When you purchase through connectedness on our site , we may pull in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it puzzle out .
Scientists have design a robot that they claim could one daytime jump 400 feet ( 120 meters ) — in high spirits enough to reset the Statue of Liberty in a single hold fast . It could even leap as eminent as 650 feet ( 200 molarity ) on the moon .
The high - jump golem is design for exploring unmanageable terrain that conventional robots would sputter to cross , such as cave system , forests and potentially other planet . It features unique optical prism - mold leg with stretchable leaping designed to maximize the transfer of elastic energy into kinetic energy during a startle .
The design for the robot was determined through ‘a combination of mathematics, computer simulations, and laboratory experiments,’ the scientists said.
The researchers tell their design could enable robots to stick out to top many sentence their own sizing , and more than six times higherthan the current criminal record . They published their finding May 24 in the journalMechanism and Machine Theory .
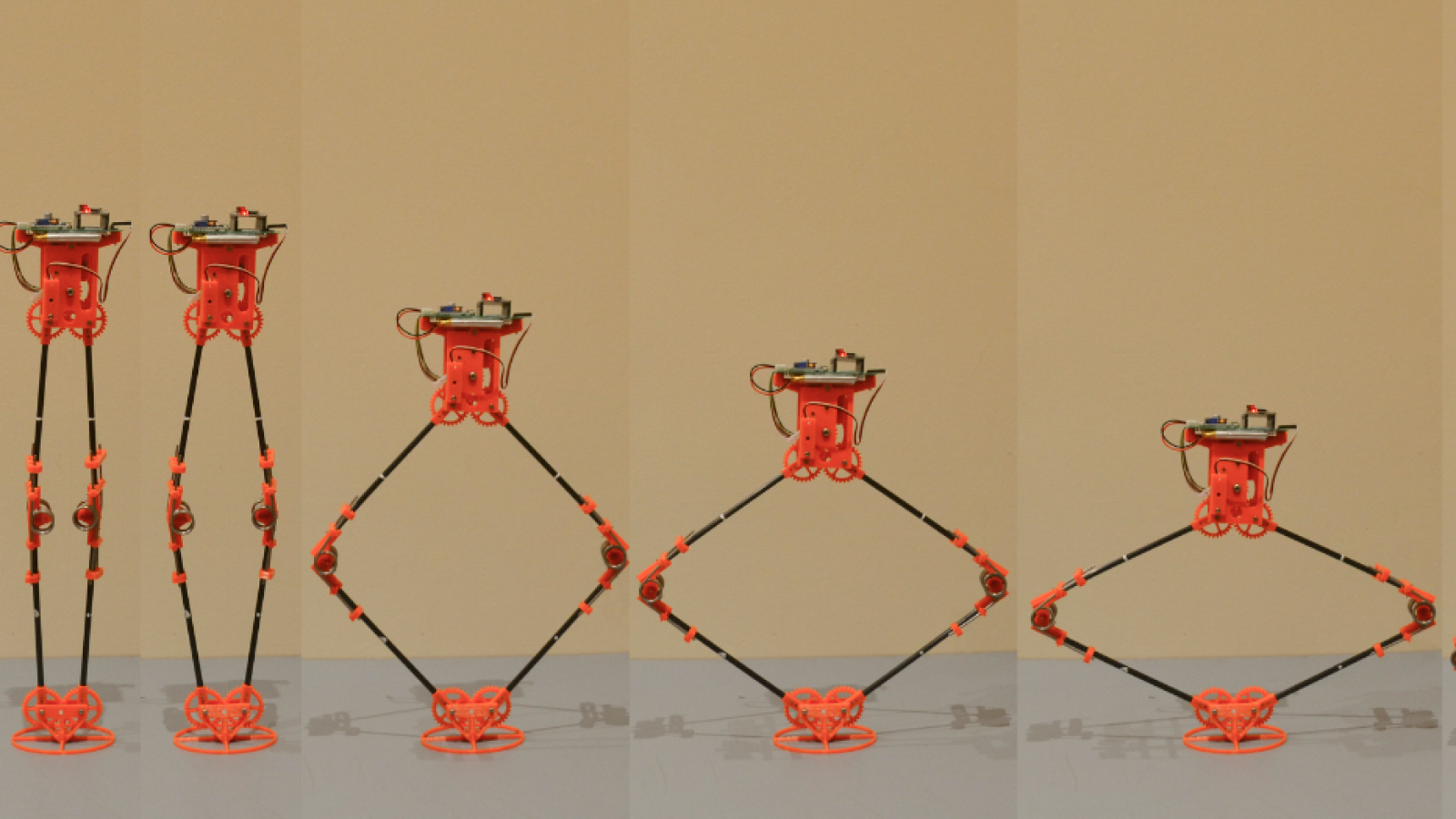
To show their design theory , the scientist build a 15.7 inch ( 40 cm ) tall robot that could jump more than 5 foot ( 1.6 m ) in the air .
" While startle golem already subsist , there are several big challenges in the design of these jumping machines , the main one being to jumpstart high enough to overcome large and complicated obstacle , " study co - authorJohn Lo , a inquiry associate in infinite robotics at the University of Manchester , said ina statement . Our design would dramatically improve the energy efficiency and execution of spring - drive jumping robots . "

