When you buy through connectedness on our situation , we may earn an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it works .
Astronomers studying the largest - ever map of the cosmos have found hints that our good understanding of the universe is due a major rewrite .
The analysis , which look at most 15 million galaxies and quasars span 11 billion years of cosmic time , determine thatdark vigor — the presumed - to - be constant force driving the accelerating expansion of our universe — could be weaken .

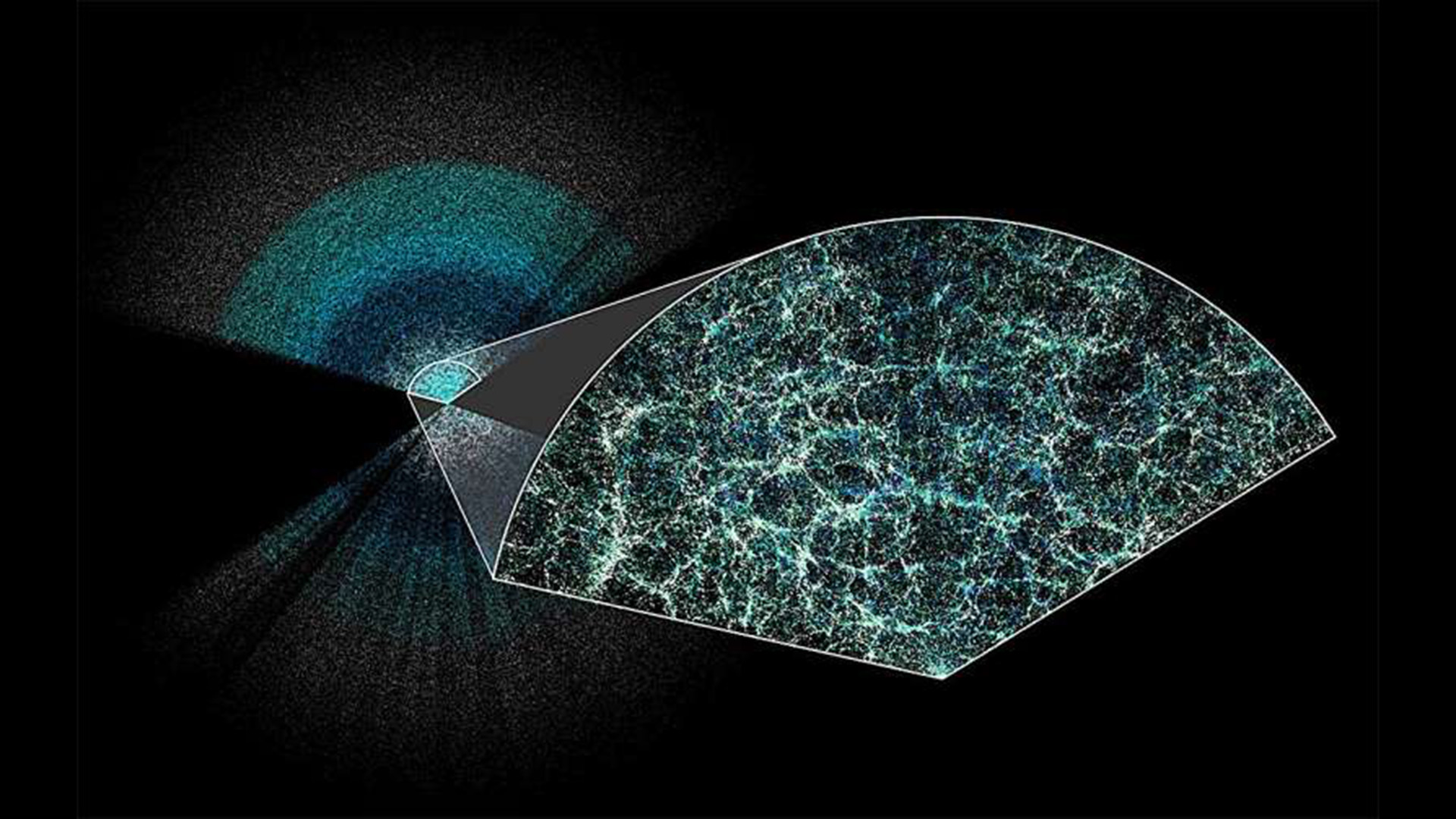
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument maps the night sky from the Nicholas U. Mayall 4-meter Telescope in Arizona.
Or at least this is what the data , collected by theDark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument(DESI ) , suggest when conflate with information carry from star explosions , the cosmic microwave background and frail gravitational lensing .
If the findings carry up , it means that one of the most mysterious forces keep in line the destiny of our universe is even weirder than first view — and that something is very wrong with our current model of the world . The researchers ' findings were published inmultiple paperson the preprint host arXiv and give March 19 at theAmerican Physical Society ’s Global Physics Summitin Anaheim , California , so they have not yet been peer - reviewed .
