When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate deputation . Here ’s how it act .
Your Einstein body process change depending on whether you ’re recall a true or a false memory , new research suggests . A " pretended " memory refer to when you remember something that did n’t happen or that actually occur at a unlike time or piazza .
Remembering past result , experiences or information tied to a specific context , such as a natal day party , first appointment or late trip to the grocery fund , is eff asepisodic memory ; that ’s oppose to semantic memory , which is relate to general knowledge and facts untethered to a time or place and not related to one ’s own past . occasional memories are largely control by a learning ability region called thehippocampus , but what encounter in the brain social system when hoi polloi misremember events has been a enigma — until now .
A specific pattern of electrical activity can be detected in neurons in the hippocampus of the brain before a false memory is recalled.
According to the new written report , published Sept. 26 in the journalPNAS , a specific pattern of electrical activity erupts in the hippocampus immediately before someone return a false retention — and it differs from the electrical body process that takes place when multitude think of an case correctly .
" Whereas prior bailiwick deploy the role of the genus Hippocampus in event memory , we did not jazz that electrical signals mother in this region would differentiate the impending callback of on-key from false memories,“Michael Kahana , senior study author and a prof of psychological science at the University of Pennsylvania , say in astatement .
interrelate : Neurons are n’t the only cells that make retentivity in the brain , rodent survey reveals
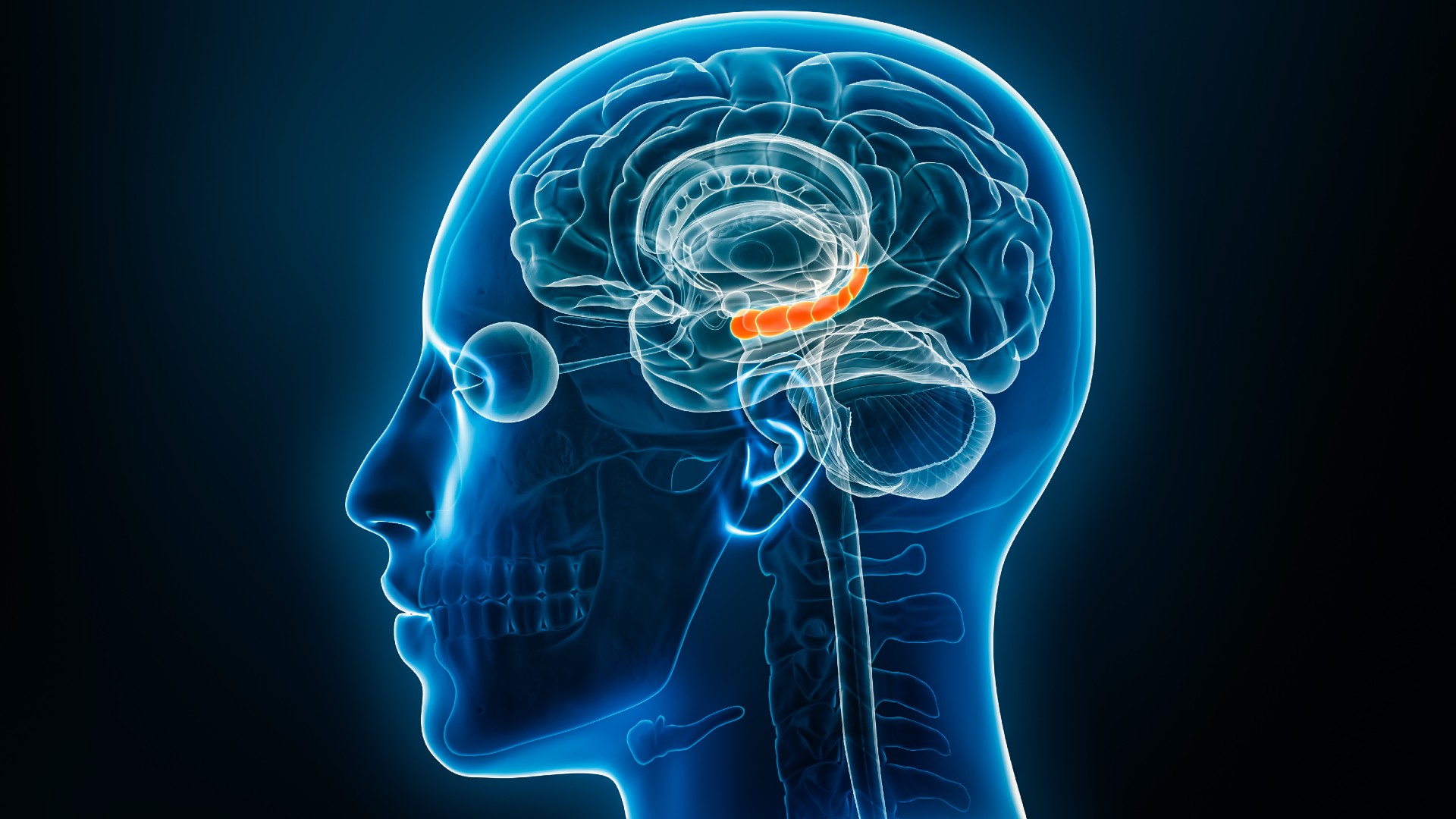
The hippocampus, pictured above, is key for recalling memories of events or experiences that happened in specific contexts.
A better understanding of this brain activeness could help prognosticate when people are die to recall a distressing false memory , far take out from its original context , the cogitation authors propose .
For example , people withpost - traumatic stress disorder(PTSD ) " often receive retention intrusions of their traumatic experiences under setting that are safe and dissimilar to the traumatic incident , " they wrote in the paper . In possibility , new medical intervention could be design to monitor and disrupt this brainpower activity to put a full point to the disturbing flashback , the bailiwick source propose .
In the new survey , the investigator recorded electric activity in the genus Hippocampus of patients withepilepsy , who ’d already had electrodes implanted in their brain so doctors could track their seizures . The team ab initio ask the affected role to study a list of unrelated Book , such as " pizza " and " clock , " and then retrieve them in any society after a brief break . Before studying the " fair game " word list , the participant had been shown a different list of Good Book that could potentially turn on up their retentivity . In such tests of occasional memory , the words are contextually bound together by their source , mean the word list on which they ’re present .

