When you buy through links on our situation , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it puzzle out .
Tiny photosynthetic microbes could be secretly thriving on Mars — hiding inside small bubble of liquid piddle in the thin layers of dust-covered ice that litter the Red Planet ’s surface , a newNASA - led study reveals .
Researchers conceive the frigid patches could be among the most bright quarry in the hunt forextraterrestrial lifewithin oursolar arrangement — and plan to recreate them in the laboratory on Earth to test the predictions .
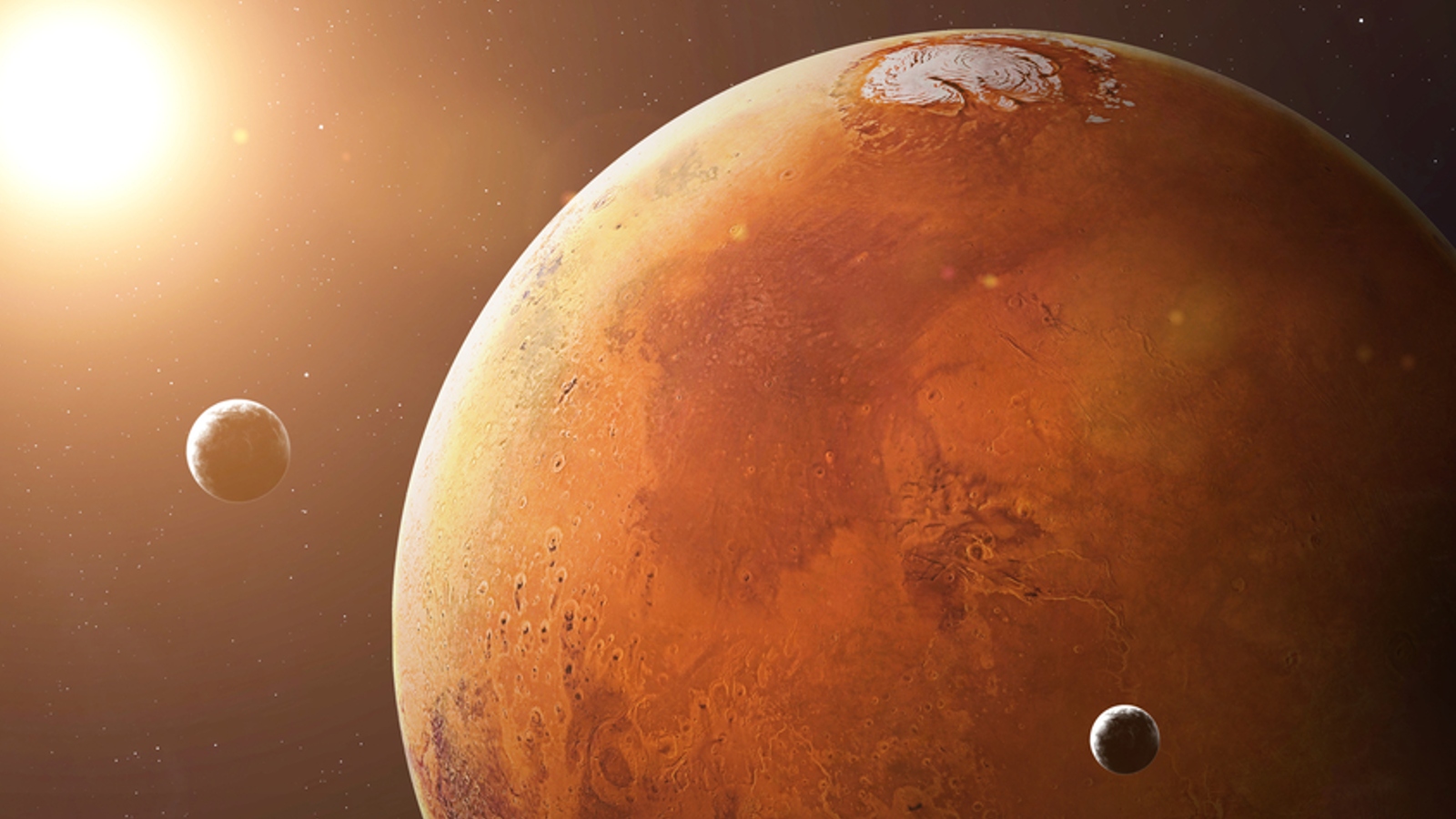

A new study reveals that photosynthetic microbes may be secretly thriving in icy structures across Mars' surface.
