When you buy through links on our site , we may realise an affiliate perpetration . Here ’s how it turn .
An challenging unexampled survey by theHubble Space Telescopeprovides the first - ever bird’s - oculus view of all known dwarf galaxies orb the Andromeda beetleweed .
The results reveal that over one thousand million of years , Andromeda and its family of gnome galaxy have experience markedly disorderly interaction — like a game of bumper railway car — liken with the relatively placid evolution of the galaxies encircle theMilky Way .

The Andromeda galaxy, seen here by NASA’s Spitzer space telescope, is the closest large galaxy to the Milky Way — but it seems to have evolved in a much different way, new Hubble data suggests.
The findings , published inThe Astrophysical Journal , demonstrate that we may not be able to extrapolate entropy about other wandflower from our understanding of our own Galax urceolata , the study authors say .
" There ’s always been concerns about whether what we are learning in theMilky Wayapplies more broadly to other galaxies , " study conscientious objector - authorDaniel Weisz , an associate professor of astronomy at the University of California , Berkeley , say in astatement . " Our work has evince that low - peck galaxies in other ecosystem have followed dissimilar evolutionary paths than what we know from the Milky Way orbiter galaxies . "
At about 2.5 million light - years away , Andromeda is the closest major galax to our own , and getting closer ; Andromeda and the Milky Way arepredicted to collide and mergein about 5 billion long time time . To the naked eye , it appears as a faint , spindle - shape target that covers about the same amount of sky as the full lunation . What is n’t visible without powerful telescope and is not well studied is the swarm of three XII smaller galaxies disperse around Andromeda , like bees around a beehive .
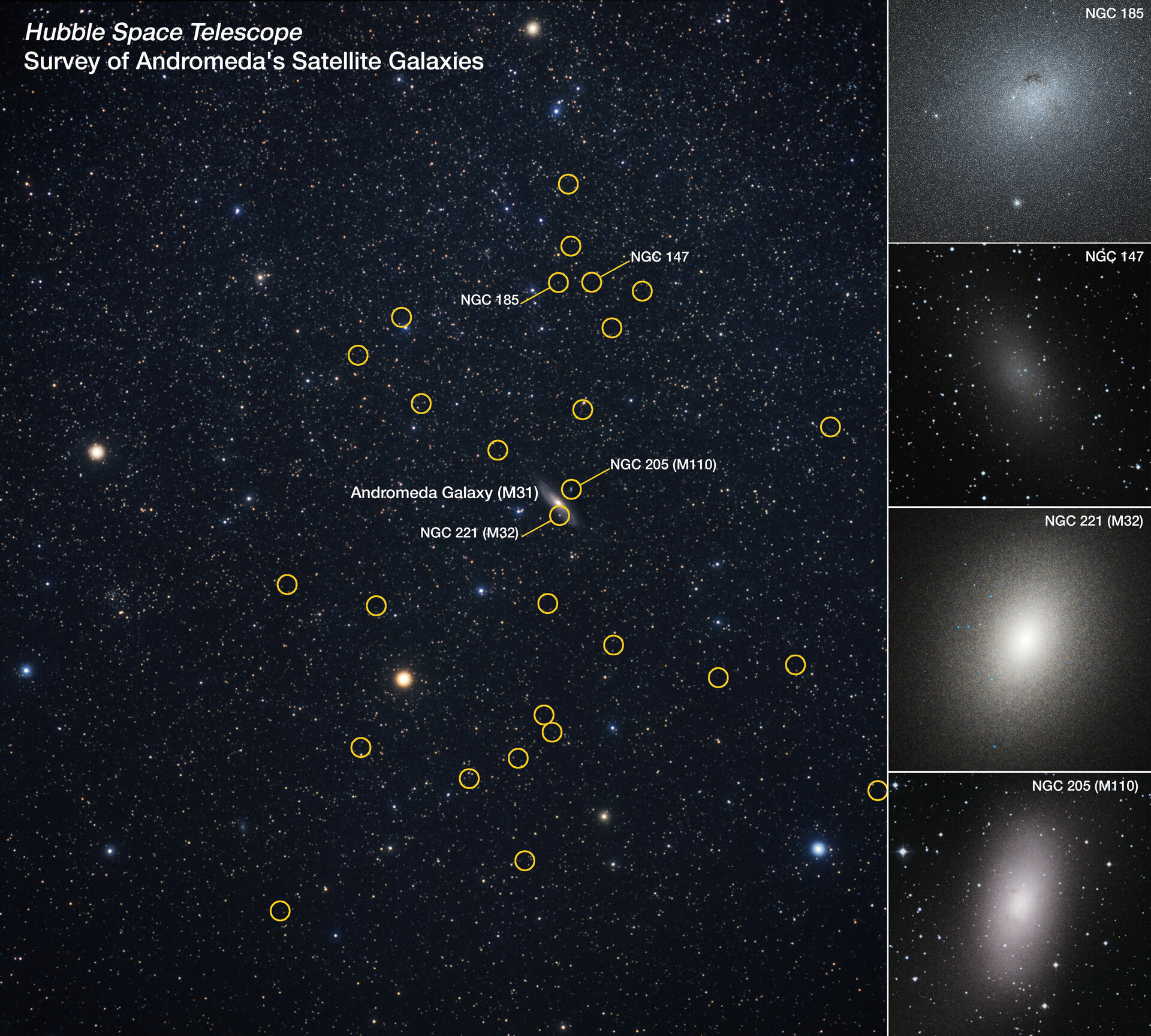
Hubble’s survey of Andromeda focused on 36 dwarf galaxies (circled in yellow) that share Andromeda’s environment. Unexpectedly, all of the galaxies appear to be arranged on a plane, orbiting in the same direction.
Related : The Andromeda Galaxy beam rosy loss in gorgeous unexampled Hubble Telescope ikon
Starting in late 2019 , Hubble spent two geezerhood cataloging ikon — as well as measurements of the locations and motion — of three dozen galaxies swirling up to 1.63 million light - years from Andromeda . These information provided Weisz and his squad the first comprehensive 3D map of our galactic neighbour ’s ecosystem . Using this information , the research worker studied the processes that drive the phylogeny of these dwarf galaxies over nearly 14 billion twelvemonth of cosmic meter .
" Everything scattered in the Andromeda system is very asymmetric and perturbed , " Weisz , principal police detective of this Hubble programme , said in the instruction . " It does seem that something significant go on not too long ago . "

