When you buy through connection on our site , we may garner an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it works .
Headphones may lastly move past one C ' old engineering science thanks to a Modern type of micro - speaker system that uses ultrasonic waves . The new audio potato chip could pave the way for noise - cancel earbuds that can also revivify the magic of audio coming from multiple direction .
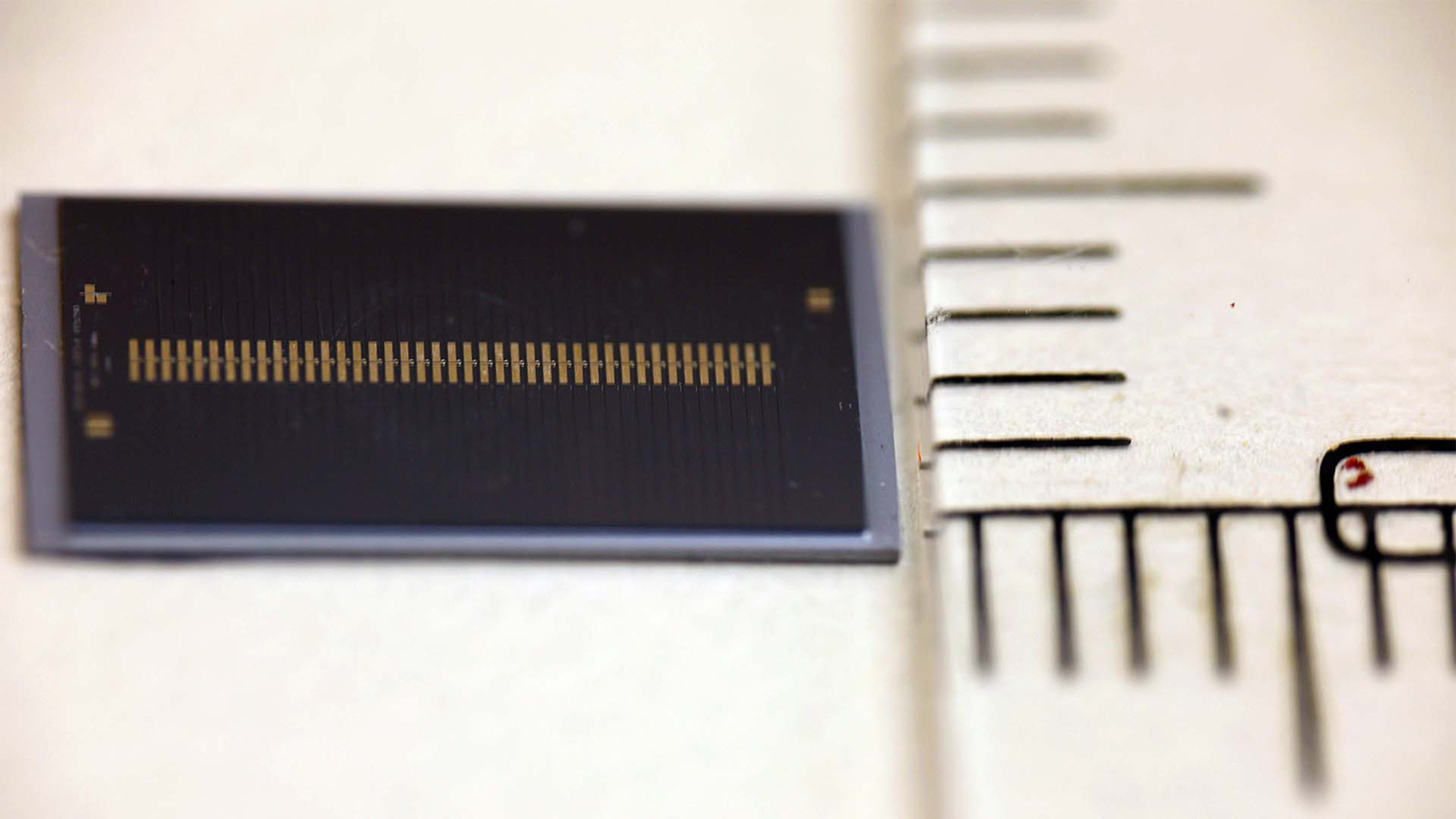
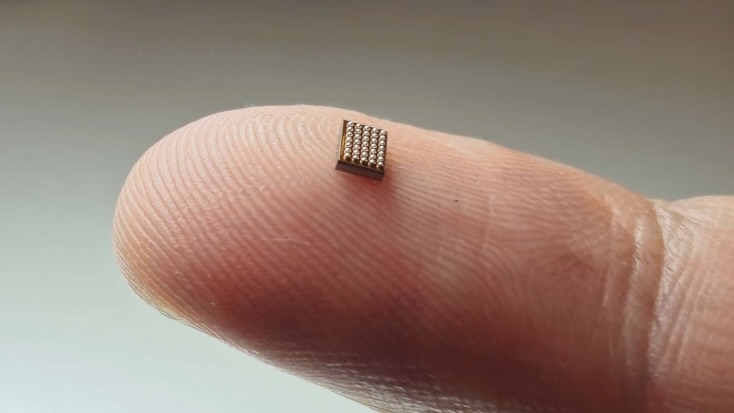
The inauguration xMEMS first showcased its audio micro chip Cypress — which measures roughly 0.25 inch by 0.25 inch ( 6.3 by 6.5 millimeter ) — at CES 2024 on Jan. 9 . It will make its way into earbuds and headphones by the remnant of next class , company spokesperson evidence Live Science .
The startup xMEMS first showcased its audio chip Cypress at CES 2024 on Jan 9.
