When you buy through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
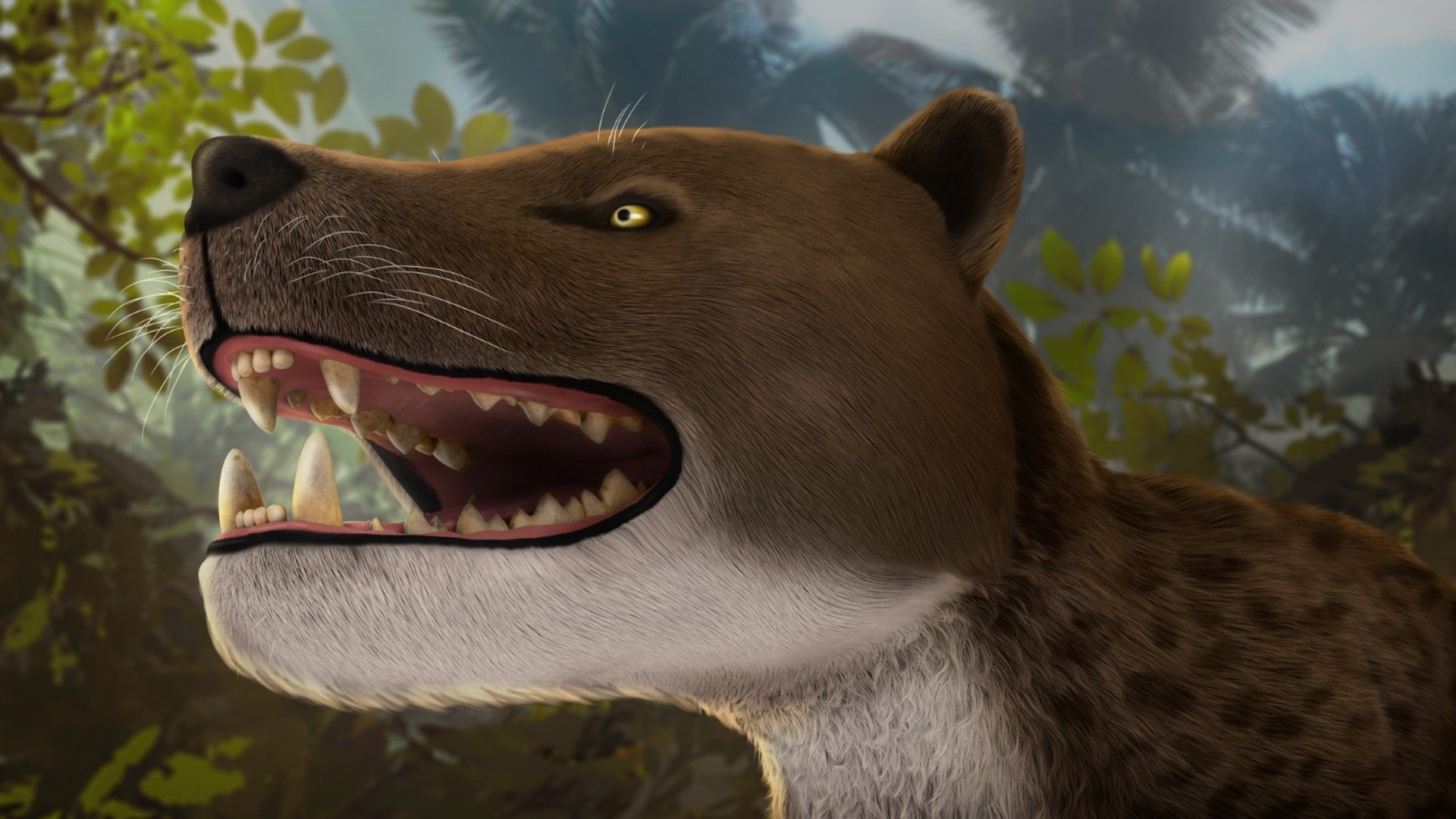
A " threat wolf " marine worm with a gargantuan jaw dominated the seas more than 500 million yr ago , finely preserved fossils show .
Scientists recently bring out the dodo of the newfound species of carnivorous worm — namedTimorebestia koprii , or " panic beast " — in northern Greenland and described it in a survey bring out Wednesday ( Jan. 3 ) in the journalScience Advances .
