When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
A golem deployed to the bottom of Siberia’sLake Baikallast summer capture footage of cracks and deformation cause by previously strange clay volcanoes — and you could ascertain the discovery in a video below .
The robot name scars leave behind behind by irruption of clay at depth of 340 to 540 feet ( 100 to 165 meters ) in two location — Malaya Kosa Bay and Goryachinskaya Bay — along the northwestern shoring of the lake . Although scientists already knewLake Baikal nurse mud volcano , the former find seat uncomfortably close to a error zona known as the Severobaikalsk , or North Baikal fault , which straddles the lakeside . Signs of recent eruptions at the bottom of the lake could point the fault is alive .
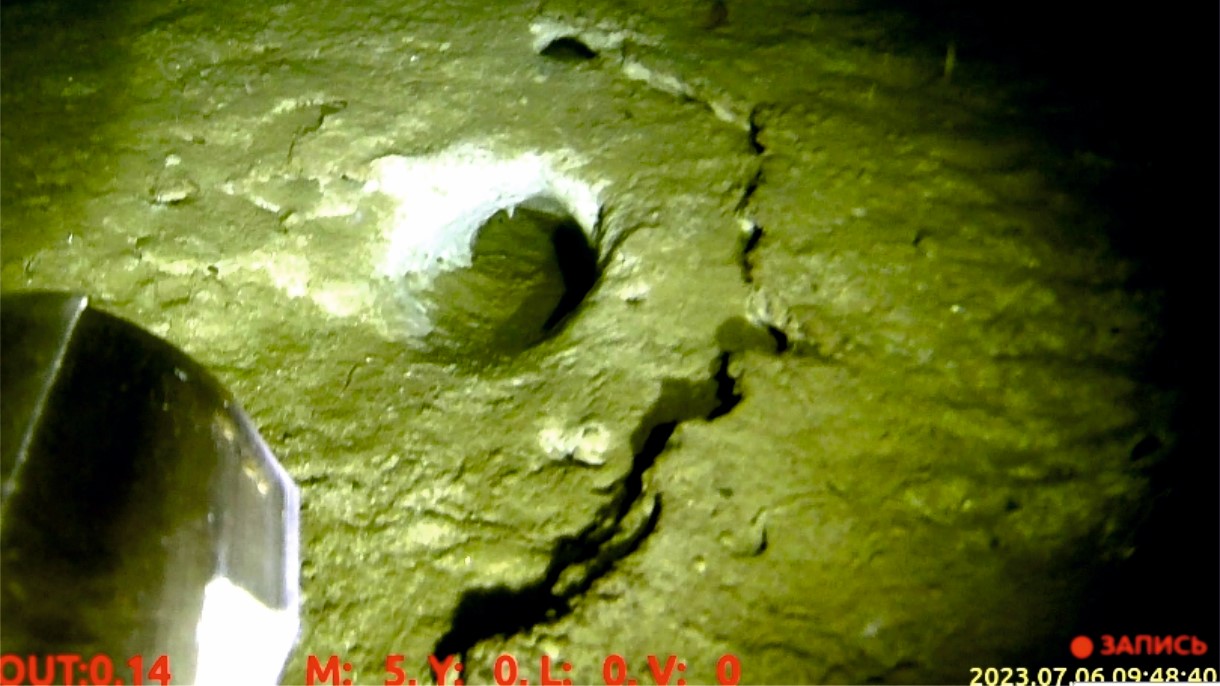