In ceremonious verbalizer , a metallic coil is enfold around a attractor , and an electric current passes through the coil . The electromagnetics generated by the passing current interacts with the magnetism of the lasting magnet , which pushes the coil back and forth like a piston . This coil is also attached to a loudspeaker system cone , or diaphragm , which pushes melodic phrase to generate sound . The technology was first proposed in the 1800s , but it ’s still used in headphones today .
However , loudspeaker designed this way are prostrate to damage , wear - and - tear and issues such as phase distortion — in which the physique of the sound waveform variety during the signal - conversion process , creating a lag and have cop audio .
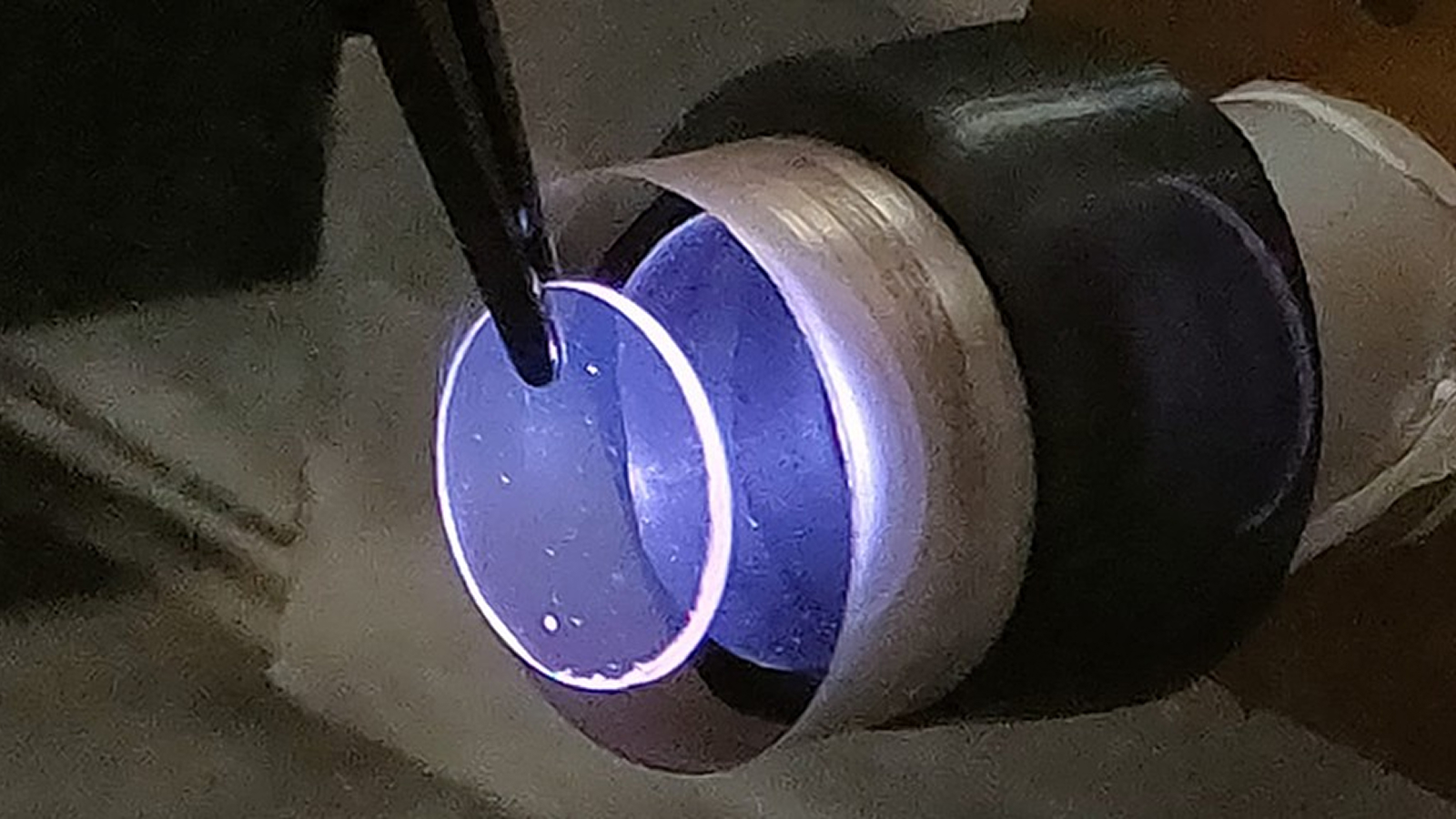
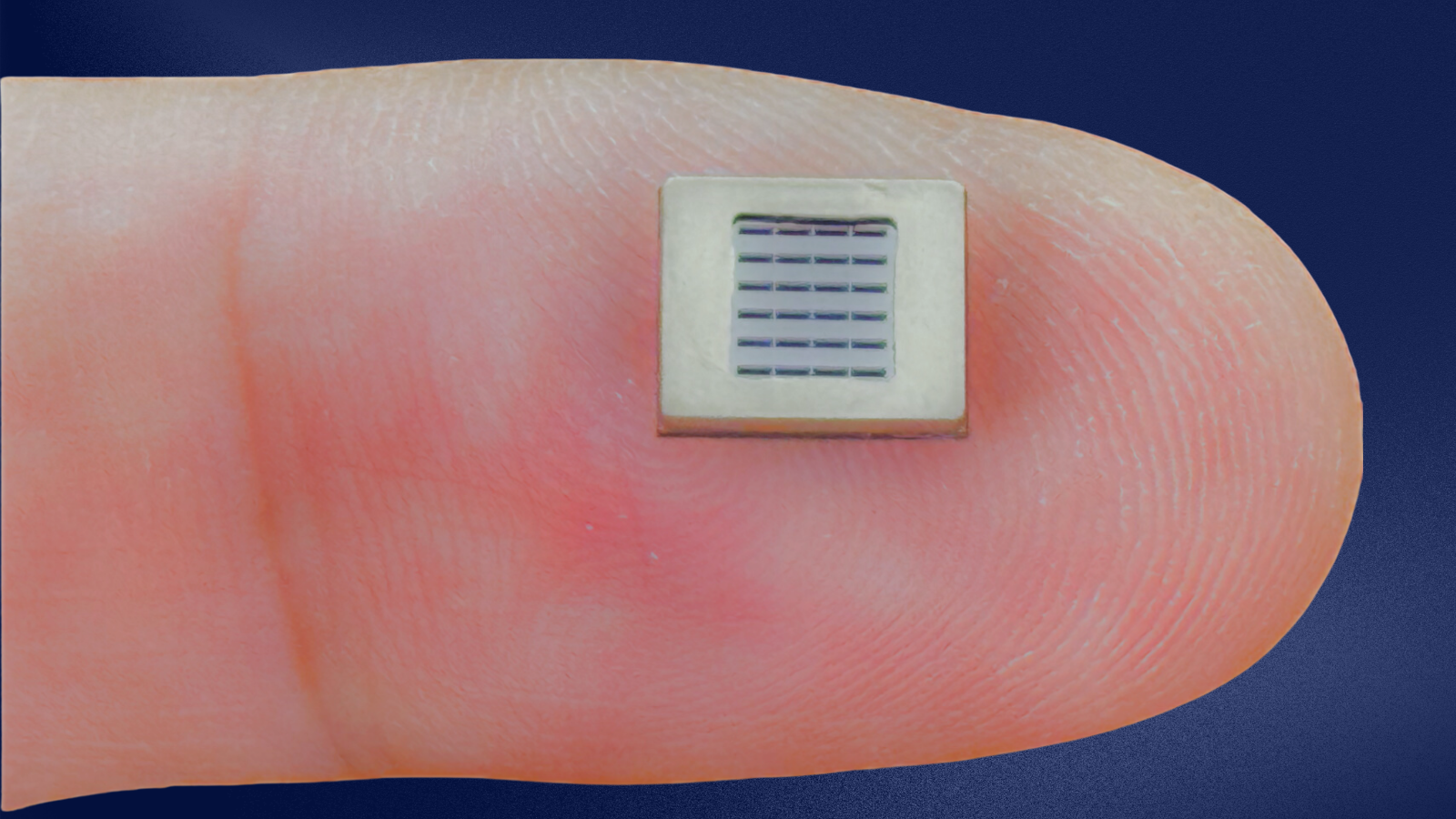