link : view a ' automaton dog ' scramble through a canonical parkour course with the help of AI
Conventional robots are typically equipped with wheels or , in the character of machines likeBoston Dynamics ' AtlasandSpot , two or four legs . While these figure run well on simple terrain , they are n’t practiced at take on obstacles like cliffs , or steep and scratchy surfaces . This is where a jumping design comes in handy .
One giant leap for robotkind
Jumping robots typically expend motor to hive away energy in a give , and then liberate this vim to propel the golem upward . Power amplification — a mechanism see in creature like fleas and locust whereby stored elastic energy is exchange to kinetic energy — enable springs to beget greater output exponent than standalone motor , result in higher jumps .
Previousjumping automaton designshave incorporate power elaboration , but they are prostrate to taking off before their spring energy is fully free , the scientist enjoin , mean their put in elastic push is not fully convert into energizing energy . These robots also be given to waste energy by moving side to side or revolve , rather of derail directly upwards .
" There were so many questions to answer and decisions to make about the frame of the automaton , such as , should it have legs to push off the primer like a kangaroo , or should it be more like an engineered plunger with a giant spring ? " co - authorBen Parslew , a fourth-year lecturer in aerospace engineering at the University of Manchester , said in the statement .

To find out which blueprint type would be good , the scientists study two golem models : one with a straight - stemma " prismatic " system and one with a rotational system .
— Meet LocoMan , the quirky golem dog that can stand up on its hind legs like a mierkat and toy with objects
— DeepMind experimenting with ' Shadow Hand ' that can withstand a severe beating in the name of AI research

— This AI - powered golem has crop out how to work out a Rubik ’s Cube in just 0.305 s
In the prismatic model , the robot ’s leg make a motion in a piston - like movement , standardized to a pogo stick . However , the extra weight at the bottom of the robot make an inertial upshot , meaning the outflow could n’t in full extend before the robot left the earth .
The rotational model , meanwhile , featured legs that moved in a circular motion , similar to a kangaroo ’s . In this model , the spinning apparent movement of the legs caused the robot to leave the primer coat before the springs had fully release their stored energy — again , cut the height and effectivity of the jump .

To speak these issue , the team combined the good of both designs . By shifting most of the robot ’s weightiness to the top and score the bottom lighter and more streamlined , they were able to meliorate its stability and vigour efficiency . also , by using directly - moving prismatic leg with leaping that extended linearly , the scientist were able-bodied to mitigate the payoff of delayed or previous take - offs .
Work is now underway to control the counsel of the jumps and rein in the kinetic energy generate when the robot land , which could be used to increase the figure of jump it can do on a unmarried charge , the scientist said . The team will also research more compendious designs suitable for space mission .









