When you purchase through tie on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
During the last ice age , humans ventured into two vast and all unnamed continent : North and South America . For nearly a 100 , researchers call back they know how this wild journeying occurred : The first people to queer the Bering Land Bridge , a massive swath of land that connected Asia with North America when sea levels were lower , were the Clovis , who made the journey shortly before 13,000 years ago .
agree to the Clovis First possibility , every Indigenous somebody in the Americas could be traced to this individual , inland migration , saidLoren Davis , a professor of anthropology at Oregon State University .

The first people to arrive in the Americas may have arrived around the Last Glacial Maximum, the coldest part of the last ice age (about 26,500 to 19,000 years ago).
But in recent decades , several breakthrough have let on that mankind first gain the so - called New World G of years before we ab initio thought and probably did n’t get there by an inland itinerary .
So who were the first Americans , and how and when did they come ?
inherited studiessuggest that the first masses to come in the Americas descend from an transmissible mathematical group of Ancient North Siberians and East Asians that mingled around 20,000 to 23,000 age ago . They get across the Bering Land Bridge sometime between then and 15,500 days ago , saidDavid Meltzer , an archaeologist and professor of prehistory in the Department of Anthropology at Southern Methodist University in Dallas and author of the Holy Writ " First Peoples in a New World , 2nd Edition " ( Cambridge University Press , 2021 ) .
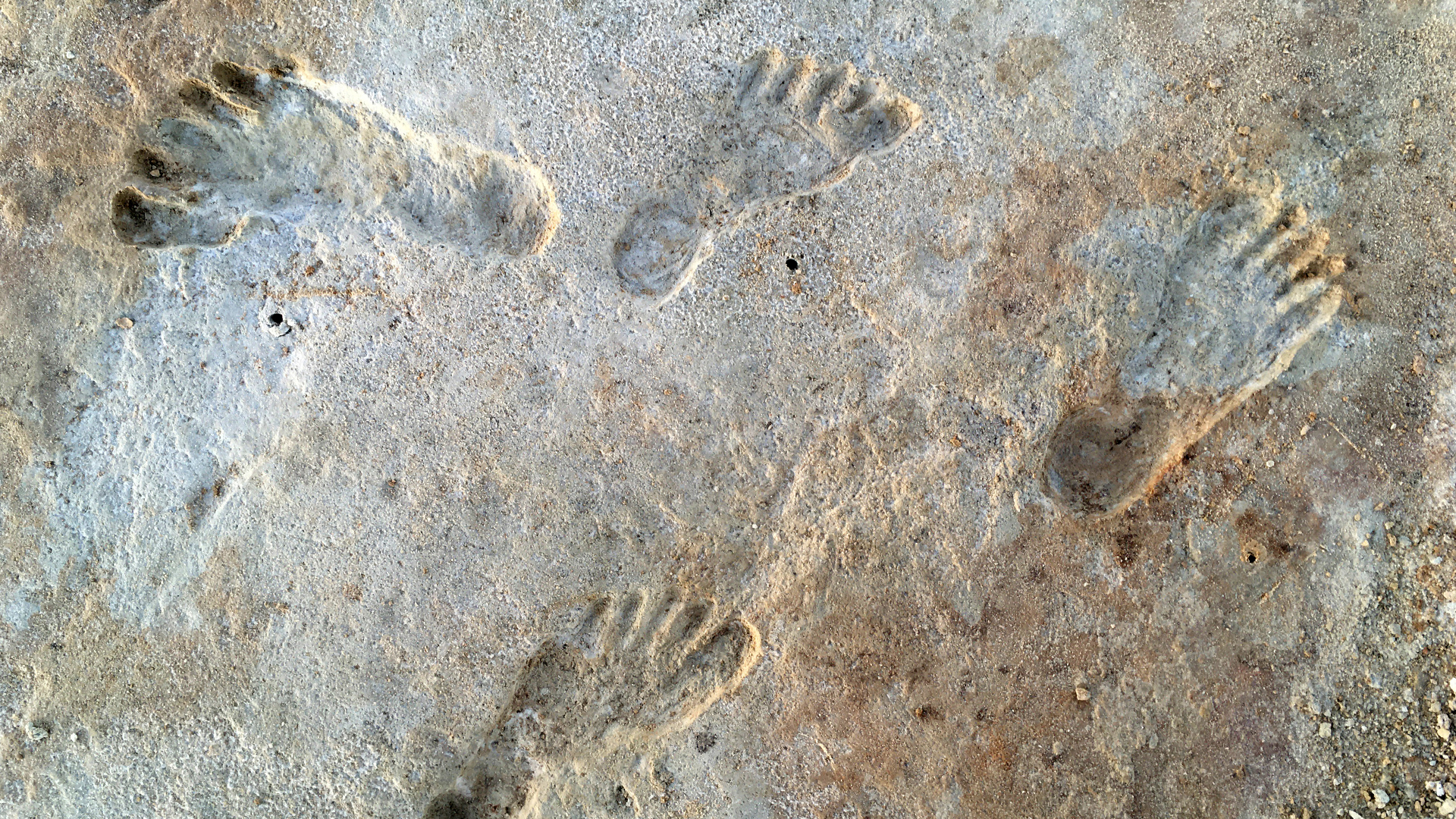

Fossilized human footprints at White Sands National Park in New Mexico date to around 21,000 to 23,000 years ago.