Fragments of an underwater mud volcano photographed 372 feet (113 meters) deep in Goryachinskaya Bay, in Lake Baikal.
Mud volcano are surface expression of deeper geological processes and form as a resolution of slurry and gas erupting from below . Crater along Lake Baikal ’s northwestern shore " mark cracks that run parallel to the Severobaikalsk geological fault " and indicate the fault " is awake , " according toOksana Lunina , a structural geologist and chief researcher at the Institute of the Earth ’s Crust in the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences ( SBRAS ) who participated in the find .
" In the North Baikal economic crisis , which is limited by this fault , there have been strong temblor in the past , " Lunina said in a translatedstatement .
The two sites where research worker deployed the robot , or autonomous underwater vehicle ( AUV ) , point intensely fractured beds blanketed with the Great Compromiser , soft sediments and erupted deposit . In the northernmost Goryachinskaya Bay location , where the footage was taken , craters around 430 feet ( 130 m ) deep were overflowing with a " mud mint , " indicating an irruption had occurred latterly , harmonise to a subject area issue in October 2023 in the journalDoklady Earth Sciences .
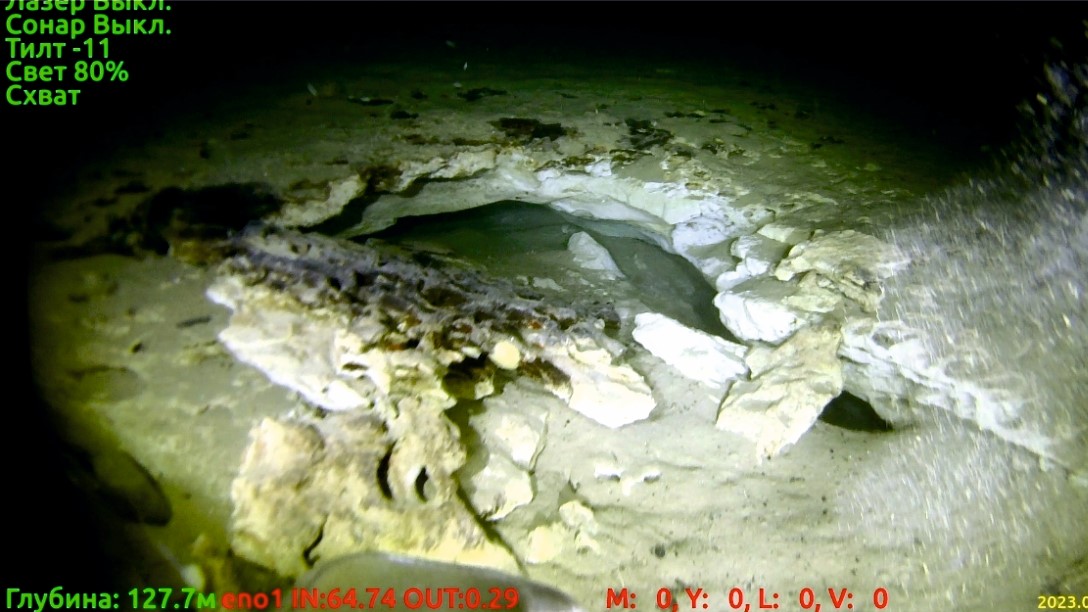

Fragments of a mud volcano photographed at depths of 420 feet (130 meters) in Lake Baikal’s Goryachinskaya Bay.
Related:‘Worrisome and even frightening ' : Ancient ecosystem of Lake Baikal at risk of authorities modification from warming
The footage exhibit layers of rock ‘n’ roll that were torn and forced up by eruption of mud and gas - saturated fluid . Boulders appear to have been " tweet out " from below , and the dusting of Henry Clay and silt on top take care disturbed and porous , the research worker notice in the bailiwick .
Deeper in Goryachinskaya Bay , around 525 human foot ( 160 m ) below the surface , researchers spotted hundreds of small , cone - shaped Crater . " They are everywhere attach to by unannealed deformation of the bottom , " they write in the study . The vent , which were 2 in ( 5 centimeters ) tall and across , were teem with amphipod and gastropods , while nearby hard surface host colonies of white-hot poriferan .

As the AUV jaunt to more or less shallow depths , " it became patent that the intact outrageous gradient was dumbly covered with mud volcano , " the researchers added . Mud volcanoes normally would n’t form at such shallow depths , because they require in high spirits temperatures and pressure sensation , Lunina say in the command .
— Watch droning dig into Siberia ’s growing ' gateway to the netherworld , ' the largest permafrost natural depression in the world
— whodunit of Siberia ’s giant exploding craters may finally be clear

— Nematode resurrect from Siberian permafrost lay abeyant for 46,000 years
Mud vent in Lake Baikal are typically fertilise by gun hydrates , which arecrystals of water and gasthat form beneath eubstance of water . flatulency hydrate can become unstable in region where tectonic processes are at free rein , due to the additional heat that is created in Earth ’s crust , Lunina tell Live Science in an electronic mail .
" But our finding could have another chemical mechanism , " Lunina said . humble movement and earthquakes in the Severobaikalsk fault could cause slurries to uprise up and come out through the bottom of Lake Baikal , she said .

These fountains of clay and dissolve gas are improbable to shake up the lake depths . " It must be a part of the Baikal ecosystem , " Lunina said .
Video cameras climb on the submerged fomite were operated by subject area co - authorKonstantin Kucher , a research worker at the Limnological Institute in the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences , Irkutsk .