When you buy through linkup on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it works .
Swarming through oursolar systemby the jillion , asteroidsare vagabond place rocks that hold clues to our universe ’s retiring — and the potency to destroy our future . In 2023 , astronomers made tremendous step in studying these elusive objects . Two challenging , multi - year mission to collect asteroid samples from blank eagre fruit and revealed that the building blocks of life were shuffle in with the cosmic rubble . Elsewhere , NASA investigator preserve studying the gory backwash of the Double Asteroid Redirection Test ( DART ) — humanity ’s first attempt to bump a potentially hazardous asteroid off course — while astronomers warn Live Science that the next killer whale asteroid could lurk hidden in the sun ’s glare .
Here ’s a recap of those exciting story to remind you that infinite rocks .

An animation of asteroid Ryugu made with images from JAXA’s Hayabusa2 mission.
‘Seeds of life’ on Ryugu
In several studies issue in February and March , scientists unveiled their long - awaited psychoanalysis of dust gather from the control surface of the " spinning top " asteroid Ryugu . The first subject revealed the mien ofmolecules that are essential to all known aliveness , including 15 aminic acids — the building blocks of protein . The 2nd study addedthe detection of U , one of the four nucleobases of RNA , a protein - synthesise mote present in all living things .
Japan ’s Hayabusa2 space vehicle garner the sample of asteroid Ryugu in 2018 before returning it to Earth in 2020 . This yr ’s analysis removed any doubtfulness that many of the construction blocks of liveliness are present in space — and may even be delivered to vernal planets via asteroid impacts . The noteworthy findings led study authorYasuhiro Oba , an astrochemist at Hokkaido University in Japan , to separate Live scientific discipline : " It is difficult to leave out the possibility that some form of sprightliness are present in extraterrestrial environments . "
OSIRIS-REx returns ‘unknown material’
Not to let Japan grab all the extraterrestrial halo , NASAcompleted its own seven - year OSIRIS REx delegacy to retrieve a sample of the asteroid Bennu — themost dangerous known asteroid in the solar scheme — successfully dropping a metal black sampling income tax return capsuleinto the Utah deserton Sept. 24 .
Within workweek , NASA scientists were analyzing the powdery black surface material while commit smaller packets of the sample tolabs around the world . NASA ’s preliminary depth psychology testify that Bennu is not only productive in H2O and organic molecules that are crucial to life on Earth , but it also hasan unknown materialthat scientist have yet to key out . Stick around for more on this story in 2024 .
Hidden ‘planet killers’ await us
Last year , stargazer discovered amile - full ( 1.6 kilometers ) " planet sea wolf " asteroidin the Lord’s Day ’s glare , which had apparently evaded detective work for decades . The asteroid stupefy no threat to Earth for at least 1,000 geezerhood — but its surprisal discovery made us at Live Science wonder : Are there more potentially deadly asteroid out there , orbiting just out of spate ?
In a particular probe , Live Science spoke to uranologist who saidthere are " definitely " more giant asteroid hide in the Lord’s Day ’s glare , as well as countless smaller ones that could unleash significant regional damage were they to pilfer into Earth ’s orbit . find asteroids near the sun involve use - ramp up infrared space telescopes , which both NASA and theEuropean Space Agency(ESA ) are hoping to deploy in the arrive decade .
DART worked — and left a huge mess
When NASA intentionallycollided its DART spacecraftwith the binary asteroid Dimorphos last September , scientists wait to change the blank space John Rock ’s orbit around its partner asteroid by at least 72 second . In the remainder , the impact change Dimorphos ' orbitby a humongous 33 arcminute , a series of papers issue in March found .
This significant variety was thanks to the force out of the space vehicle ’s impact and the massive feather of debris that spewed from Dimorphos after the collision . This epic plume , along with a " cloud of bowlder " that were jettison from the asteroid ’s airfoil , were captured in vivid detail in newHubble Telescope images exhaust in July .
This mess is a skilful matter ; it proves that DART was successful in changing the target asteroid ’s trajectory , vindicate the " energising impactor " method acting of asteroid deflexion . That ’s good to do it , if a rock like Dimorphos ever poses a exonerated menace of come to Earth . ( Thankfully , no known asteroids pose such a scourge for at least 100 years . )

An animation of asteroid Ryugu made with images from JAXA’s Hayabusa2 mission.
