When you purchase through radio link on our site , we may pull in an affiliate military commission . Here ’s how it work .
Astronomers have discovered the first known instance of a sister ace " sneezing . " The cosmic spark , which may have occurred as lately as a few hundred years ago , reveals how babe stars eject most of their magnetic energy very early in their evolution — a shedding mechanism that stops their high-pitched - spinning profile from breaking apart .
researcher observed the cosmic sneeze in range captured by the Atacama Large Millimeter / submillimeter Array ( ALMA ) observatory , a Seth of radio scope located in Chile ’s Atacama Desert .

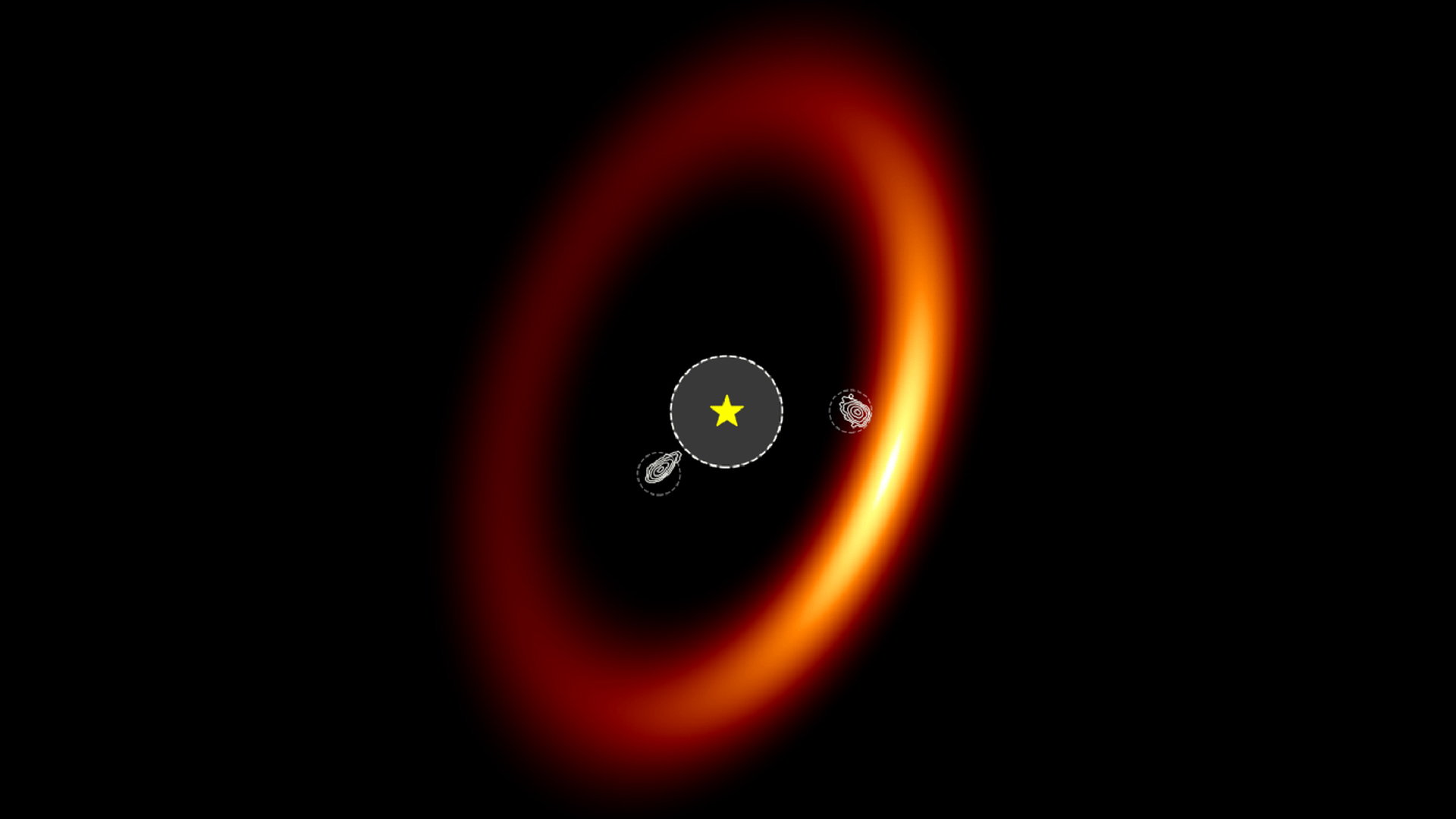
An artist’s conception of a “sneeze” of dust, gas and magnetic energy expelled from a baby star.