But some archaeological site hint that people may have hit the Americas far before than that .
For instance , there arefossilized human footprintsin White Sands National Park in New Mexico that may date to21,000 to 23,000 years ago . That would mean human arrived in North America during the Last Glacial Maximum ( LGM ) , which occurred between about 26,500 to 19,000 year ago , when Methedrine sheets cover much of what is now Alaska , Canada and the northerly U.S.
Other , more ambiguous data propose the first people arrived in the Western Hemisphere by25,000or even31,500 , years ago . If these date can be confirm , they would paint a much more complex picture of how and when human beings reached the Americas .
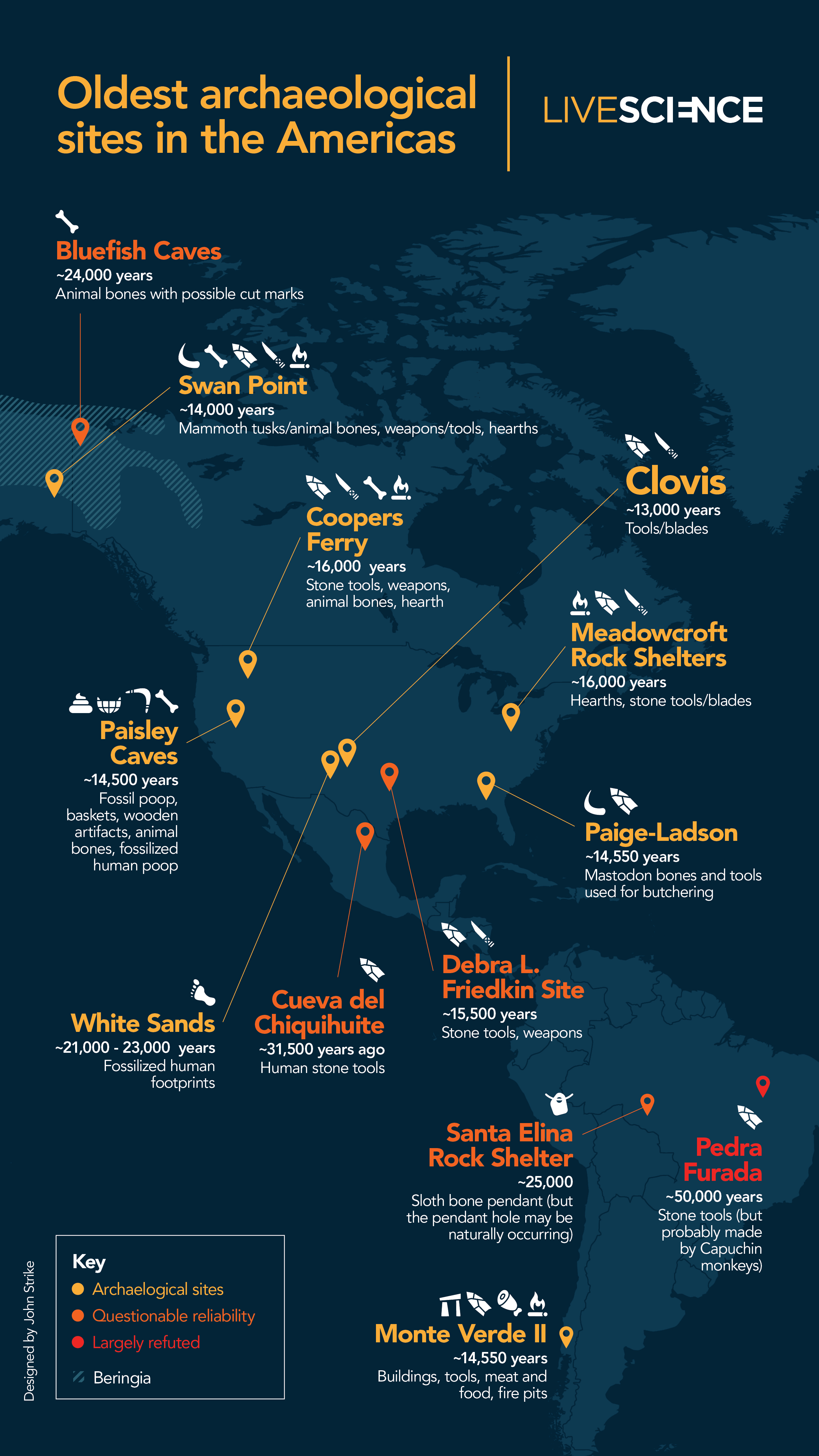
This map of North and South America shows some of the more accepted, questionable and largely refuted archaeological sites left behind by the first Americans.
