When you buy through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Mouse , louse or squirm — in all these creatures , the same principle channelise the geological formation of super strong connection between nerve cell in thebrain , a new subject field confirms . The research helps validate the idea that , regardless of coinage , there ’s a universal mechanics that underlies how brain networks work .
Different animals carry contrasting numbers of neurons in their brains , ranging from hundreds in worm to tens of billions in mankind . Neuronsform connectedness with each other , call synapsis , that enable information to pass from one part of the brain to another in the form of electrical sign . Together , these connections form a internet that enable animals to function and process selective information about the world .
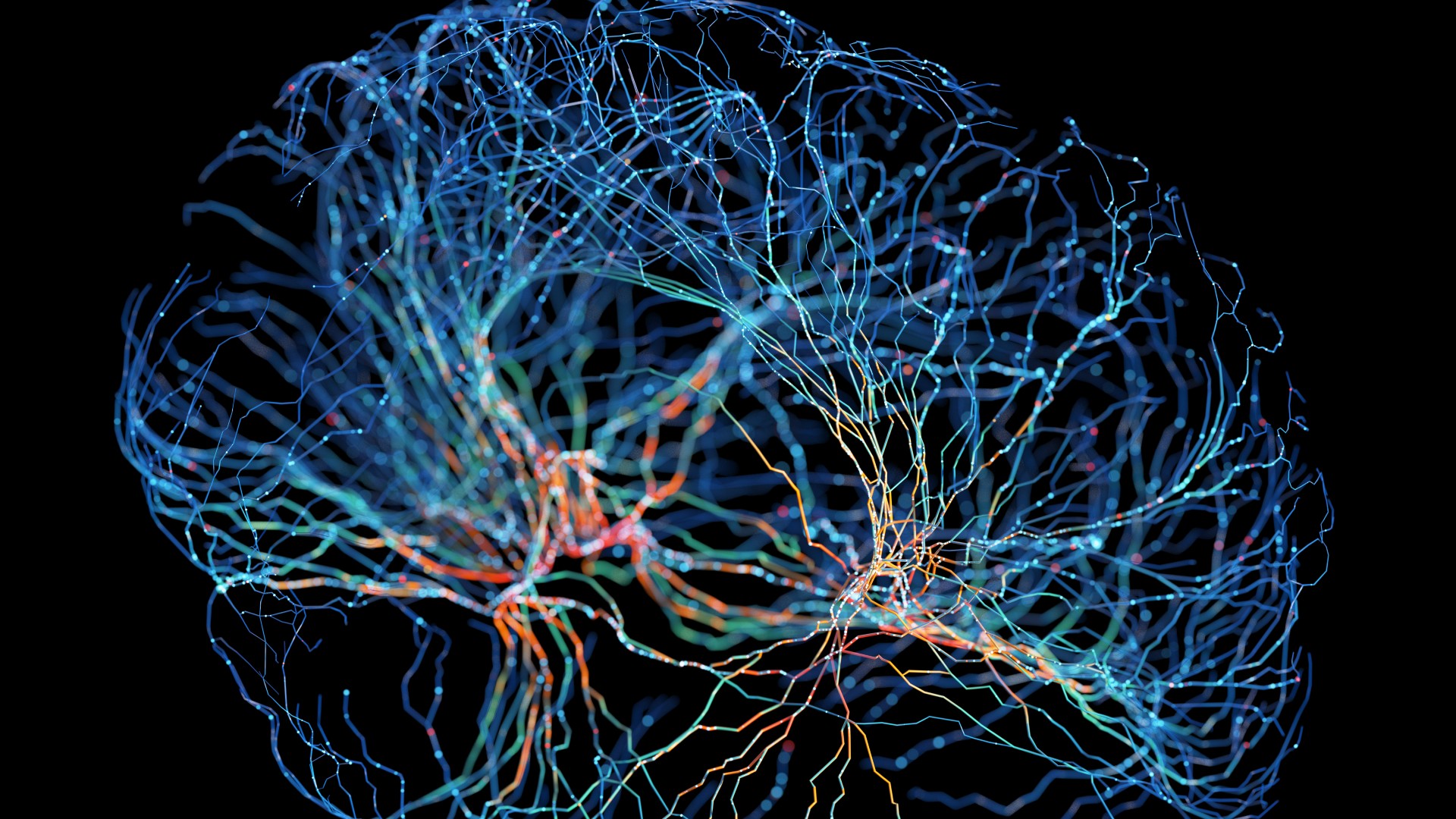
The new study revealed that rare, extremely strong connections in the brains of several animal species form in the same way, which may improve our understanding of the human brain.
This web is flexible ; it isalways changing and rearrange . Some of the connections between neurons are clean debile and thus well better and interchange , while a small chemical group are super impregnable . These strong radio link are have sex as " heavily - dog " connections because , on a graph of connexion denseness in the brain from depressed to mellow , they ’re the outlier plotted at the dense closing of the scale — like the shadow of an brute .
These heavy - tailed connexion run a bigger function in controllingmajor cognitive processes , such as encyclopedism and memory , compared with the debile connections that far outnumber them in the brain . However , it was obscure whether these strong links spring via simple , known principles of web organization or via mechanism that were species - specific , according to the authors of the novel study , published Wednesday ( Jan. 17 ) in the journalNature Physics .
Related:3D mathematical function plot human mental capacity - cell ' antennae ' in dainty contingent