When in doubt, nuke it out
While DART worked even well than expected , the logistics of actually pull through Earth from an incoming asteroid might be far trickier than this missionary work suggests . At the International Academy of Astronautics Planetary Defense Conference held earlier this class , scientists were tasked with deflecting a hypothetical asteroid measuring about three time the size of it of Dimorphos . The team ’s pretending showed that redirecting such a whopper of a rock would requiresimultaneously launch between 39 and 85 rocketscarrying kinetic impactors — a " completely impractical " solution , conference participantBrent Barbee , an aerospace engineer at NASA ’s Goddard Spaceflight Center , evidence Live Science .
The good solution , fit in to the simulations , is to detonate a individual atomic explosive near the asteroid . Such a blast would instantly vaporize the tilt ’s outer layer , kicking up a gargantuan debris plume able of shove the asteroid off its hit path . But in either case — the kinetic impactors , or the nuke — scientist would likely need at least five class of planning to get the business done , so the preferably we can detect any potentially hazardous asteroid , the better .
A ‘dinky’ surprise
In November , NASA ’s Lucy ballistic capsule made a close flyby of the half - international nautical mile - extensive ( 0.8 km ) asteroid Dinkinesh , which orbits in the master asteroid belt ammunition between Mars and Jupiter . In the weeks leading up to the close approach , astronomers acknowledge a unusual flickering from the asteroid . The rationality , they found out , was thatDinkinesh has a secret moon — a