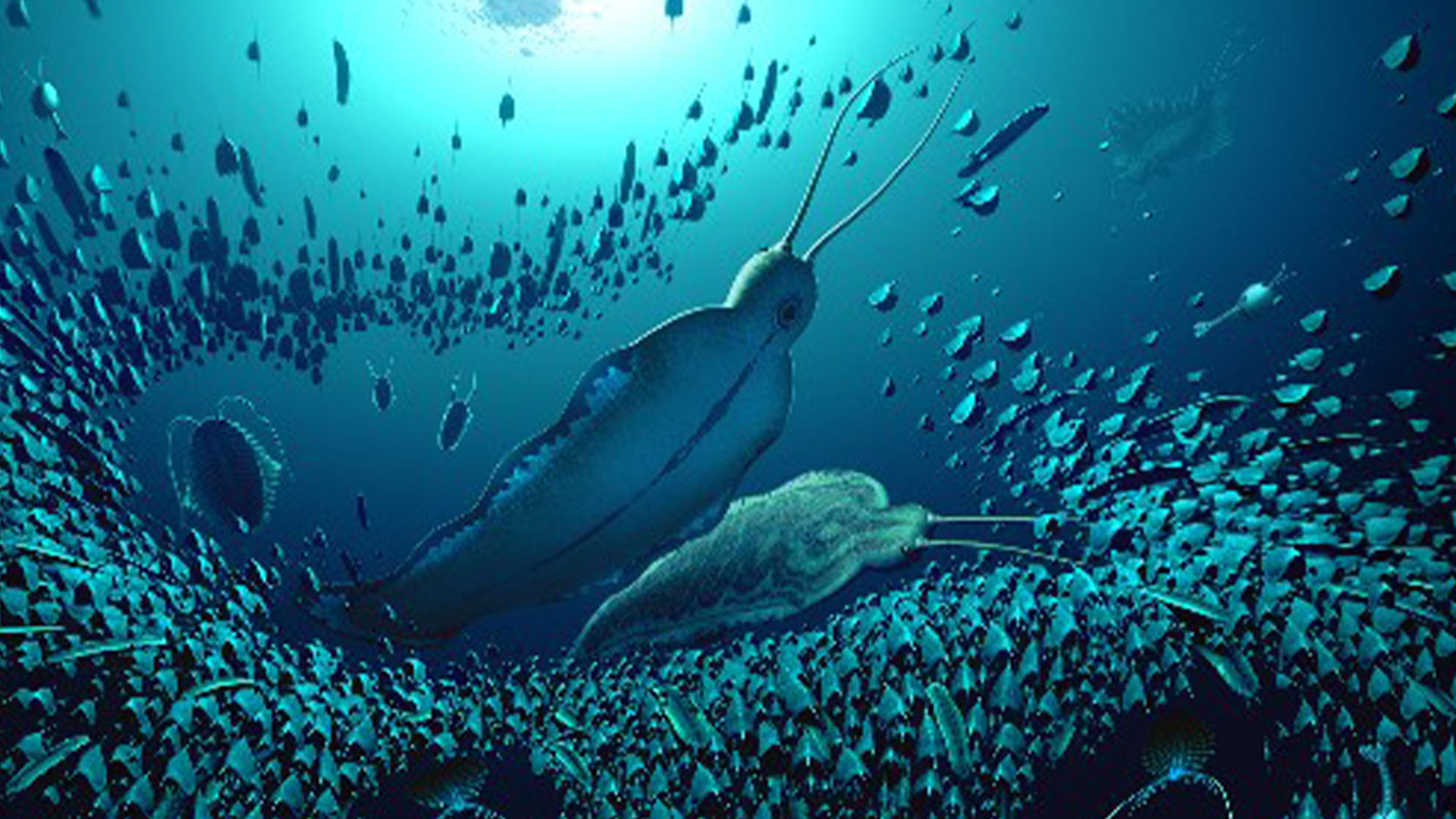
An illustration of the giant Cambrian predator that lived around 518 million years ago in what is now Greenland.
Existing during the early Welsh period ( 541 million to 485.4 million geezerhood ago ) , the predator had a run-in of fins flank each side of its consistency and a duo of foresightful antennae . It could produce to be up to 12 inches ( 30 centimeters ) long , making it one of the largest swim animals in its time period , harmonize to the discipline .