Related : What ’s the earliest grounds of world in the Americas ?
Archaeological evidence of the first Americans
Almost all scientists agree , however , that this unbelievable journeying was made potential by the emergence of Beringia — a now - submerge , 1,100 - mile - wide ( 1,800 kilometers ) land mass that connected what is now Alaska and the Russian Far East . During thelast frappe age , much of Earth ’s water was freeze in ice mainsheet , stimulate ocean spirit level to descend . Beringia turn up once H2O in the North Pacific drop around 164 animal foot ( 50 meters ) below today ’s levels ; it was tolerable by foot between 30,000 and 12,000 years ago , Meltzer andEske Willerslev , a geneticist at the University of Cambridge , wrote in a 2021 critical review in the journalNature .
From there , the archeological picture gravel muddier . The older interlingual rendition of the tarradiddle originate in the 1920s and 1930s , when westerly archeologist describe sharp - edged , leaf - shaped stone lance decimal point near Clovis , New Mexico . The people who made them , now dub the Clovis masses , lived in North America between 13,000 and 12,700 years ago , base on a2020 analysisof bone , charcoal and plant corpse found at Clovis sites .
At the time , it was thought that the Clovis traveled across Beringia and then moved through an ice - free corridor , or " a gap between the continental ice weather sheet , " in what is now part of Alaska and Canada , Davis , who lead excavations at an ancient North American website inCooper ’s Ferry , Idaho , told Live Science .
