When you buy through links on our site , we may garner an affiliate deputation . Here ’s how it work .
In 2020 , astronomer mention for the first time what appeared to be a star engulfing one of its orbiting planets . But now , fresh grounds show something else actually happened .
A major planet certainly assemble its demise at the behest of its asterisk , but now the way it happened seem much different . Rather than this sensation expanding , it drew the planet closer and nearer until it was consumed , fresh grounds fromNASA’sJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) reveals . This novel event serve as an equally absorbing first — even if it ’s not what astronomers ab initio believed it to be . The researchers published their finding April 10 inThe Astrophysical Journal .

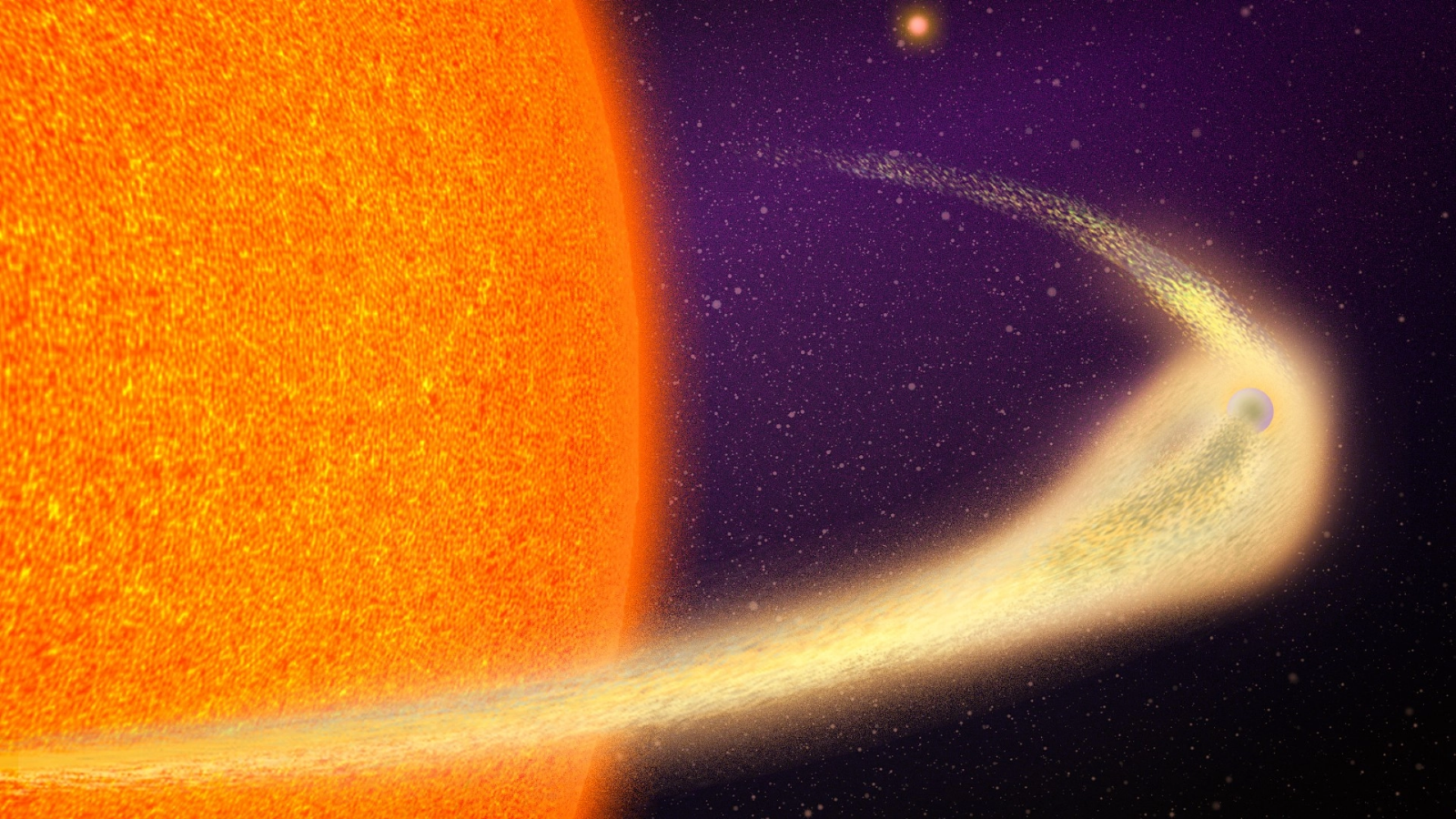
JWST’s observations of what is thought to be the first-ever recorded planetary engulfment event revealed that the star did not swell to swallow the planet, but the planet’s orbit actually slowly depreciated over time, as seen in this artist’s concept.
" It ’s not every day that we regain these kind of event , " the cogitation ’s first author , Ryan Lau , an adjunct astronomer at the National Science Foundation National Optical - Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory in Tucson , Arizona , told Live Science . This is " in all likelihood the first planetary engulfment event that was caught in the act . "
The heavenly event , dubbed ZTF SLRN-2020 , involves a star and its Jupiter - size of it planet , located in theMilky Wayapproximately 12,000 clear - years from Earth . While watching the star , researchers noticed a burnished flash of optical light , betoken that something — most potential a tumid planet — had been engulf by the star , leave only a cloud of dust behind .
‘A very different scenario’
Initially , researchers thought the star was like to the Dominicus and was follow the raw sprightliness cycle per second of sunlike wiz . A 2023 newspaper published in the journalNaturedescribed the star as participate its final stage of life as a red giant , in which it balloons importantly as it exhausts its supply of H fuel . The sun will meet this destiny in about 5 billion twelvemonth , ultimately swallow Mercury , Venusand , likely , Earthin the operation .
But the data fromJWST"paints a very dissimilar scenario , " Lau allege . As JWST ’s Mid - Infrared Instrument and Near - Infrared Spectrograph gathered information from the scene of the crime , a new characterisation come out . The reflection revealed that the hotshot had not been emit light in the flesh of infrared wavelengths expect from the transition into a flushed giant . In other Son , it was n’t as bright as await , indicating that the carmine giant process likely was n’t afoot .
relate : After 2 year in blank , the James Webb telescope has broken cosmogony . Can it be fixed ?

As for the devoured planet , the team purpose that it orbited unusually close to its host star — even closer thanMercuryorbits the sun . in the end , the Jupiter - size planet started moving nigher and closer to its star in a process called orbital decay . Lau and his team attribute this orbital decay to tidal interactions , a phenomenon in which strong gravitational forces between two celestial bodies can change the kinetics between those bodies .
— Newly observe comet SWAN just ' ignite ' with a bright , frozen salvo . Is it a cold volcano ?
— record book - breaking ' dead ' galaxy describe by JWST lived tight and die out young in the early cosmos
— Astronomers are shocked to encounter our galaxy ’s approximate neighbor is being bust to shreds
The whole cognitive operation in all likelihood took just a few months , Lau say . After the satellite spiraled in toward the star topology , it made contact with the headliner ’s surface . From there , drag forces sucked it into the ace ’s substance , where it was to the full engulfed . The whiz then ejected the planetary material , which created the brightening event first detected in 2020 . This ejection also included longer - lasting infrared wavelengths and dust , which conduct astronomer to believe that the star had expanded , when , in fact , it did not .
event like these can be laborious to spot because the loose signatures they make are often quite faint . With the first step of theVera C. Rubin Observatory , Lau tell , these observational signatures — and their connect events — could become much easier to discover .
" We should be finding mode more of these , " Lau said . " That ’s one thing I ’m very mad about . "
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to move into your showing name .