Mars is a surprisingly frosty mankind : The planet hasfrozen sand dunes covering its north magnetic pole , elephantine slab ofcarbon dioxide ice above its south poleand monumental chunks of frozen waterburied near its equator . However , it also has low sub - zero features , include temporary hookup of stale pee ice left behind by ancient snow drifts that cling to specific spots on the planet ’s surface , such as the bottoms of gully and ravine .
In a new report , published Oct. 17 in the journalCommunications Earth and Environment , researchers created computer models to simulate the term within this moth-eaten airfoil ice and plant that it could contain flyspeck bubble of meltwater , which can act as miniature " habitable zona " for microbic sprightliness left over fromMars ' watery past .
The researcher proposed that the conceal dental caries could provide unmarried - celled being with three key requirements forphotosynthesis : liquid H2O , carbon dioxide gaseous state from Mars ' wispy atmosphere and sunlight , which shine through the fragile ice above . The sparkler could also theoretically shelter bug from potentially baneful solar radiation andcosmic rays , which bombardon Mars ' surface because of the planet ’s deficiency of magnetised shielding .
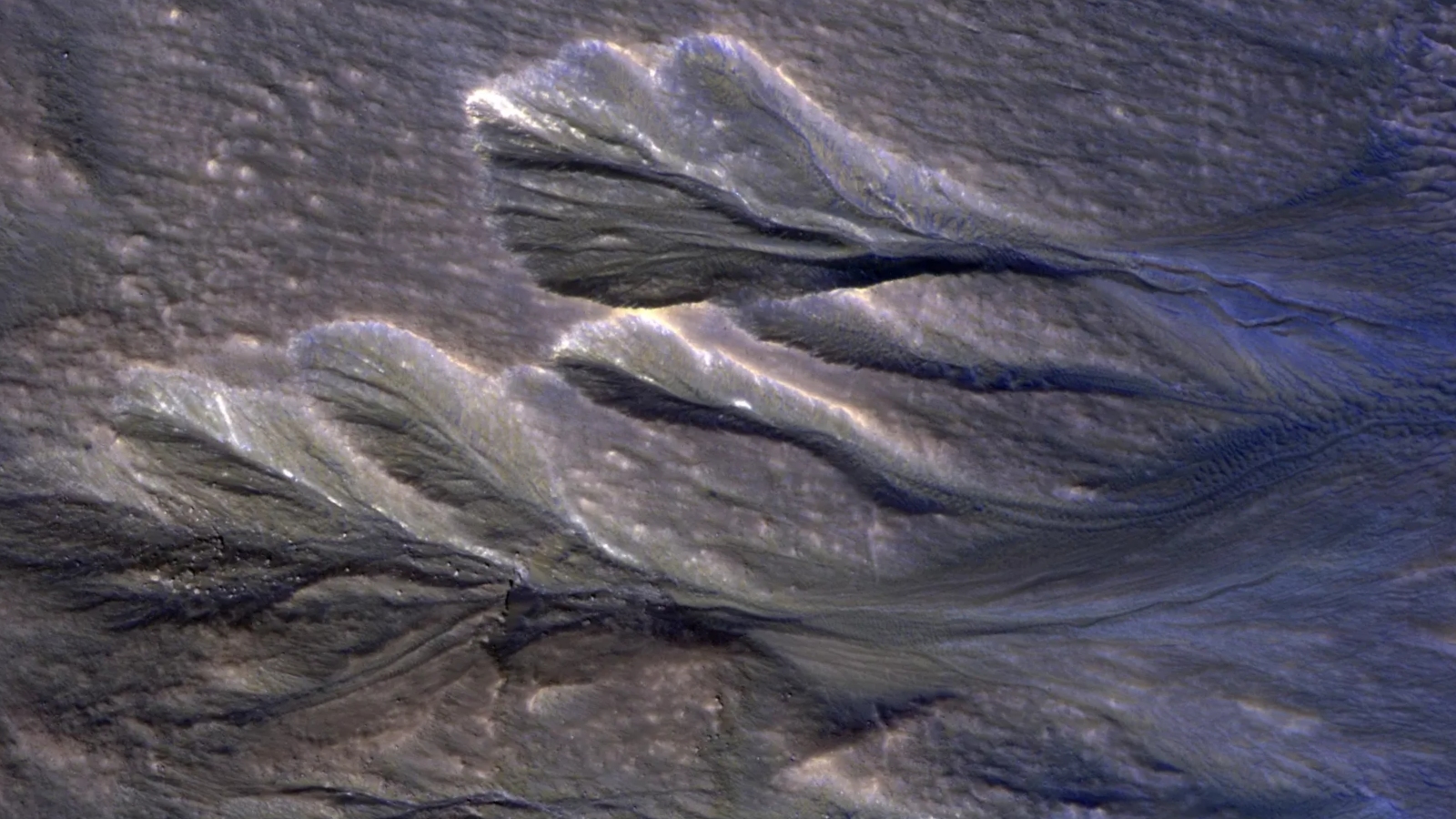

Martian gullies have often been found to contain dusty ice. These false-color images of gullies in Mars’ Terra Sirenum show streaks of ice (white) spread along some of the deepest trenches.
Related : NASA may have unwittingly incur and killed alien living on Mars 50 years ago , scientist call