The wizard in interrogative sentence is a faint infant star embedded in a dense gasoline cloud list MC 27 roughly 450 light - years from Earth in the configuration Taurus . The cosmic place of origin is a roiling ring of gas and junk known as a protostellar platter , where unstablemagnetic fieldsinteract with flatulence and intermittently blast out as spike and electric arc coated with gas and detritus . This outgrowth , know as interchange imbalance , propels the leaked cloth away from the disk at roughly thespeed of speech sound , the researchers reported in a written report published Thursday ( April 11 ) inThe Astrophysical Journal .
" This discovery was unexpected,“Kazuki Tokuda , an astronomer at Kyushu University in Japan and the lead writer of the subject area , evidence Live Science . While previous telescope notice of the stellar glasshouse had n’t revealed the peculiar structures , ALMA blot streamers not only escaping the disk but also much further by , break the sister star " sneeze " multiple times in the past tense . Such episodic behaviour helps the baby star maintain a compact saucer around it , the research worker say .
" It is not yet sealed whether this summons is universal , " Tokuda say . Gas - packed , star - forming cloud that are riddled with magnetic fields increase the likeliness that a star sneezes , he say . Similar structures bulge out of protostellar magnetic disc elsewhere have been reported but remain unconfirmed , offering early hints that such expulsions of abundant magnetic theatre could be a omnipresent method by which stars evolve .

A view of the Taurus Molecular Cloud.
Related : Uranus and Neptune are n’t made of what we thought , new study steer
Baby’s first sneeze
Stars are hold from the gravitative crash of huge , opaque cloud of junk and gas . The newborns spin up as the collapse extend . Astronomers have long suspect that stars must somehow slow their rotation in their first 100,000 years , otherwise their mellow whirl would break them aside .
Aleading theoryposits they do this by kick out a considerable amount of magnetized free energy . Previous telescope observation back up the " magnetic braking " hypothesis , because a star that adjudge onto all its magnetic energy " would generate magnetic fields many orders of order of magnitude stronger than those observed in any know protostar , " Tokuda said in astatement .
Interchange unstableness was theorized as one such method for magnetic braking in the late nineties and has long been consider as a mechanics that could interrupt disk . " It has often been consider an unsuitable mechanism and rarely discussed for the astronomic observing community , " Tokuda told Live Science . The new observations evoke it ’s prison term to take the hypothesis a spot more seriously .