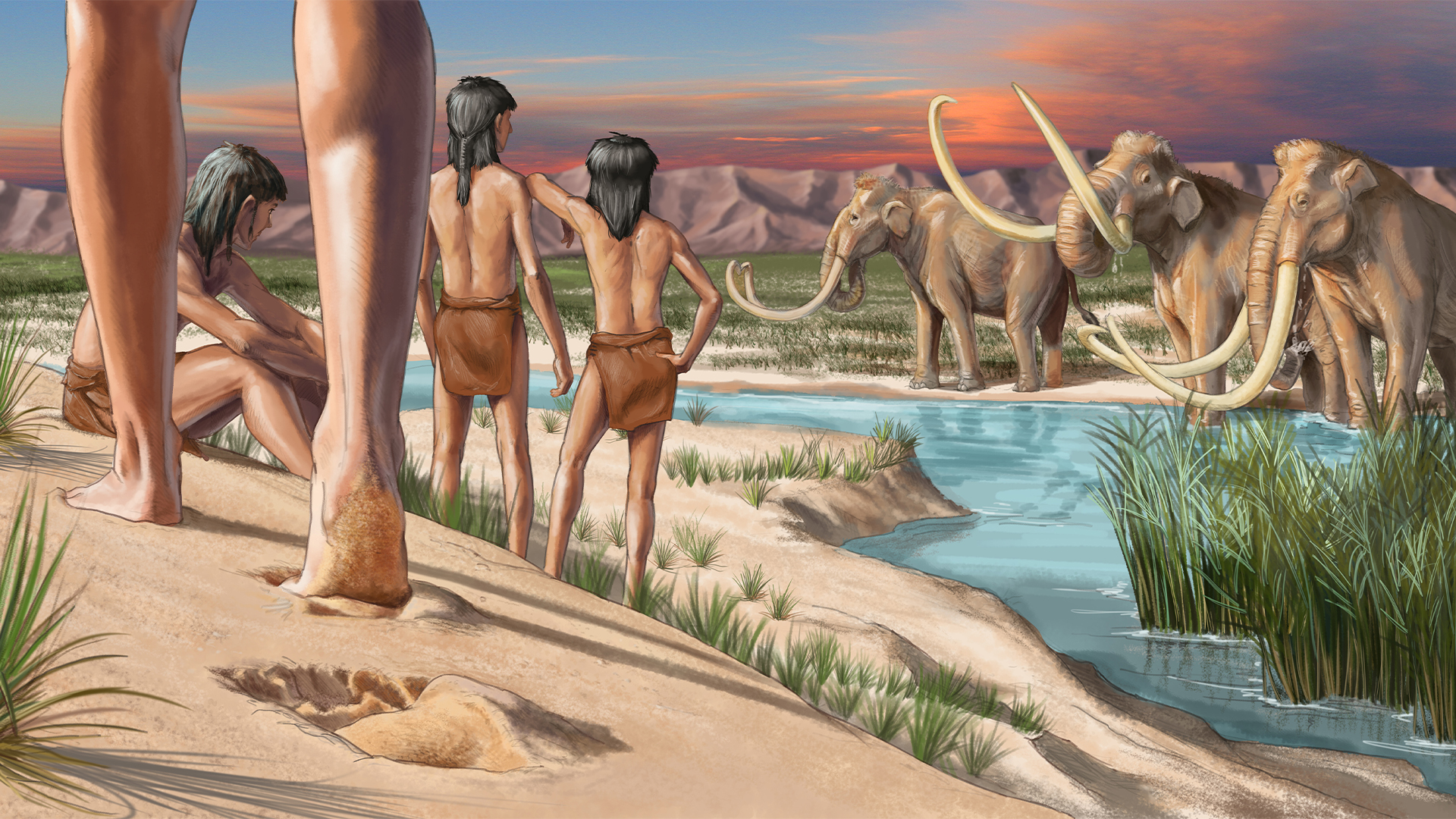

The first Americans, seen here eying mammoths at an ancient lake, descend from the Ancient North Siberians and a group of East Asians, who paired up around 20,000 to 23,000 years ago, genetic studies find.
" Once they exited , they spread chop-chop throughout the Americas , bearing a signature stone tool known as the Clovis fishgig level , " which was belike used tohunt megafauna , such as mammoth and bison , as well as smaller plot . For X , it was challenging to suggest the first Americans arrive any in the first place than 13,000 long time ago .
Slowly , however , new discoveries commence turn back the clock on the first Americans ' arrival . In1976 , researcher learned about the site of Monte Verde II in southerly Chile , which carbon 14 dating indicate was about14,550 year previous . It took decades for archeologist to accept the geological dating of Monte Verde , but soon , other sites also labor back the date of world ' reaching in the Americas .
ThePaisley Cavesin Oregon contain human coprolite , or fossilize poop , dating to about 14,500 class ago . Page - Ladson , a pre - Clovis site in Florida with stone puppet and mastodon castanets , dates to about14,550 yr ago . And Cooper ’s Ferry — a site that includes stone tools , animate being bones and charcoal — dates to around16,000 class ago . Then , in 2021 , scientist announced much more ancient traces of human occupation : fossilize footprints in White Sands , New Mexico dating to between21,000 and 23,000 years ago .