That something , the research worker posit , was a hit between Andromeda and a large galaxy a few billion years ago . The potential perpetrator could be mussy 32 , a satellite galax of Andromeda and its bright fellow . astronomer suspect that M32 , which isvisible to Andromeda ’s bottom go forth , is the remnant core from the uniting .
“No one knows what to make of that”
Analysis of the Hubble observation also unveil a unparalleled universe of galaxies around Andromeda that has not been discover around the Milky Way , grant to the young subject .
This group began mold most of its stars early on and continue to do so at extremely modest rates and for much longer than uranologist would bear . Given the intense gravitational pull of Andromeda , these galaxies should have been stripped of their asterisk - form gun long ago , alike to what is observed around the Milky Way .
" This does n’t come out in calculator simulations , " subject area tether authorAlessandro Savino , an astrophysicist at the University of California , Berkeley , said in the same statement . " No one know what to make of that so far . "

The survey also reveal that half of Andromeda ’s dwarf Galax urceolata electron orbit in a unique , flat plane , all moving in the same counsel — a form not observed around other galax , include our own .
— Unproven Einstein theory of ' gravitational memory ' may be real after all , new field soupcon
— Fast radio burst traced to the outskirts of an ancient ' graveyard ' galaxy — and the cause remains a whodunit

— Euclid scope fleck uncommon ' Einstein ring ' concealment near Earth — and an ancient , unnamed galaxy behind it
" That ’s weird , " Weisz said in the financial statement . " It was actually a entire surprisal to incur the satellite in that conformation and we still do n’t full understand why they appear that path . "
The galaxies assembled into the " Great Plane of Andromeda " do n’t expose distinguishable trait , such as traffic pattern in star formation . This propose the aeroplane is not a physically distinct social organization but rather a serendipitous contour whose origins are not yet fully understood , the investigator say .

" There is a lot of diversity that needs to be explained in the Andromeda satellite system , " Weisz said in the statement . " The way things amount together matter a luck in sympathize this galaxy ’s chronicle . "
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your display name .











