When you buy through linkup on our land site , we may bring in an affiliate delegation . Here ’s how it works .
The oldest continents in our galaxy may have arisen 5 billion years before globe ’s , young inquiry suggests — and that mean there may be multiple worlds in theMilky Wayharboringalien lifeeven more advanced than our own .
Astrobiologists call back a planet postulate to have sure features to tolerate life history : oxygenin its standard pressure , something to shield organisms from dangerous radiation and fluent water , for a start . Although big land masses are n’t strictly necessary for living things to emerge , Earth ’s history shows that they ’re important for spirit to fly high and subsist for long periods of metre . So , if an exoplanet had continents before Earth , it follow that there might be older , more advanced lifetime on that world .
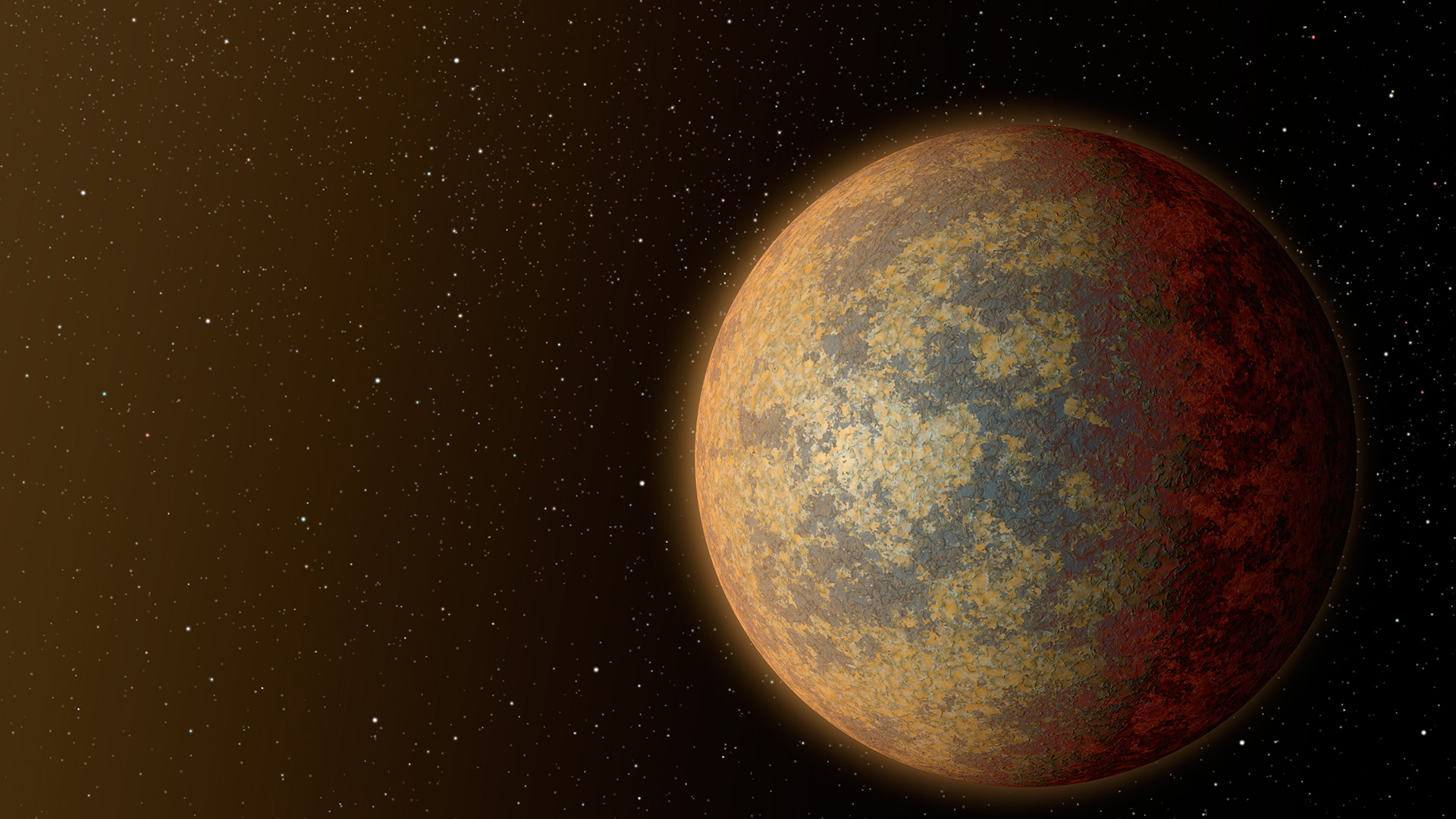
This artist’s rendition shows one possible appearance for the planet HD 219134b, the nearest confirmed rocky exoplanet found to date outside our solar system.
This line of thought ledJane Greaves , an astronomer at Cardiff University astronomer in the U.K. , to answer the question : When did the first continents appear on a major planet in our galaxy ? Turns out , two exoplanets ' continents — and perhaps life — may have arise four to five billion years before Earth ’s .
If spirit on another satellite had a five - billion - twelvemonth head start , it " could potentially host life more evolved than us , " Greaves wrote in a work , put out in the September payoff of the journalResearch Notes of the American Astronomical Society .
Continents form due toplate tectonics , the front of plates of rock that float atop the molten viscera of a planet . Heat from a planet ’s inwardness keeps that magma from hardening and halting continents ' movement . That heat come in from radioactive elements — like uranium-238 , thorium-232 , and potassium-40 — in the satellite ’s heart , which give off energy as they decay .
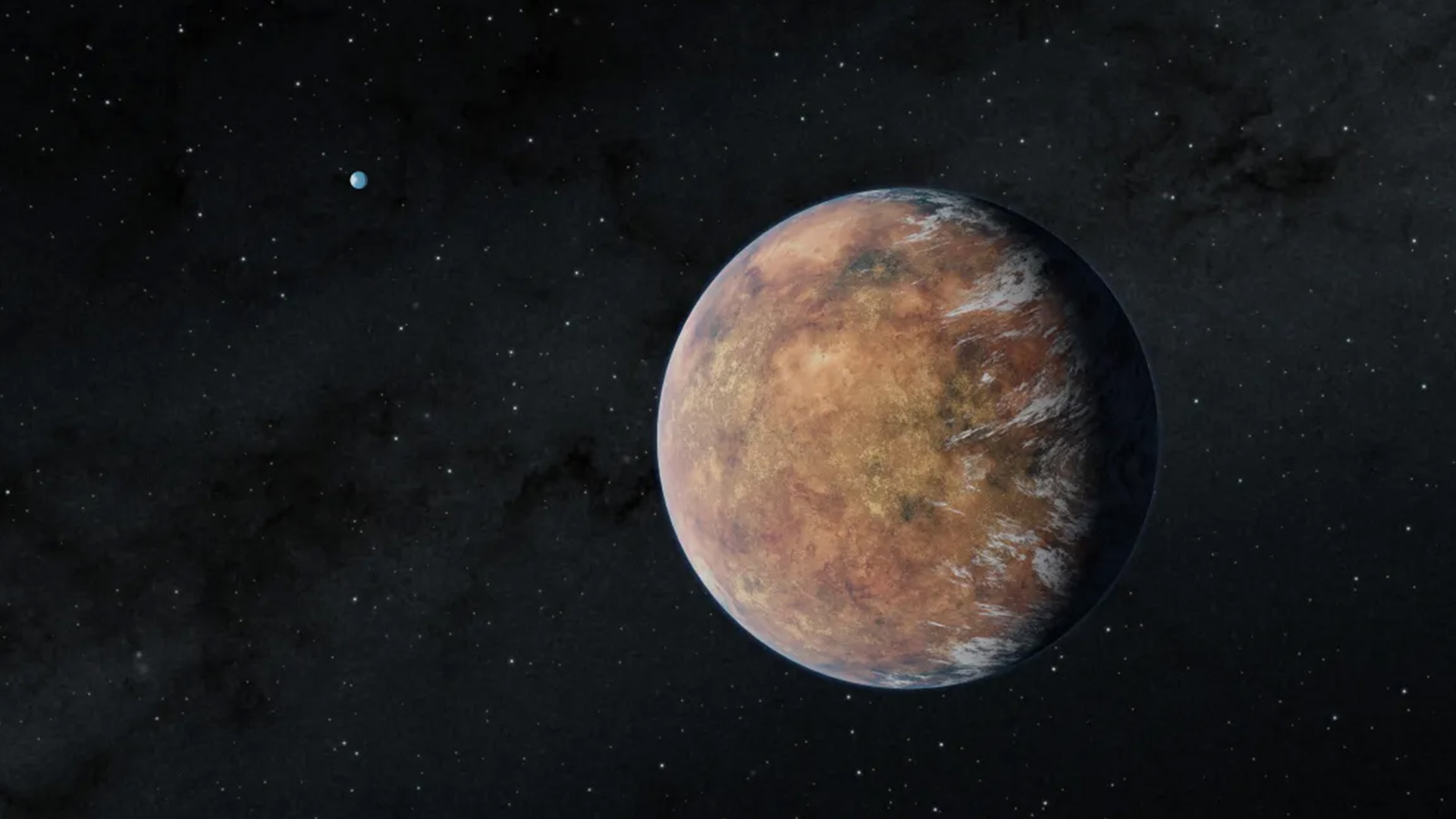