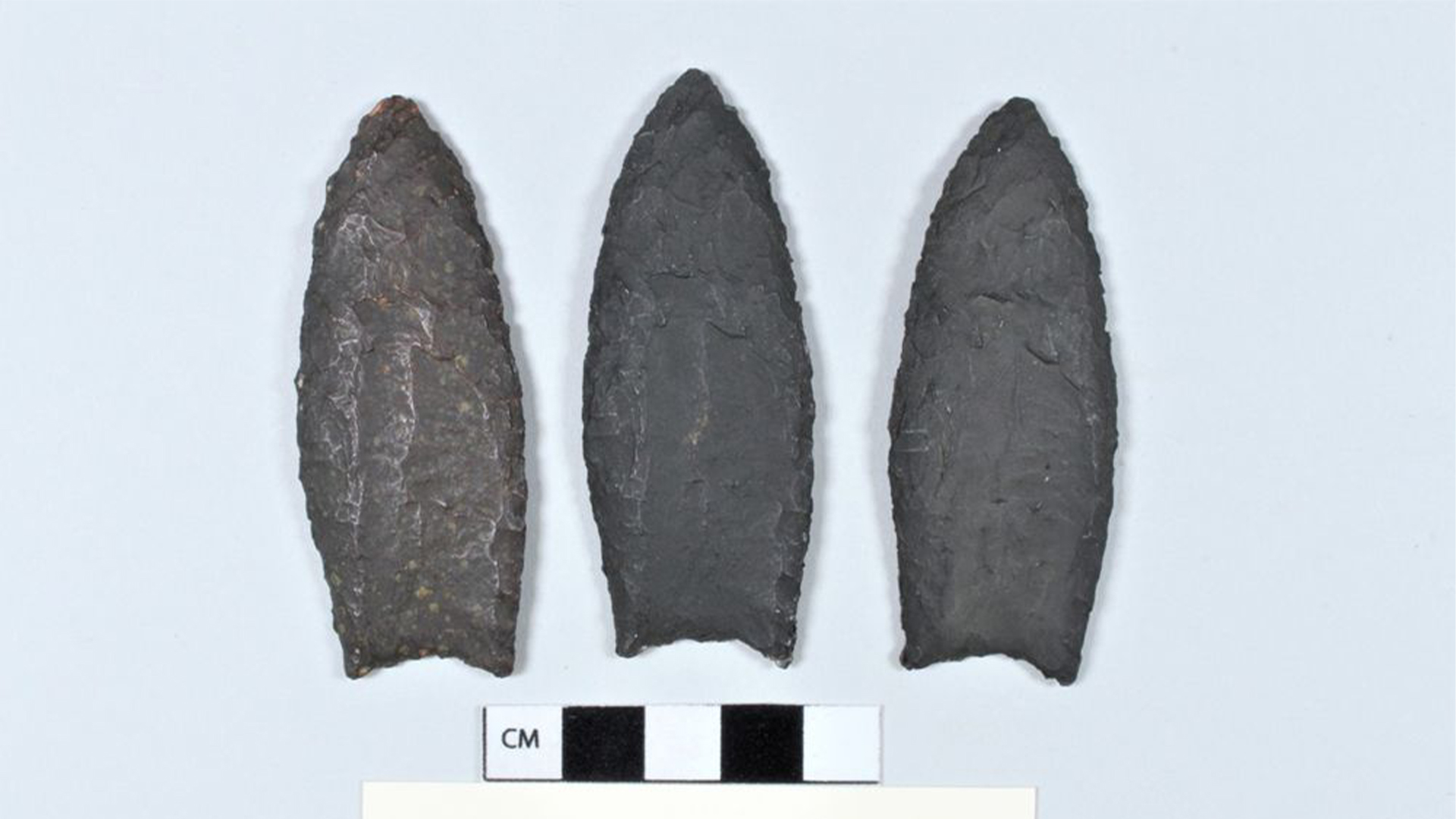

Three plaster casts of Clovis points; the originals were found in Connecticut in 1974. For decades, archaeologists thought that the Clovis were the first people to arrive in the Americas.
Related:13 of the oldest archeologic sites in the Americas
There are heaps more sites , although some of the older ones are controversial . For instance , some archeologist said 31,500 - year - oldrocks in a remote Mexican cavewere stone tools made by human being , but arebuttalargued that the rocks got their physical body by nature . Another site , in Brazil , holdsgiant sloth bonesthat may have been modified by humans at least 25,000 long time ago , but a narrow hole in the bones could have occur by nature , Davis tell Live Science . And50,000 - yr - old stone toolsat Pedra Furada in Brazil may have actually been made by capuchin monkeys , a 2022 sketch in the journalThe Holocenefound .
Sites such as White Sands and Cooper ’s Ferry have big implications for how the first the great unwashed arrived in the Americas . It ’s thought that the deoxyephedrine - spare corridor through North America did n’t fully open up untilabout 13,800 years ago . So if human race were in the Americas long before then , they in all likelihood traveled there along the Pacific seacoast .