Related:500 million - yr - old worm with ' shuriken ' spike name after gigantic ' Dune ' sandworms
" Timorebestia were giants of their day and would have been close-fitting to the top of the solid food chain,“Jakob Vinther , a palaeontologist at the University of Bristol in England , saidin a argument . " That makes it equivalent in importance to some of the top carnivores in modern oceans , such as sharks and stamp , back in the Cambrian full point . "
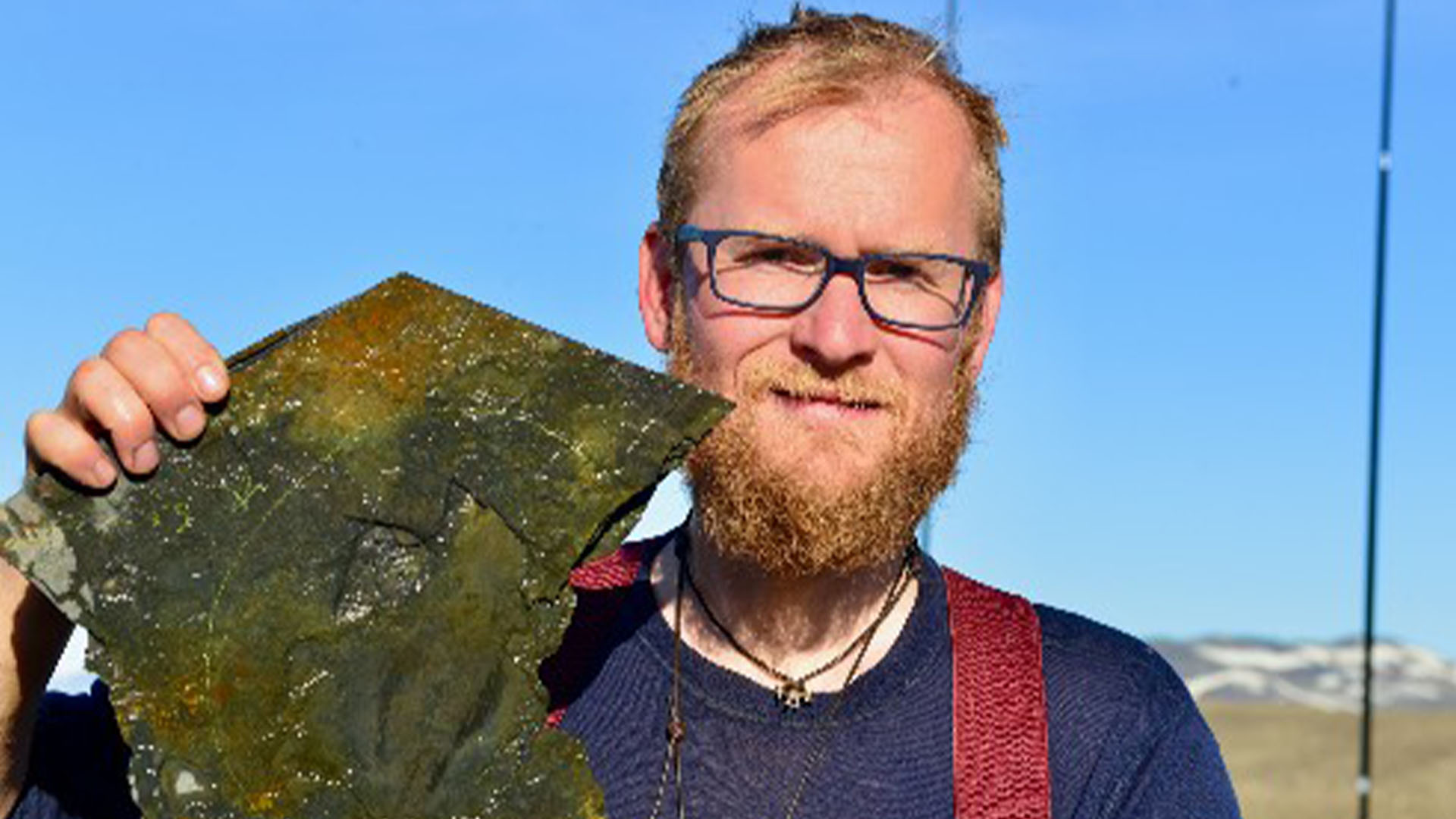

Paleontologist Jakob Vinther, at the Sirius Passet locality in 2017, shows the largest specimen ofTimorebestiaafter it was found.
Discovered in sediments get it on as the Sirius Passet formation of Greenland , some of theTimorebestiasamples were so well bear on that the scientist could take apart the worms ' digestive systems to determine some of what these carnivores were eating when they died . Most of the prey present in the worms ' guts were devil dog bivalved Cambrian arthropod known asIsoxys . The scientist even discovered one fossil louse with anIsoxysstill in its jaw part .