" It ’s lawful that the DESI results alone are reproducible with the elementary explanation for dark energy , which would be an unchanging cosmologic invariable , " co - authorDavid Schlegel , a DESI project scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in California , told Live Science . " But we ca n’t ignore other data that extend to both the sooner and later universe . Combining [ DESI ’s results ] with those other data point is when it gets truly uncanny , and it appears that this dark energy must be ' dynamic , ' meaning that it changes with time . "
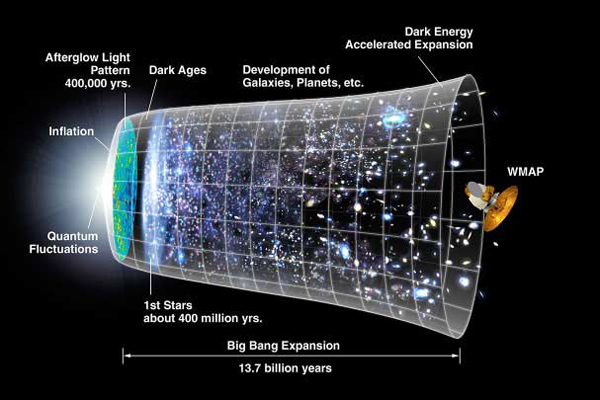
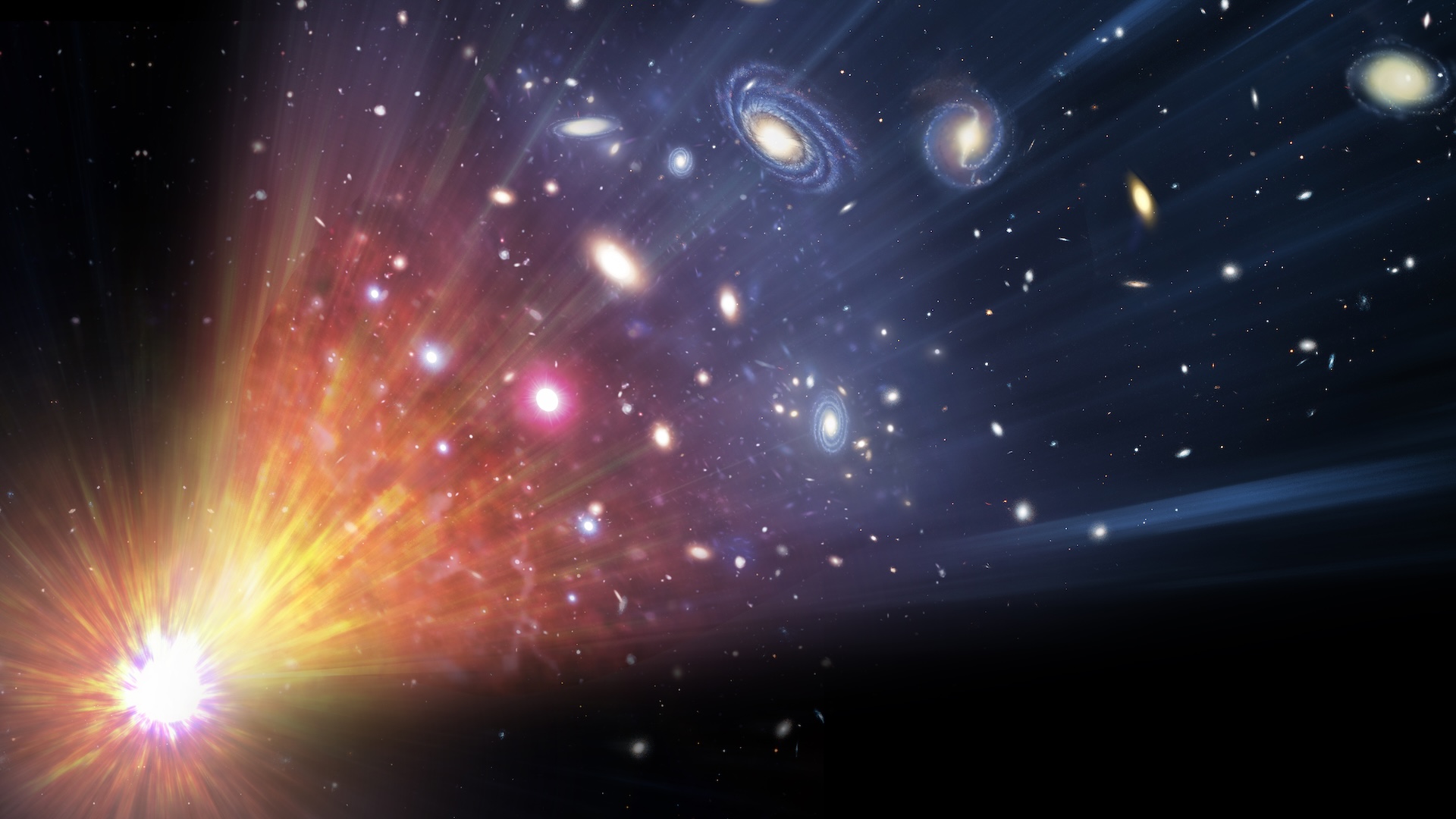
An artist’s illustration of the universe’s evolution to the present day, with its expansion being driven by dark energy.
The evolving cosmos
Dark energyanddark matterare two of the universe ’s most puzzling components . Together they make uproughly 95%of the cosmos , but because they do not interact with lighting , they ca n’t be detected directly .
Yet these components are primal ingredients in the reigning Lambda frigid dark matter ( Lambda - CDM ) model of cosmogony , which map the growth of the cosmos and portend its last . In this mannequin , dark matter is responsible for holding beetleweed together and accounts for their otherwise inexplicably muscular gravitative pulls , while dark energy explains why the universe ’s expansion is accelerating .
touch on : Could the universe ever stop expatiate ? New possibility proposes a cosmic ' off switch '

