When you purchase through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate deputation . Here ’s how it crop .
Vampires do n’t only haunt the pages of classic novels and spook us in repugnance movies — they ’re also lurking inside thehuman soundbox .
In new research , scientists have found that several bacterium responsible for animation - imperil bloodstream infections enter our blood because they are attracted to the liquidity , or serum , within it . This is most potential because human line of descent contains a molecule — the amino acid L - serine — that bacteria can use as food . The research worker behind the subject field have knight this phenomenon " bacterial vampirism . "

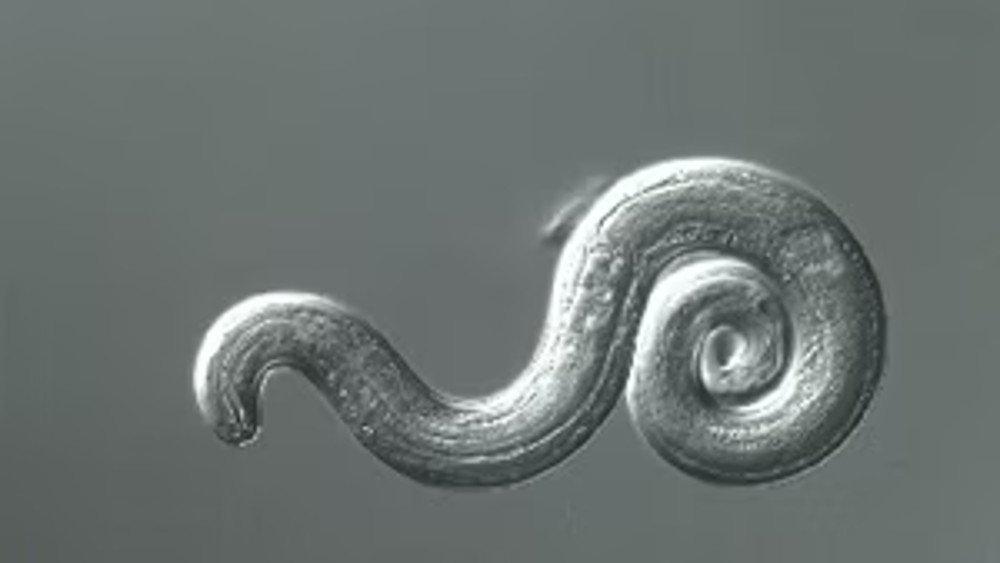
Gut bacteria pictured above under a microscope, are attracted to human blood because it contains important nutrients.
The scientists concentrate on three species of bacterium commonly found in the human bowel that belong to to the Enterobacteriaceae kinsfolk , calledSalmonella enterica , Escherichia coliandCitrobacter koseri . They found that all three species exhibit these vampire - like traits when exposed to blood serum try from human .
bacterium werealready knownto be attracted to L - serine ; however , the new findings demonstrate how this reaction could specifically help disease - do bacteria obtrude upon our parentage .
Members of the Enterobacteriaceae sept are commonly associated withbloodstream contagion , which can lead tosepsis , or blood intoxication . Blood isnormally sterile , mean it ’s destitute of bacterium and other potential pathogen , so when bacterium end up in the blood it can be a big problem .

As many of these Enterobacteriaceae bacterialive in the intestines , the great unwashed with conditions that handicap their enteral immune defence — such asinflammatory gut disease(IBD ) — are at specially gamey risk ofdeveloping bloodstream infections .
Related : cholesterin - gobbling bowel bacterium could protect against sum disease
Until now , though , scientist did n’t sympathise on the dot why these bacteria are attract to human blood . Uncovering their genus Dracula - same tendency could therefore lead to new treatment for deadly bloodstream infections , say the source of the new study , which was bring out Tuesday ( April 16 ) in the journaleLife .

" By learning how these bacteria are able to detect informant of blood , in the future we could develop new drug that stymie this ability,“Siena Glenn , lead study writer and postdoctoral student at Washington State University , say in astatement . In short , these drugs could be to bacterial vampires what garlic and crucifix are to fictional vampires .
" These medicines could improve the lives and health of people with IBD who are at gamey jeopardy for blood stream infections , " Glenn said .
In their study , Glenn and colleagues grewS. enterica , E. coliandC. koseriin petri dishes . They then introduced human serum onto these dishes , simulating how these bacteria may be exposed to human stemma during intestinal hemorrhage , for instance .