Isoxyswere " very coarse at Sirius Passet and had longsighted protective spines , pointing both send on and backwards , " to facilitate them avoid being eat , study co - authorMorten Lunde Nielsen , a former doctorial student at the University of Bristol , said in the statement . " However , they clearly did n’t wholly succeed in avoiding that fate , becauseTimorebestiamunched on them in outstanding quantity . "
— terminal moments of dinosaur and mammalian ’s epical ' mortal combat ' conflict uphold by volcanic extravasation
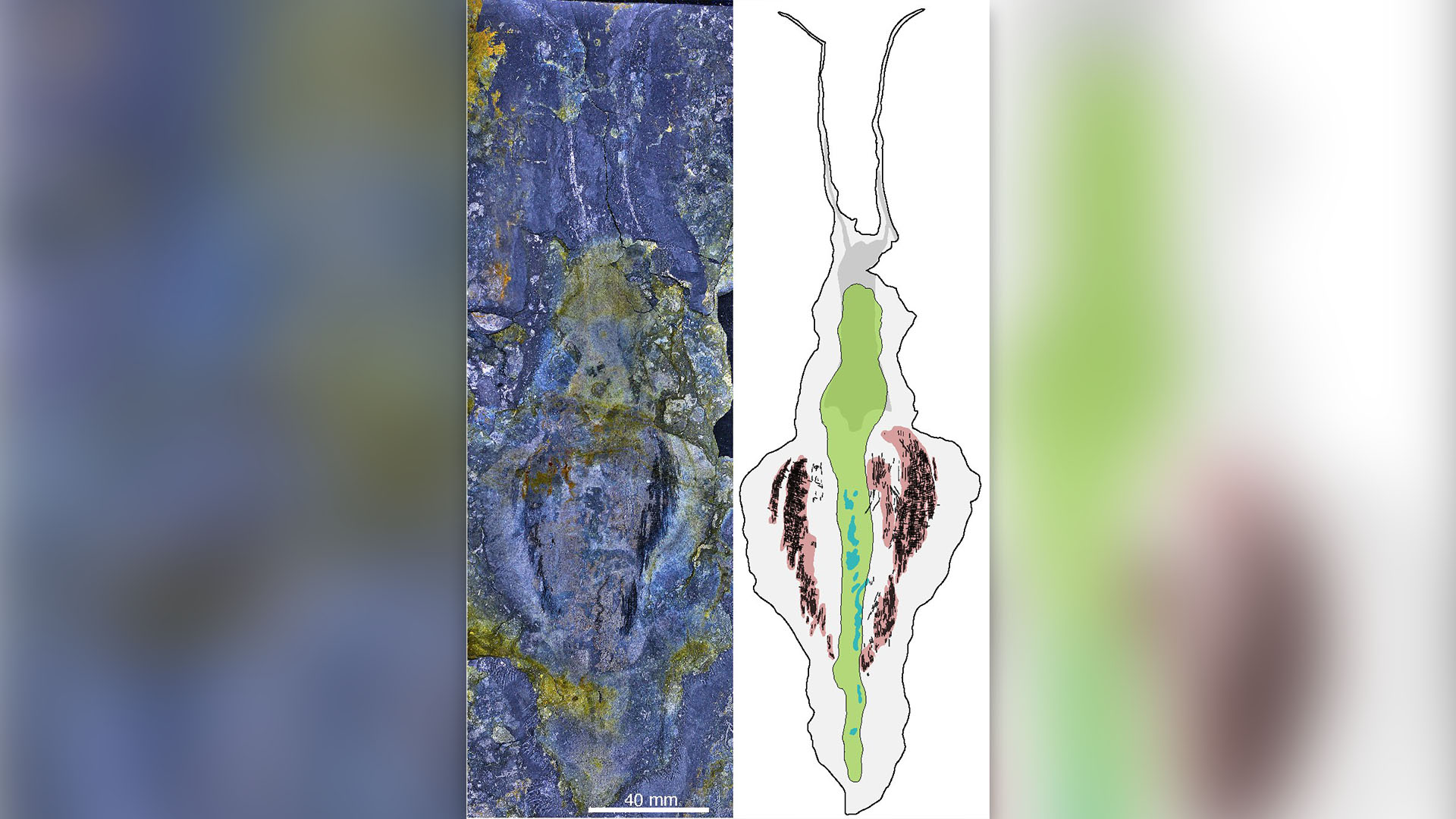
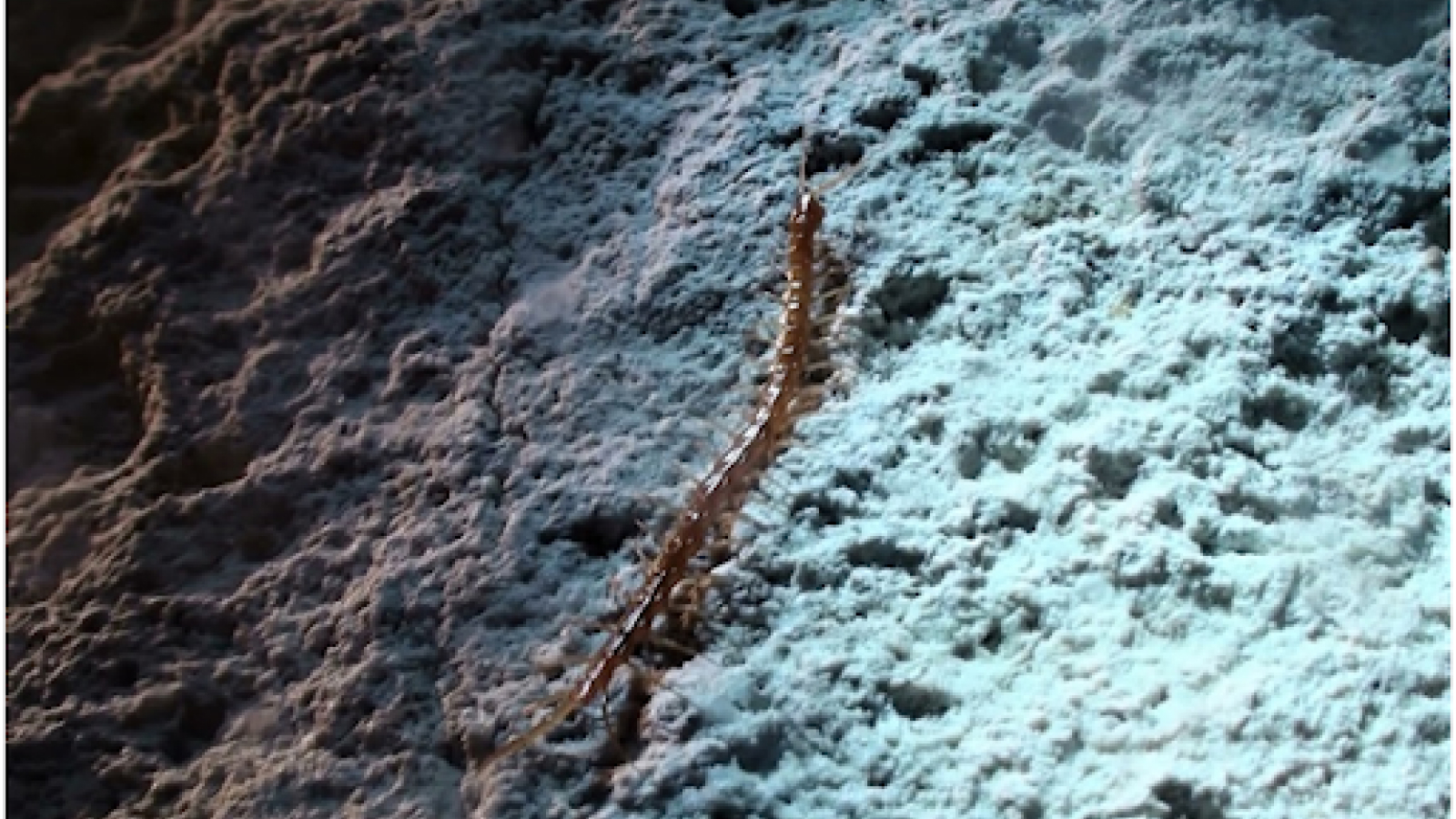
The fossil of a nearly 12-inches-longTimorebestia kopriinext to an illustration of it.
— 462 million - year - old fossilised optic and brains uncovered in ' secret ' Welsh fogy situation
— Trilobites had a hidden third oculus , novel fossils expose
By bombard theT. kopriisamples with a beam of electrons , the scientists revealed a mettle center on their belly known as the ventral ganglion . The comportment of this brass bundle , which in all likelihood helped the worms control their locomotory muscle , is unique to a living mathematical group of petite marine worms known as pointer worms , or arrowworm . This shows that theT. kopriiare distant relatives of modern - Clarence Day chaetognaths , the subject field authors wrote . However , one of the key differences between these ancient worms and living arrowworm is the locating of their jaws .

" Today , pointer worm have baleful bristle on the exterior of their oral sex for catching prey , whereasTimorebestiahas jaw inside its head , " work co - authorLuke Parry , a paleobiologist at Oxford University , said in the program line . " Timorebestiaand other dodo like it put up linkup between closely related organisms that today appear very different . "
















