When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate military commission . Here ’s how it works .
The Gulf Stream decelerate dramatically at theend of the last ice agewith dire impression on organism in the Atlantic , scientist have regain . This discovery could help researchers forecast how Atlantic current will shift in reaction to climate change today .
The Gulf Stream is a warm ocean current that originate in the Florida Straits between Florida and Cuba , before skirting the U.S. East Coast and Canada and crossing the North Atlantic to Europe . The heat it carries maintains temperate condition in Europe and to some extent North America . The current forms part of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation ( AMOC ) , which transports balmy amnionic fluid from the Southern Hemisphere to the Union and then back down toward Antarctica in a jumbo loop topology .
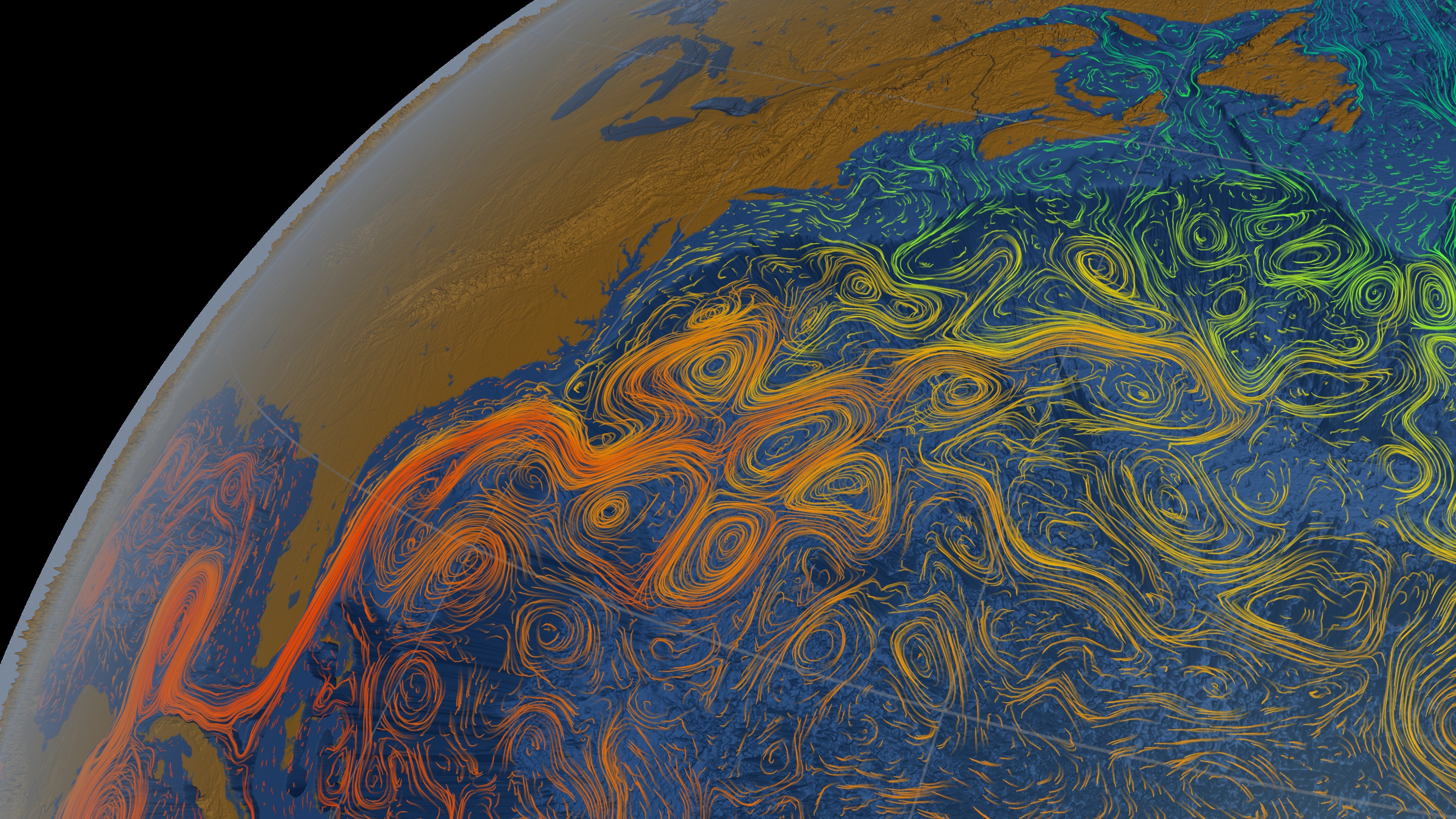
NASA visualization showing the Gulf Stream as it unfurls from the Florida Straits across the North Atlantic Ocean. The current is colored according to sea surface temperature. Red is equivalent to around 90 degrees Fahrenheit (32 degrees Celsius) while green is equivalent to roughly 55 F (13 C).
Previous models showed theGulf Stream is weakeningand theAMOC may be secretive to crumple , with grave implications for the climate . Now , a fresh study publish Thursday ( May 9 ) in the journalSciencehas found that a decline in the Gulf Stream potentially import trouble for ocean critters that reckon on the nutrients the current transportation from the Torrid Zone to the North Atlantic .