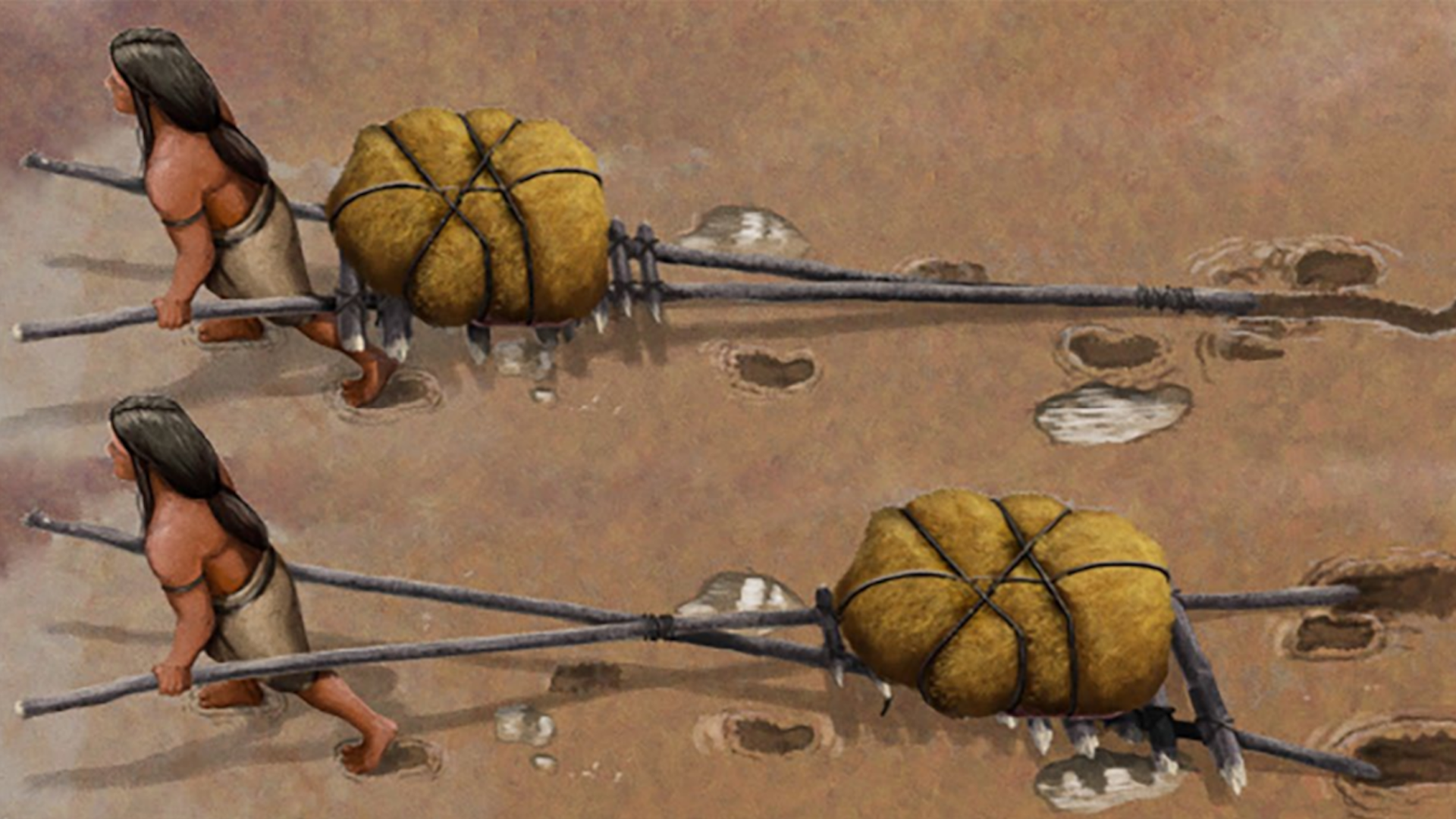
That coastal journeying could havebeen made by foot , by watercraft , or both . But no fogy or archeological evidence of this journey has been unearthed .
" We ’ve never found a boat ; we ’ve never institute a submerged land site out on a 16,000 - year - older shoreline in British Columbia , " Davis said .
Still , the coastal road is n’t flaky . " There ’s a lot of grounds that suggests that masses had the capability to do large sea crossings , " Davis said . For instance , hoi polloi used boats to get through Australia byaround 50,000 old age ago .