The Cypress micro - verbalizer , on the other handwriting , is a silicon chip with two portion : an app - specific integrated circuit ( ASIC ) , which process the electrical signals from a profound single file ; and an ultrasonic transducer . This latter component translate the sign into sound waves using the piezoelectric event — in which a material changes loudness ( or moves ) when a stream is applied to it .
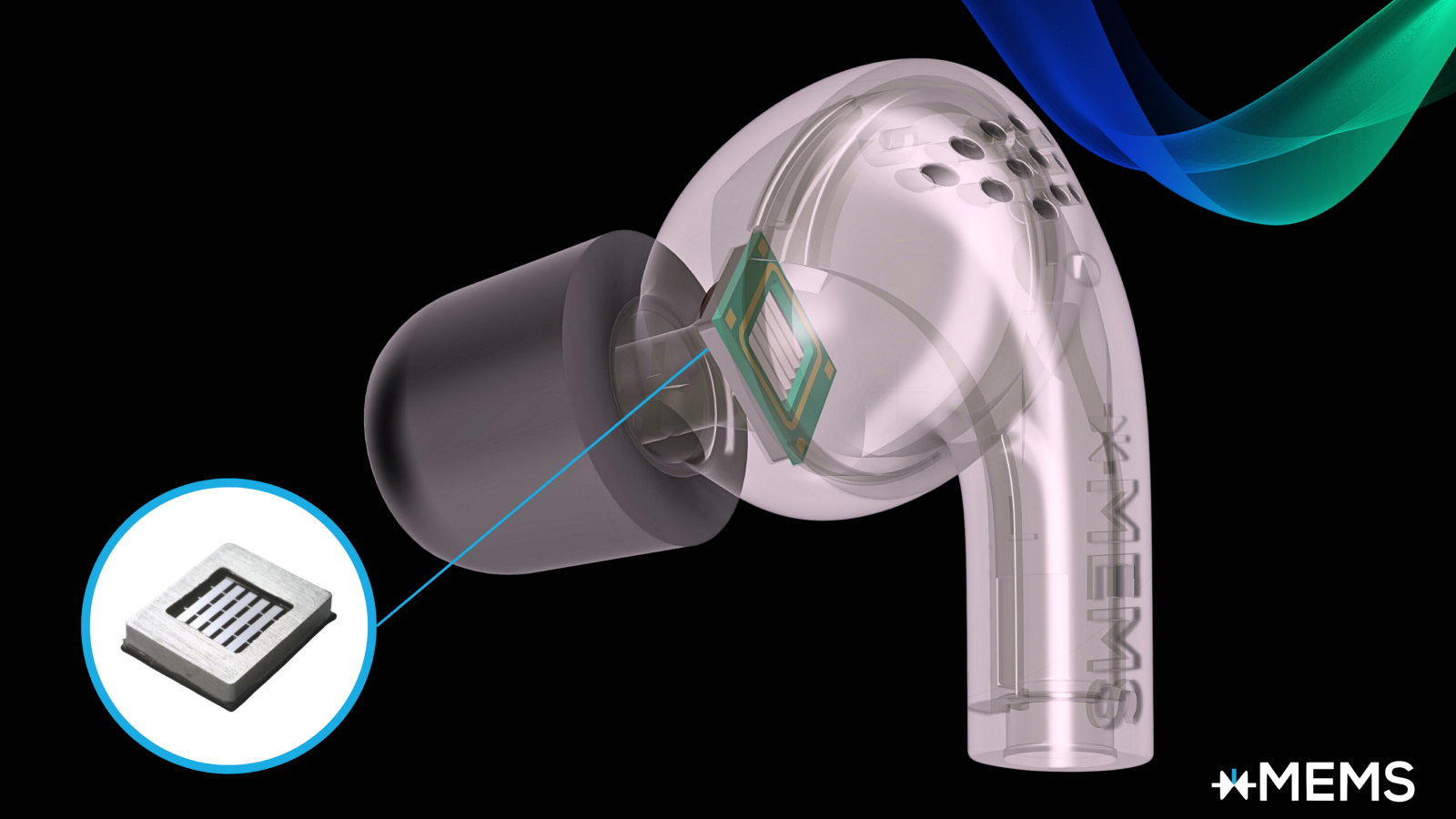
According to comapany representatives, the new audio chip will make its way into earbuds and headphones by the end of next year.
Related : These randomness - cancel earpiece can filtrate specific sounds on command , thanks to deep learning
The transducer is made of micro - electromechanical systems ( MEMS ) — microscopic machines that contain electronic and moving parts . They are wide used in consumer electronics such as buzzers and sound receivers .
Like sometime technologies , the Cypress transducer moves air to generate wakeless wafture . Unlike most MEMS , though , which are made up