The rhythm of electrical activity in the hippocampus differed dramatically when patients correctly call back a intelligence from the fair game list or falsely remembered one that had n’t been included . This electrical bodily process seem less than a second before they enounce the word and then fade quickly afterward .
Interestingly , if a patient incorrectly recalled a word from the other list they ’d been shown , their hippocampal rhythms were more similar to those hear when they recollect right words . The calendar method differed most importantly when they sound out a Son they ’d never been show . The author hypothesized that this was likely because the affected role were in the same situational context — sitting at the same seat in the same elbow room — when they hive away the retentiveness of the Christian Bible on both lists . In other words , the share circumstance made the memories more similar to one another in the brain .
— ' Muscle memories ' get ' zipped and unzipped ' in the encephalon , like calculator files

— How does the brain computer storage memories ?
— ' Short - terminal figure memory illusions ' can heave human recollections just seconds after case , study suggest
In a 2nd experiment , the source asked the patient to study and recall related password , categorized as flowers , fruits and louse . The importance of situational linguistic context was also express in this trial . For example , after a patient studied the efflorescence list , if they recalled an wrong but similar word of honor , such as " sunflower " instead of a " lily , " their hippocampal rhythm was more similar than if they ’d call back a word that was completely unrelated , such as " clock . "

The authors wrote that these finding may explain how the hippocampus distinguishes between similar memories made in dissimilar contexts — for exemplar , what you cooked for dinner tonight versus last dark . And it may pave the way for fresh therapies to treat diseases where memory recollection goes haywire . However , it ’s still unclear whether these electrical signature are really responsible for for the assumed computer storage or just go on at the same time . Future studies could search this by by experimentation cook brain action , the authors indite .
result to ' cocktail party problem ' could avail people with hearing passing
scientist hijack the human eye to get it to see a brand - newfangled color . It ’s call ' olo . '

What are neural processing units ( NPUs ) and why are they so important to modern computing ?