The authors based their conclusions on dodo and sediment records from a brief cooling event between 12,900 and 11,700 year ago , known as the Younger Dryas . The cold snap temporarily reversed a period of global warming during the transition from thePleistocene epochto the currentHolocene epoch .
Related:‘We were in disbelief ' : Antarctica is behaving in a way we ’ve never see before . Can it recover ?
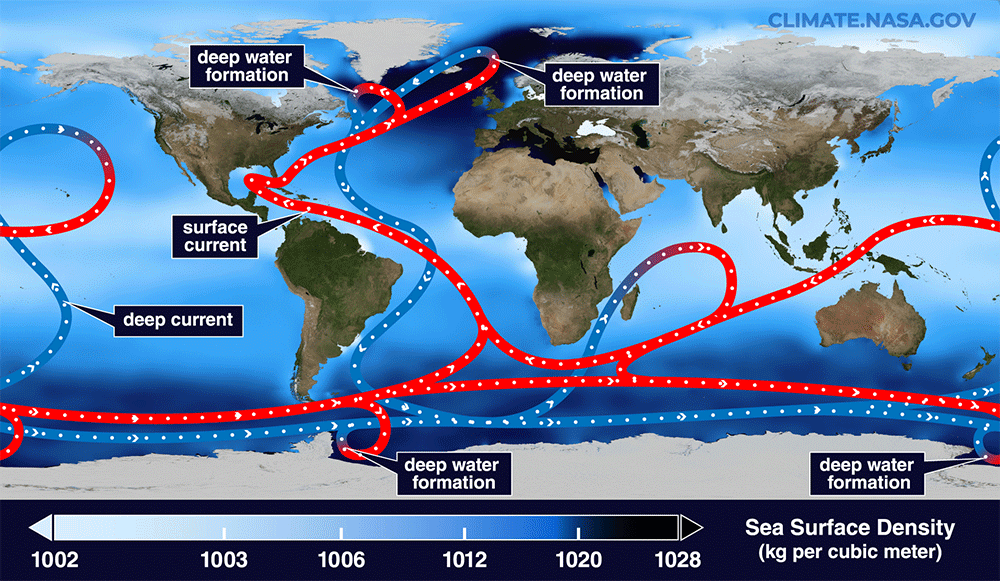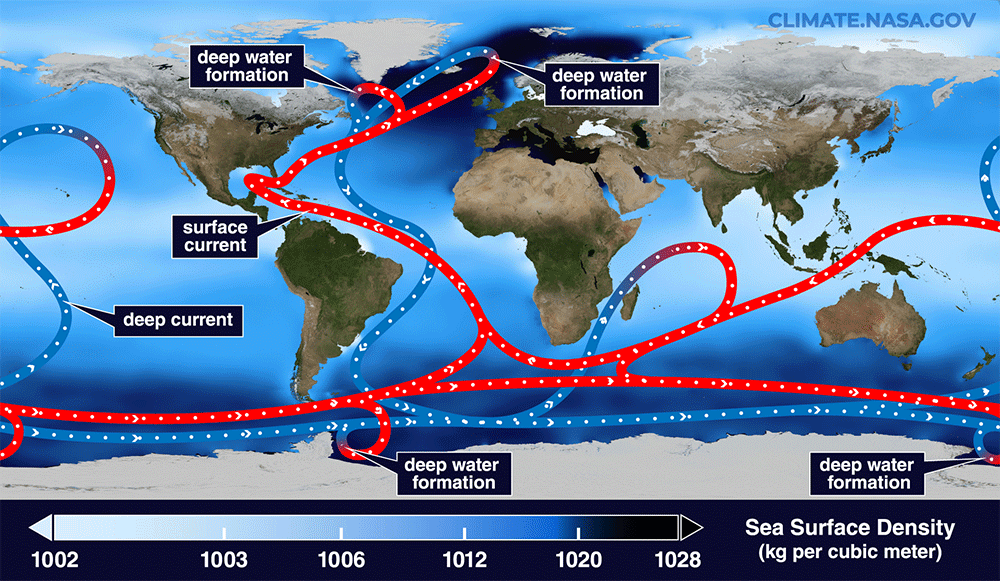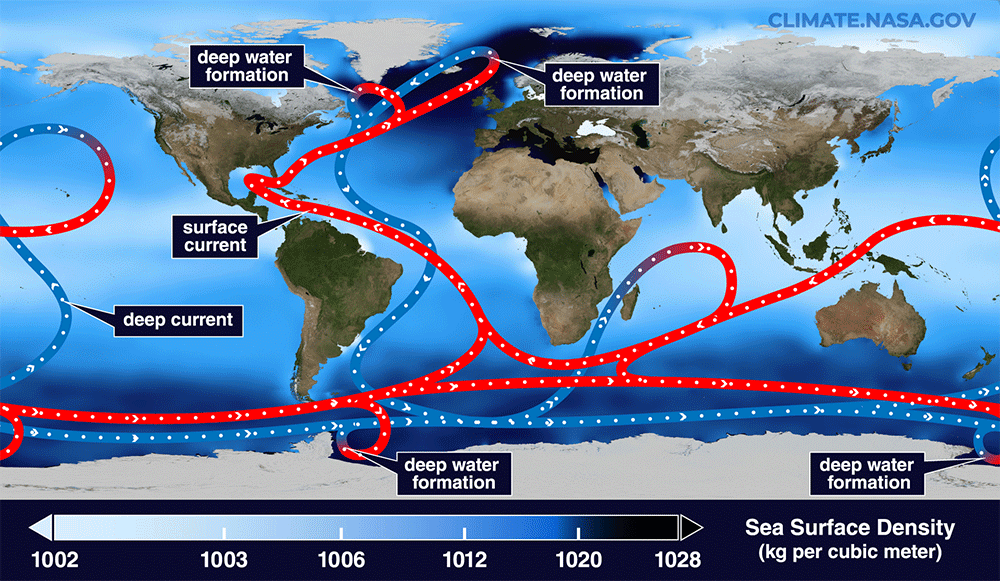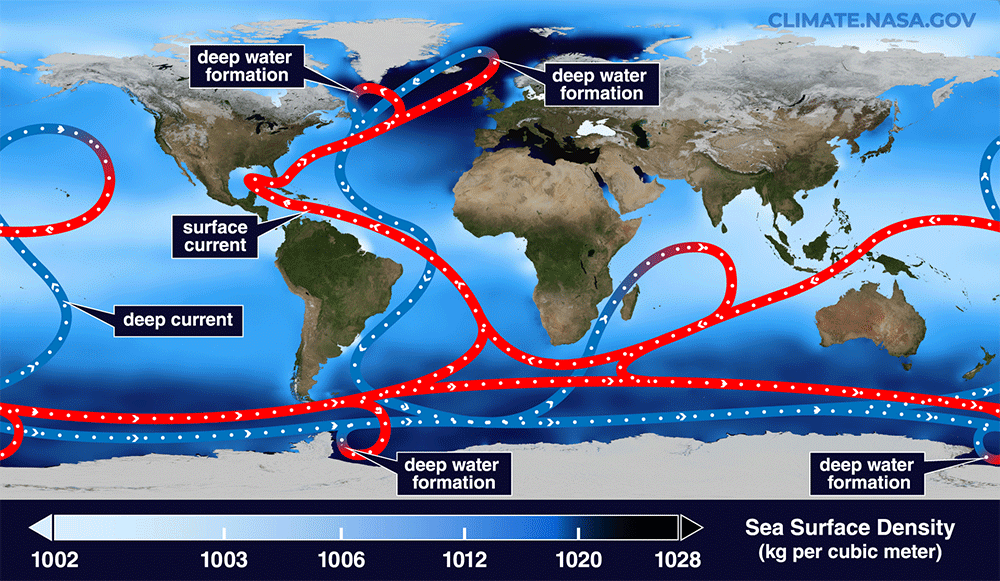
A simplified animation of the global conveyor belt of ocean currents, including the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) in the Atlantic Ocean.
" There are multiple lines of evidence that the AMOC counteract during the Younger Dryas cold separation that punctuate the transition out of the last chalk age , " the researchers compose in the written report . " Although the details of the background clime state and timescale of change take issue from those of the present day , this past climate issue provides an opportunity to test the mechanisms that have been identified in the climate model . "
To reconstruct the condition that prevailed in the Gulf Stream during the Younger Dryas , the researchers examined the nourishing content of microscopical fossils and sediment cores from the Florida Straits . The team found that nutritious content dropped during the Younger Dryas compared with the millennium immediately before and afterwards . This starved photosynthetic organisms in the North Atlantic that convert these nutrients and sunshine into organic matter . Their declension likely sent ripple through the food chain , affecting populations of fish and other ocean creature .