flyspeck 0.15 mile wide of the mark ( 220 m ) rock’n’roll that pass periodically in front of its larger companion , make the flicker .
Dinkinesh is the smallest asteroid ever explored by a space vehicle , and there ’s no mode these observations could have been made from Earth — a good reminder that the good way to study asteroid is to get up close and personal .
An even dinkier surprise…
But there ’s another plait : Dinkinesh ’s secret moonturned out to be two petite synodic month touching . Known as a contact binary , the moons take on a goober shape that has been observed in much big asteroids in our solar organization but never in rocks as tiny as these . As Lucy proceed its journeying toward Jupiter to analyze a group of asteroids do it as the Trojans , more surprises will sure take after .
A lunar visitor
in the end , another asteroid turned out to be more than it seemed this yr . Kamo’oalewa , a Ferris - wheel - size rock chunk that passes within 9 million miles ( 14.4 million km ) of Earth every April , may actually be a part of the moonthat got blast off in an ancient impact .
Prior studies had show that the sway has a similar theme to the moon , but a newspaper published in October calculated how an ancient asteroid impact on the moon could have send Kamo’oalewa fly into its current trajectory near Earth . What ’s more , the study find oneself there could be other glob of the lunar surface orb near our planet that were launch into quad by the same encroachment or similar I . merely put : Earthmay have more moonsthan we think .
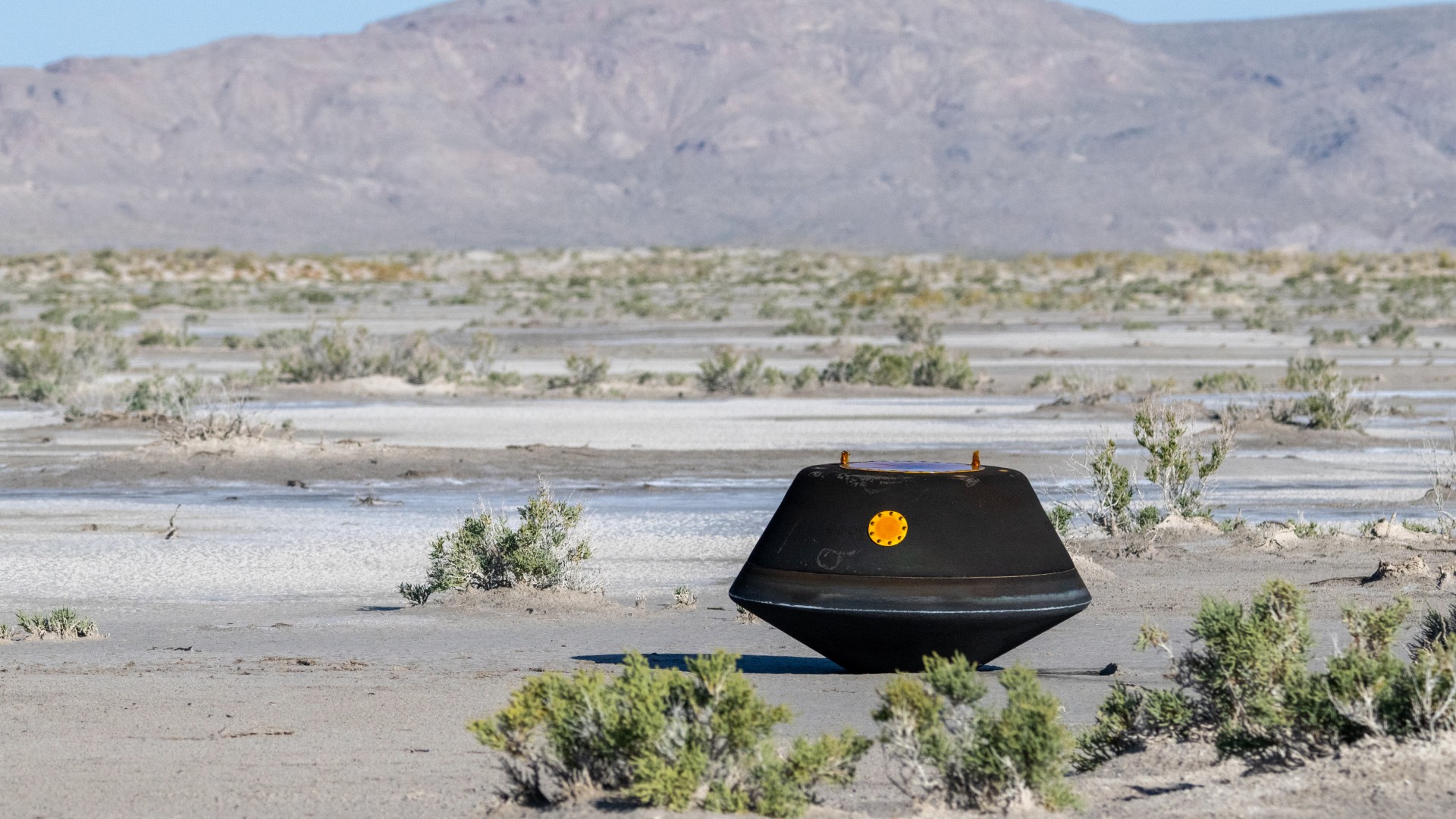