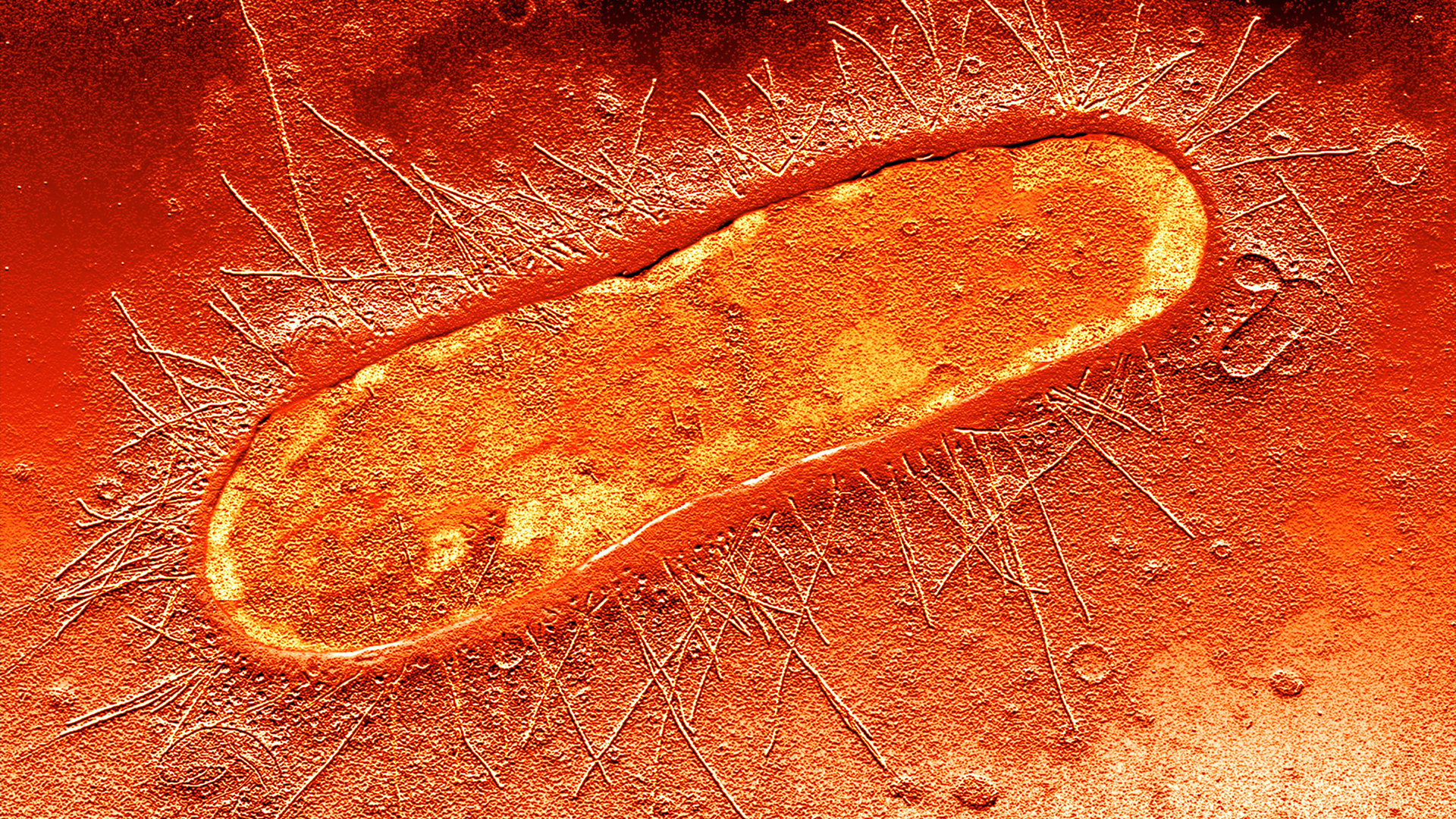
The bacteria straight off responded to the serum , swim toward its source within less than a minute . Using a in high spirits - resolution microscope , the squad also discovered that theSalmonellabacteria possess a protein that interact with cubic decimetre - serine in the serum .
This protein , a receptor called Tsr , is found across the whole Enterobacteriaceae syndicate , suggesting that L - serine is a central chemical in descent that these bacteria smell .
" This field of study is interesting in that it firmly show that bacterium are attracted to human serum , most in all likelihood due to their attraction to the molecule L - serine , which is quite prevalent in serum,“Navish Wadhwa , an adjunct prof in the Department of Physics and the Biodesign Center for Mechanisms of Evolution at Arizona State University , who was not need in the research , told Live Science in an electronic mail .

— uncommon meningitis and blood stream infection on the rise in the US , CDC warns
— Bacteria can evolve electric resistance to life - saving drug they ’ve never seen . Here ’s how .
— serious ' Bemisia tabaci ' are a growing terror , and antibiotics ca n’t turn back their rise . What can ?

" While bacterial attraction to 50 - serine has been experience at least since the 70s , this field of study places it in the context of emcee - bacterial interactions , " Wadhwa read . It reveals how this sensing ability can specifically draw bacteria towards human profligate .
Going forrader , it would be valuable to see if and how other substances in blood , such as sugars and small-scale molecules , might attract bacteria to human blood serum , he said . This could point to additional ways to forbid the blood - sucker from intrude on our vein .
Ever wonder whysome masses build muscle more easily than othersorwhy freckles come out in the sun ? institutionalise us your questions about how the human body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the open product line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your head answered on the website !