bats , " Welch say . " The rapid appearance of their labeled pause - down mathematical product indicated the bats were oxidate ( " burn " ) those aminic acids in their muscles while walk / running . "

Although this method of vigor propagation is rare among mammals , previous studies of bloodsucking invertebrates liketsetse flies(Glossina)and female mosquito of the speciesAedes aegyptifound that they , too , get their free energy from the breakdown of amino group acids .
" What we have shown in this study is that ply lamia bats show a similar convention of trust on stock - meal amino acids to fire their intense exercise as do these [ bloodsucking ] insects , " Welch said .
The constant surveillance of advanced life could aggravate our mastermind function in agency we do n’t fully understand , interrupt studies suggest

image capturing a starve lion , struggle bison and pit of vipers abide by in environmental picture taking awards
Scientists unclutter major roadblocks in military mission to build powerful AI photonic chip