The sample return capsule from NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission is seen shortly after touching down in the desert, Sunday, Sept. 24, 2023, at the Department of Defense’s Utah Test and Training Range.
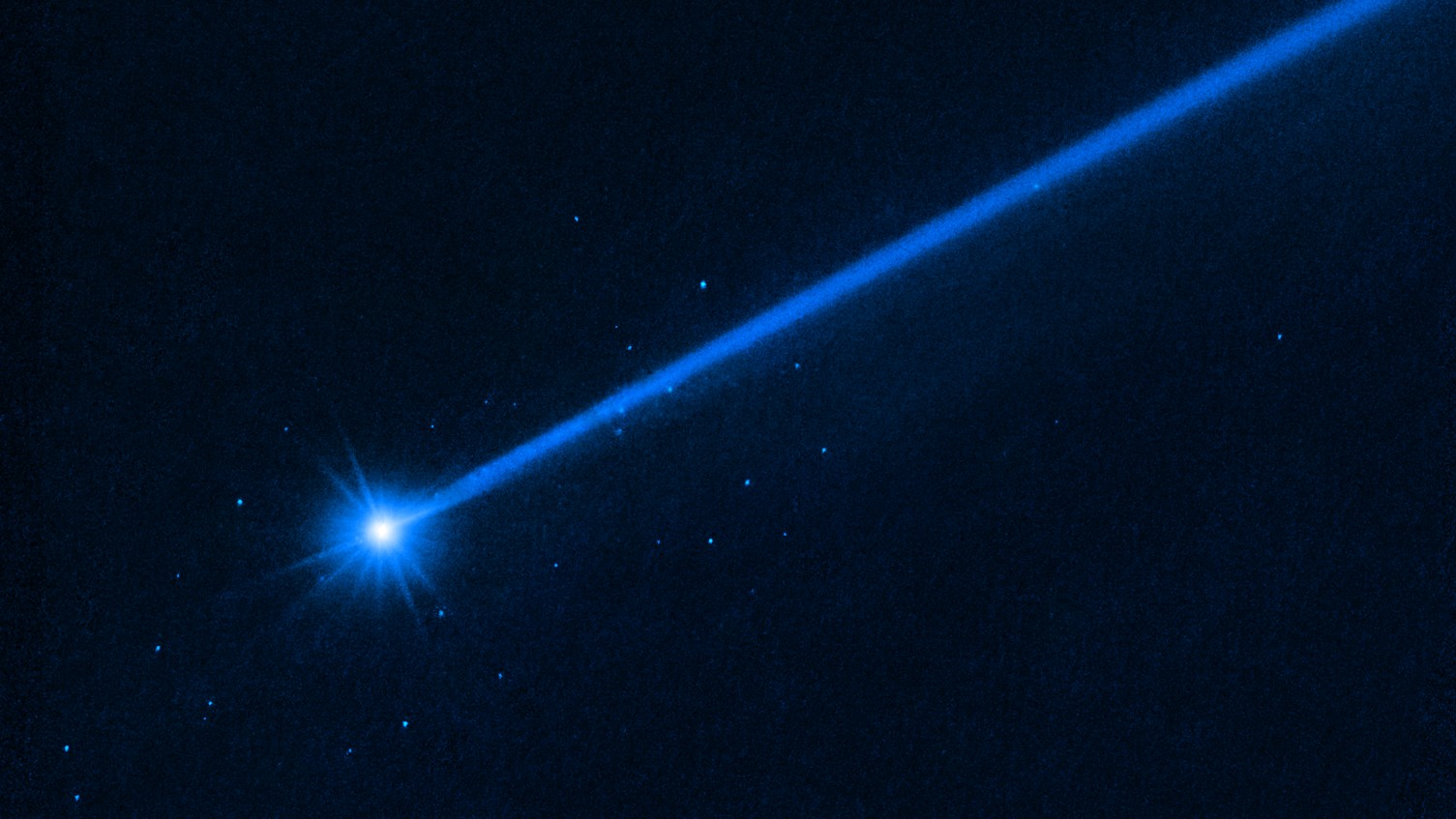

The light blue dots around the bright body of asteroid Dimorphos are all boulders knocked into space during NASA’s DART mission.
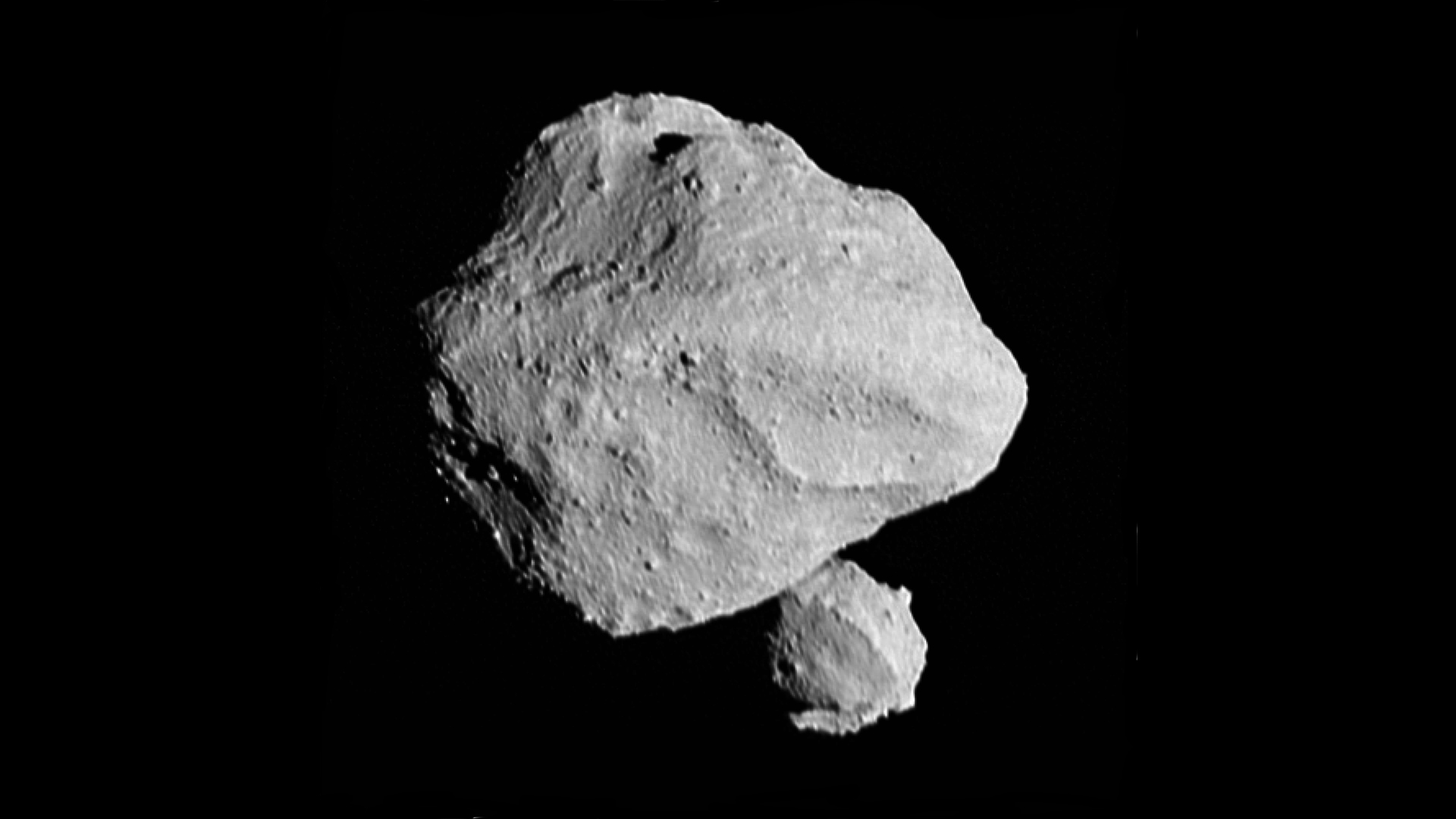


This image shows the “moonrise” of the satellite as it emerges from behind asteroid Dinkinesh as seen by the Lucy Long-Range Reconnaissance Imager (L’LORRI), one of the most detailed images returned by NASA’s Lucy spacecraft during its flyby of the asteroid binary.
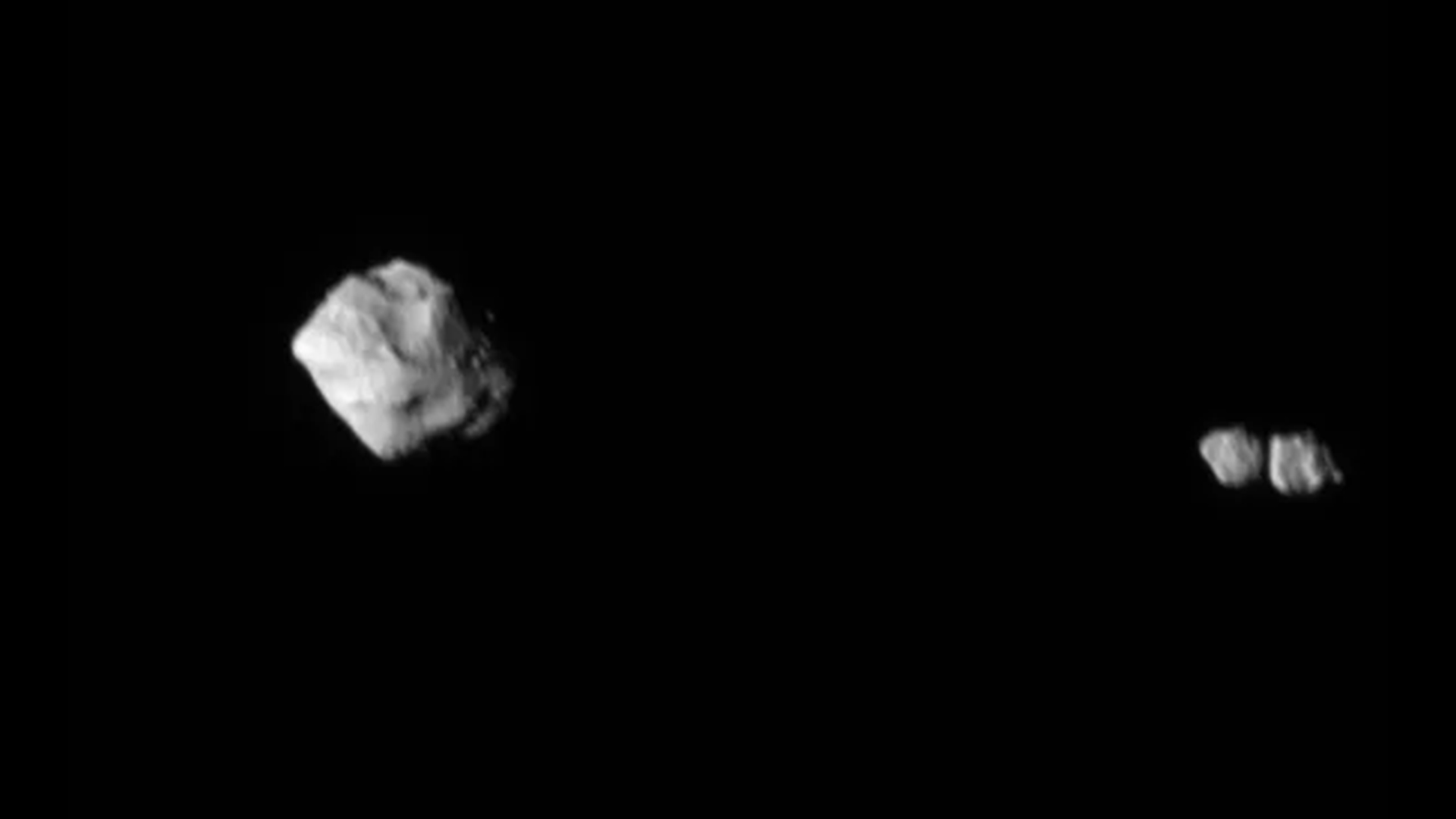

Dinky asteroid’s hidden ‘moon’ is actually two moons in disguise.
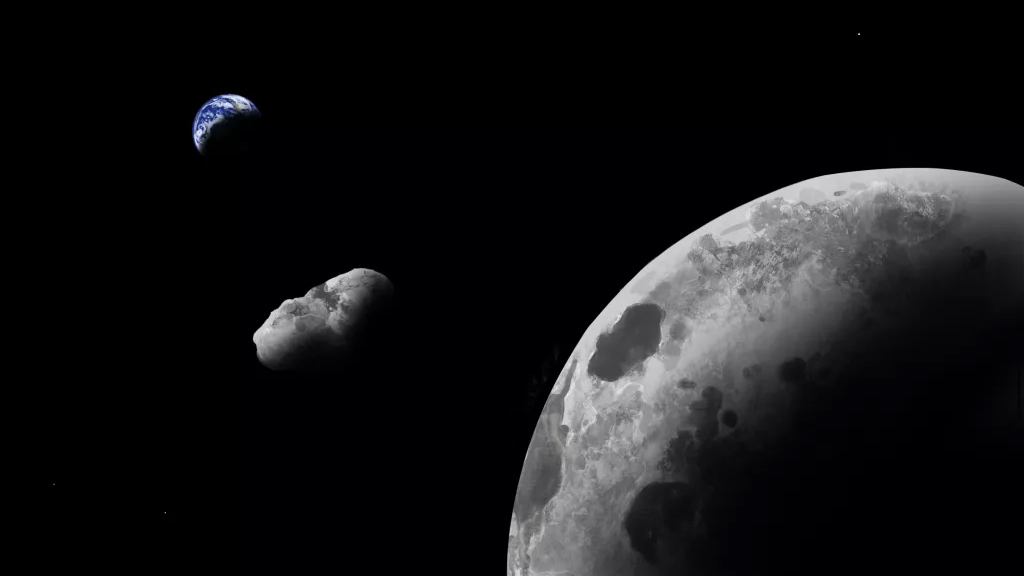

Kamo`oalewa near the Earth-Moon system.