" In this simulation , as the AMOC and nutrient stream weaken , the alimentary content of the upper North Atlantic and primary productiveness both decline , " the researchers wrote in the study . The drop in nutrient content at the base of the Gulf Stream was tie in to slug current in the Southern Hemisphere , where the AMOC unremarkably picks up nutrient - rich waters and flog them northerly .

— Antarctic stream supplying 40 % of world ’s deep ocean with nutrients and oxygen decelerate dramatically
— Every 2.4 million years , Mars tugs on Earth so hard it changes the ocean storey
— Heat waves are hitting the abstruse sea floor , with potentially ruinous resultant

This shot from the Younger Dryas bolster current clime models that prefigure nutrient transportation to the North Atlantic Ocean will nosedive if the AMOC and Gulf Stream continue to slow up , according to the survey . The resulting decline in primary productiveness would affect important North Atlantic fishery and may also limit how much CO2 the oceans can take up , the researcher wrote .
Worryingly , while the AMOC only undermine during the Younger Dryas , late research has identifiedsigns that the flow may be on the verge of collapse .
Jellyfish Lake : Palau ’s brine puddle with a toxic bottom and aerofoil waters brim with millions of man-of-war

deep substance spotted swirling across the surface of the Baltic Sea — Earth from blank space
The unceasing surveillance of modern life could worsen our brain purpose in ways we do n’t fully understand , raise up study suggest