— bailiwick of ' twinned ' stars finds 1 in 12 have killed and eat on a planet
— Group of 60 extremist - timid stars orb the Milky direction could be new type of beetleweed never determine before
— 13 billion - year - old ' streams of star ' get a line near Milky Way ’s center may be earliest building cylinder block of our beetleweed
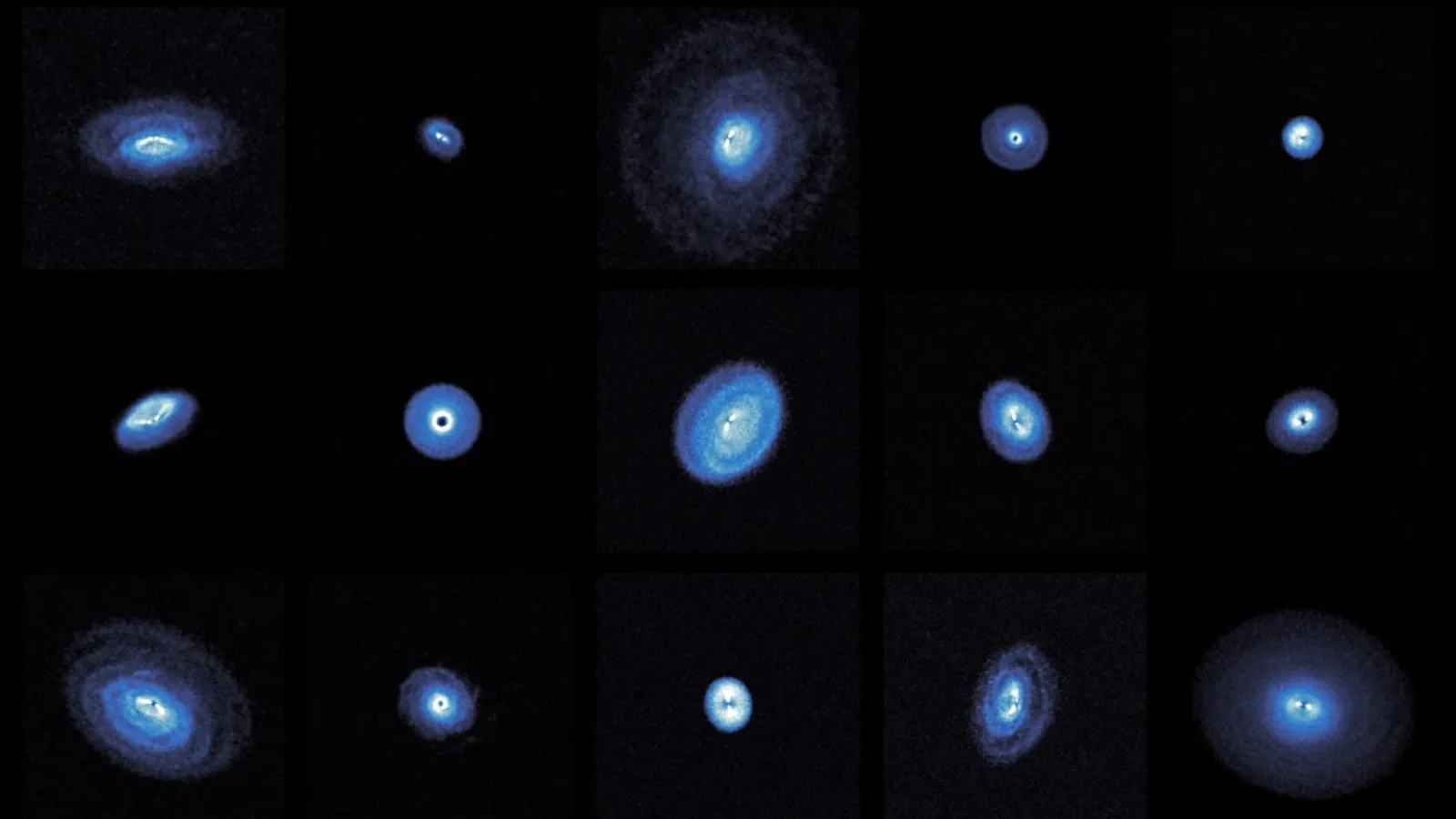
just what happens to the expelled gas , dust and magnetized energy is an open question . Tokuda suspects it remains in interstellar space for eons , although it ’s potential that the material would eventually make its way back to the star , he say .
In the coming months , Tokuda and his team plan to look into the specific conditions and environments that trigger the " sneezes " and whether they affect planet formation . Given planet combine out of the same cloud of gas and detritus as stars , Tokuda said it is possible that protoplanets also moult spare magnetized energy , but " there has been no theoretic and experimental research to date that specifically addresses this theory . "