Despite these uncertainty , researchers have harness out some of the wildest theories . For case , the first Americans were n’t Pacific Islanders who boated across the open ocean , because people did n’t transmigrate to Polynesia untilaround 3,000 year agoand genetic grounds prove that the first Americans are onlyvery distantly concern to Polynesian .
too , genetic study reign out the " Solutrean hypothesis , " which posit that Paleolithic Europeans come across the Atlantic around 20,000 days ago , according to the 2021 Nature revue .
Genetic evidence
Geneticists meditate the first Americans be given to paint a more consistent picture than archaeologists do , in the main because they ’re using the same human clay and genetic datasets . Genetic analysis have chance that Ancient North Siberians and a group of East Asians paired up around 20,000 to 23,000 year ago , Jennifer Raff , an associate professor of anthropology at the University of Kansas and author of the book " Origin : A Genetic chronicle of the Americas " ( Twelve , 2022 ) , told Live Science .
Soon after , the universe burst into two genetically discrete group : one that remain in Siberia , and another , the basal American branch , which emerged around 20,000 to 21,000 year ago . Genetic data suggest the descendent of this basal American branch cross the Bering Land Bridge and became the first Americans .
interrelate : Did cats really vanish from North America for 7 million years ?

The basal American branch then divide into three groups : unsampled universe A ( UPopA ) , a mysterious " genetic " ghost that has " only been detected indirectly from the genomes " of the Mixe , of what is now Mexico , Raff said;Ancient Beringians , who have no known living descendants ; and Ancestral Native Americans ( ANA ) , whose descendant live on today .
All three of these groups finally made it to North America , but their deviate genetics indicate that they crossed in freestanding campaign , Meltzer and Willerslev wrote in the revaluation . Some did n’t make it very far ; The Ancient Beringians enter Alaska but never made it to the south of the continental deoxyephedrine sheet . The last known Ancient Beringian , known as the " Trail Creek individual , " died around9,000 class ago in Alaska .
Meanwhile , the ANA lineage undergo several splits , indicate that these citizenry settled in different areas of North America as they had limited gene flow between them , Raff say . There was one splitbetween 21,000 and 16,000 years agoand then a 2nd one around 15,700 age ago . During this 2nd split , the Northern Native Americans — whose living posterity let in loudspeaker of the Algonquian , Salishan , Tsimshian and Na - Dené speech communication groupings — break from the Southern Native Americans ( SNA ) , who spread southward and whosedescendants admit the Clovis , Raff said .

Every known living and deceased Indigenous " individual Confederate States of Canada belongs to SNA , " Raff enjoin .
What’s next?
Ideally , archaeologists would wish to find more web site from all of these branch , specially any clay that could explain the genetic science behind the people at White Sands between 23,000 and 21,000 year ago . " Right now I ’m really eager to find evidence that reconciles the comportment of the great unwashed at White Sands during the LGM … and the genetical signature tune of migration that seems to have occurred later , " Raff told Live Science in an e-mail . " As well , sites from Eastern Beringia that can serve us better understand the movement of people through that region . " But that ’s a intriguing task .
For one , when archaeologists do uncover exceptionally preserved internet site , they find that " up of 90 % of what people made and used was perishable . It ’s industrial plant fiber , it ’s feather , it ’s animal tegument and the alike , " saidEdward Jolie , an associate professor of anthropology at the University of Arizona and the associate conservator of ethnology at the Arizona State Museum .
Such organic artifact and remains typically continue well only in uncommon fate : extremely sozzled , dry or cold places , such as caves , rock shelters or water - logged land site , Jolie told Live Science .

— When did the Isthmus of Panama form between North and South America ?
— Was Manhattan really sold for $ 24 worth of beads and gewgaw ?
— What were the largest predators in North America ?

Even if there are other well - preserved organic - stuff - rich site waiting to be come upon , many scientists are n’t looking for them . Instead , they are stuck in a Clovis mentality , hunting for the gem tools ancient the great unwashed craft , saidMatthew Bennett , a prof of environmental and geographic sciences at Bournemouth University in the U.K. and a drawing card with the step archeological site at White Sands .
But grounds of these long - lost people can also be establish in the remains of the animals they butcher , the oxford gray they fire , the tools they crafted and the love ones they buried . Bennett and his colleagues are focused on the fossilised footprints these ancient individuals provide behind , and the athletic field wo n’t move forward until more archeologist concentrate on such evidence , Bennet tell Live Science .
" There are other types of grounds other than stone shaft , " he said .