It would be well-heeled for next astronauts and colonist to reach the dusty ice and find oneself these bubble , which nominate them an even more appealing seat to look for extraterrestrial life , the researchers wrote . " If we ’re trying to rule life anywhere in the world today , Martian trash exposures are probably one of the most accessible places we should be face , " study hint authorAditya Khuller , a planetary scientist atNASA ’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory , say in astatement .
According to the research worker , cereal of dark - colored dust buried beneath thin layers of Earth’s surface frosting can be heated by sun glow through the chalk , creating pockets of space that occupy up with melting water . This is perhaps one of the only place where liquid water could promptly form on Mars because ice normally rarefy — or turns straight into gasolene — when it gets heat , the researchers wrote .
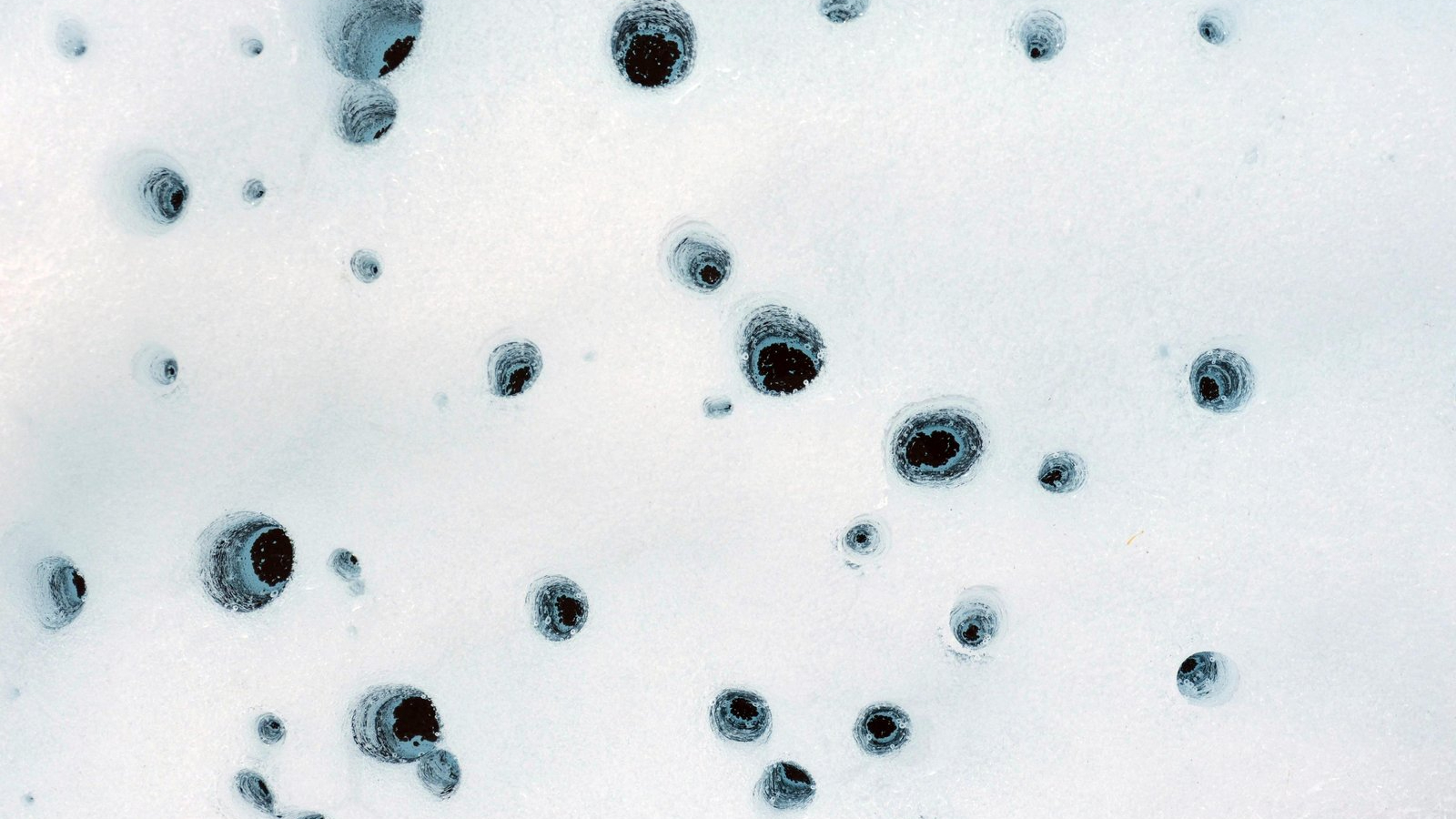
On Earth, cryoconite holes can also form in the surface of ice masses. These holes formed in Alaska’s Matanuska Glacier in July 2012.
A similar operation happens on our planet : When dust gets trapped within snow , glaciers and ice sail , it create space make love as cryoconite holes , which often hold liquid body of water — and sometimes living .
" This is a common phenomenon on Earth , " field co - authorPhil Christensen , a planetary scientist at Arizona State University , enjoin in the affirmation . " dim C. P. Snow and ice can melt from the interior out , letting in sunlight that warm up it like a nursery , rather than melting from the top down . "