of piezoelectric quartz glass or ceramics , Cypress use a raw class of thin piezoelectric films made from lead zirconate titanate ( PZT ) .

The PZT is incorporate as a layer in the semiconductor fabrication process together with a silicon talker diaphragm layer . When enforce in this way , the films can acquire in high spirits - resolution , high - quality sound , party representatives tell Live Science .
The ASIC chip first receive and interprets the electrical signals and carry them to the piezoMEMS transducer . The thin film vibrates at a high ultrasonic frequence , generating air pulses that map out to the original audio signal . This generates air pressure inside the Cypress chip . Finally , demodulation piezoMEMS valves change this acoustic vim into audio at frequencies we can listen .
— supersonic waves are everywhere . Can you hear them ?

— Best running headphones 2024 : Unleash the power of music
— Beats Fit Pro review
Unlike schematic Speaker , the speaker yield indicate near - zero form shift , xMEMS representative said in astatement , and is , therefore , more suitable to features such as spatial audio , which simulates the experience of being surrounded by speaker in different locating .
The Cypress chips could also be used to make better racket - cancelling technology , which get a tailored sound wave to cancel ambient interference . In theory , Cypress ' quicker mechanically skillful response and near - zero phase coherency should enable gamy - frequency randomness to be canceled , which headphones today struggle to mask . This front in the Cypress chip also generate far more get-up-and-go and pressure sensation at low frequencies — 40 times more than the troupe ’s old non - supersonic micro - utterer microprocessor chip — which outfit it with anti - racket needed to scratch these sounds .