" It has been have intercourse for some fourth dimension that the phone number of neurons that a neuron is connected to vary wide with some nerve cell in the internet being highly - plug into hubs,“Marcus Kaiser , a professor of neuroinformatics at Nottingham University in the U.K. , who was not involved in the enquiry , enjoin Live Science in an electronic mail .
" However , across species , the distribution of weights [ strengths ] of a connector also varies widely , " he said . The team desire to see if this variation might stem from dispute in how each metal money ' brain comes to be wired .
The authors psychoanalyse maps of the wiring between neuron , called connectomes , based on the brains of computer mouse , fruit flies and two worm coinage . They make these maps by study tissue sample with specialised imaging techniques .

To deduce how heavy - tail connections may form , they used the data from the connectomes to develop a mathematical model base on a principle of neuronal self - organization known as Hebbian plasticity . This principle can be tote up up with the phrasal idiom " neuron that fire together , electrify together . " In other word , when one nerve cell repeatedly activates another via chemical subject matter , the connection between the two cadre gets stronger . This basic rule underlies how welearn and form memories .
However , some previous research has suggested that Hebbian dynamics alonemay not completely explainanimals ' power to rewire their synapses and strengthen connexion between neurons .
The writer ' model confirmed that Hebbian plasticity explained the shaping of heavy - shadow connections in all of the animal they studied , without the need for additional mechanisms specific to each species . In addition to explaining heavily - tailed connecter , this principle probable guides neuron ' tendency to cluster together and form tightly knit radical depend on their bodily function levels , the researcher said .

To make their model better resemble a real genius , the authors ensured it describe for some randomness in its web formation , they said in astatement . They sham that nerve cell would typically rearrange and connect due to their activity , as in Hebbian moral force , or every which way , with synapses sometimes disconnect or work without clear reason , Christopher Lynn , first author of the new field of study who conducted the research while at the City University of New York ( CUNY ) Graduate Center , said in anotherstatement .
" Overall , this is a promising first footstep to explicate the variant in synaptic weight [ the strength of connections between nerve cell ] across biologic neural networks , " Kaiser enounce .
— Most detailed human brain function ever contain 3,300 cubicle case

— In a 1st , AI neuronic net captures ' vital aspect of human intelligence operation '
— Newfound ' mind signature tune ' linked to multiple psychiatrical disorder
However , a restriction of the article may be that the authors only compared a few features in their mannequin to real neuronal networks , he said . For illustration , they tested flock with their model but not other features you ’d expect to see in brainpower networks with heavy - tail connections , he say . These include modules — densely connected region of neurons — and short overall path length , meaning the space between the cellphone .

The authors did n’t consider human brains in the piece of work , but they call back that studying this on the face of it universal principle of connection development could help scientist better understand the structure and map of the brain in many animal , including human .
" These findings could help us better understand how the change of connection arises in the human brain and how the brain heals and recovers after injuries,“Dietmar Plenz , principle police detective at the National Institute of Mental Health , who was not involve in the inquiry , told Live Science in an email .
Ever inquire whysome people build muscle more easy than othersorwhy freckles come out in the sun ? broadcast us your questions about how the human body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject short letter " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answered on the website !