A wide kind of photosynthetic organisms go in cryoconite hole , such as algae , fungi and cyanobacteria . During winter , when temperature drop and the holes refreeze , these lifeforms come in into a hibernation - alike stasis where they efficaciously pause all key function until the holes reform in summertime , the researchers spell . Any potential Martian microbes may do something similar , they lend .

Based on the new computer manakin , researchers think that the meltwater bubbles could form in trash up to 9 base ( 3 meters ) cryptic , as long as the dust content is low ( less than 1 % ) . However , this is only probable to chance at latitudes between 30 degree and 60 degrees . Any closer to the major planet ’s magnetic pole , and the chicken feed will likely be too cold for bubble to make .
— ' Spiders on Mars ' fully awakened on Earth for 1st prison term — and scientists are pipe up with joyousness
— ' Martian dog ' and oodles of other mysterious blobs found hiding under Mars ' north pole in new ' somberness map '

— scientist spot ancient ' smiley look ' on Mars — and it could bear signs of life
The team plans to proceed hit the books this nominate phenomenon , using extra information processing system manakin and Earth - based experiments to determine more about how and where it might happen .
" I am working with a team of scientists to develop ameliorate simulations of if , where , and when dust-covered ice could be melting on Mars today , " Khuller told Live Science ’s sister siteSpace.com . " Additionally , we are renovate some of these stale ice scenario in a laboratory setting to see them in more particular . "

NASA Mars orbiter uncovers scoring ' wish paint drip down a wall ' on Martian surface
NASA rover learn out - of - place ' Skull ' on Mars , and scientists are nonplus
What ’s hiding under Antarctica ’s ice ?