Newly discovered Earth-size planet TOI 700 e orbits within the habitable zone of its star in this illustration. Its Earth-size sibling, TOI 700 d, can be seen in the distance.
Most of those radioactive elements came from catastrophic cosmic events , likesupernova explosionsand collisions between the dead husks of giant virtuoso , known asneutron stars . Traces of those element can be observe in the wavelengths of light that star emit . In her new work , Greaves used storey of uranium-238 and potassium present in nearby stars , plus the eld of stars as measured by theGaia planet , to estimate when a hypothetical rocky satellite around each of these whiz became hot enough for plate plate tectonics to go forth .
She found that the first Continent formed around nearby Dominicus - like stars up to 2 billion years to begin with than Earth ’s scale architectonics began . The sometime continent of a nearby star are around HD 4614 , about 20 scant - old age from Earth . Earth ’s bulge out clip , however , is median for our cosmic neighbourhood .
Two star stand out from the ring , though : The planets of two stars a minute low than our sun ( HD 76932 and HD 201891 ) , place 70 to 110 light - years by from us respectively in a region recognise as the"thick platter " , could have formed continent up to 5 billion class originally than us . establish on her sample of just 29 stars and uranologist ' current best estimates for how likely a major planet is to be inhabitable , Greaves wrote , " there could be two systems in this sampling alone with biosphere more advanced than here on Earth . "

— Mirror - corresponding exoplanet that ' should n’t exist ' is the shiniest earth ever discovered
— New course of exoplanet — half - rock , half - water — discovered orbiting blood-red dwarf
— James Webb scope catch its first - ever lineal image of an exoplanet

Determining potentially interesting and inhabitable planets , like these describe by Greaves , is crucial preparation forNASA ’s future Habitable Worlds Observatory , which uranologist will use to observe world - alike planets — and hopefully signs of living — in the 2040s . Greaves hopes next study will analyze more stars to determine if they could have major planet with plate tectonics , which , she wrote , " could help to bring out more one-time organisation where life on land could pre - date that on Earth . "