But despitecountlessobservationsof these hypothetical dark entitiesshapingouruniverse , scientists are still timid where they come from , or what they even are . Currently , the practiced theoretical explanation for glowering energy is made by quantum field theory , which describes the vacuity of space as fill with a ocean ofquantum fieldsthat fluctuate , create an intrinsic energy density in empty infinite .
In the wake of the Big Bang , this vim increases as space lucubrate , creating more vacuity and more energy to push the universe apart faster . This suggestion assist scientists to tie moody vim to thecosmological constant quantity — a hypothetical inflationary energy , grow with the cloth of space - clip throughout the universe ’s life story . Einstein key out it Lambda in his theory ofgeneral relativity .
" The problem with that theory is that the numbers do n’t supply up , " saidCatherine Heymans , a professor of astrophysics at the University of Edinburgh and the Astronomer Royal for Scotland who was not involved in the survey . " If you say : ' Well , what sort of energy would I ask from this sort of vacuum ? ' It ’s very , very , very , very different from what we measure , " she tell Live Science .

" It ’s kind of exciting that the universe has thrown us a curveball here , " she added .
Scanning the dark universe
To figure out if dark vitality is changing over time , the astronomers turned to three years ' Charles Frederick Worth of data from DESI , which is mounted on the Nicholas U. Mayall 4 - meter Telescope in Arizona . DESI pinpoints the monthly emplacement of million of galaxies to study how the existence expanded up to the present solar day .
By compiling DESI ’s watching , which includes almost 15 million of the best measured galaxies and quasars ( extremist - brilliant objects powered by supermassive black holes ) , the researchers came up with a unknown result .
learn on their own , the telescope ’s reflexion are in " infirm tension " with the Lambda - CDM model , suggesting dark energy may be losing strength as the universe eld , but without enough statistical significance to break with the model .

But when paired with other observations , such as the existence ’s leftover light from thecosmic microwave background , supernovas , and the gravitational warping of Christ Within from distant galaxy , the likeliness that dark vitality is evolving grows .
In fact , it pushes the observations ' disagreement with the standard model as far as 4.2 Sigma , a statistical measure on the cusp of thefive - Sigma resultphysicists use as the " aureate monetary standard " for annunciate a Modern find .
interrelate : After 2 year in space , the James Webb telescope has broken cosmogeny . Can it be fixed ?

Whether this result will hold or fade over meter with more data is undecipherable , but astrophysicist are growing confident that the discrepancy is less potential to disappear .
— Cosmic nullity may explain the universe ’s acceleration without dark energy
— ' Heavy ' dismal affair would rip our understanding of the universe aside , Modern research suggest

— Something inconspicuous and ' fuzzy ' may lurk at the Milky Way ’s centre of attention , raw enquiry suggest
" These data seem to point that either colored energy is becoming less important today , or it was more important early on in the population , " Schlegel said .
Astronomers say that further answers will come from a flotilla of raw experiments investigate the nature of dark matter and dark energy in our universe . These include theEuclid space telescope , NASA’sNancy Grace Roman Space Telescope , and DESI itself , which is now in its fourth of five years scan the sky and will measure 50 million galaxies and quasi-stellar radio source by the time it ’s done .

" I remember it ’s just to say that this solution , select at face - value , look to be the self-aggrandizing intimation we have about the nature of dark energy in the [ rough ] 25 years since we discovered it,“Adam Riess , a prof of astronomy at Johns Hopkins University whowon the 2011 Nobel Prize in physicsfor his team ’s 1998 discovery of dark energy , told Live Science . " If substantiate , it literally says dark zip is not what most everyone thought , a electrostatic source of energy , but perhaps something even more exotic . "
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your display name .