When you purchase through links on our site , we may take in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
A first - of - its - kind , exalt map has revealed fresh secrets about a mysterious , flower " zombie star " ambuscade in the remainder of a supernova that light up Earth ’s sky more than 800 years ago . The " 3D motion picture " testify that the remains of the starring plosion are unusually wonky and are still exploding at a constant speed .
In 1181 , stargazer inChinaand Japan spot a new champion shining near the constellation Cassiopeia . Historical record of this " guest star " show that the bright billet persisted for around six months , from August of that year until February 1182 .
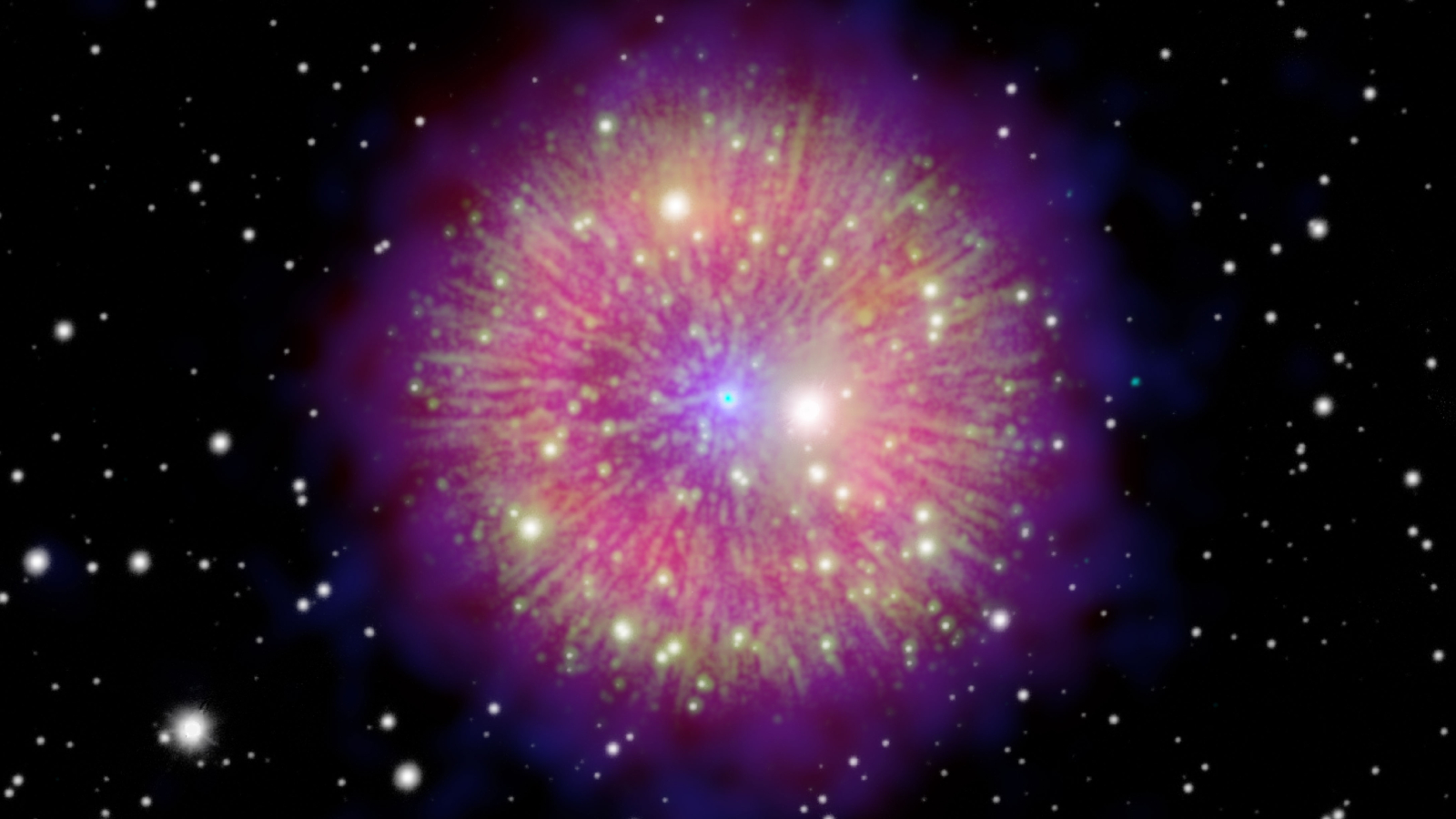

The nebula Pa 30 is the remnant of a powerful supernova that created a “guest star” spotted by Astronomers in the 12th Century. At its heart lies an undead white dwarf star.
Today , researchers know that the starring imposter was actually a brawny supernova , or exploding ace , known as SN 1181 . However , its origin remain a closed book until 2021 , when astronomersfinally confirmed that the supernova came from the nebula Pa 30 — a giant cloud of gas wider than our entiresolar arrangement .
Previous observations of Pa 30 revealed a white dwarf star at the center of the nebula . The superdense object is all that stay of the exploding star that lit up the night sky 843 year ago . It burn intensely at around 360,000 grade Fahrenheit ( 200,000 degree Celsius ) , making itone of the hottest stars in the known universe . usually , break loose wizard get completely ripped asunder when they go supernova , which makes this type of remnant a peculiarity .
Related : James Webb telescope watches ancient supernova instant replay 3 times — and confirms something is gravely haywire in our sympathy of the universe
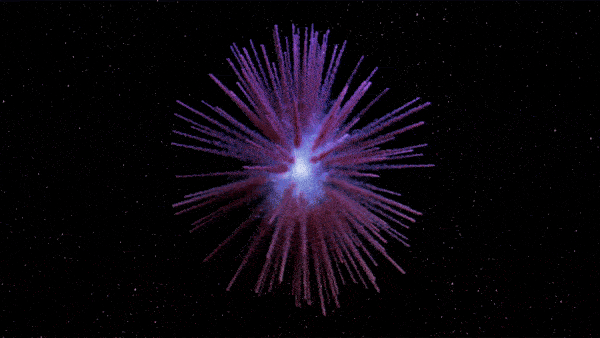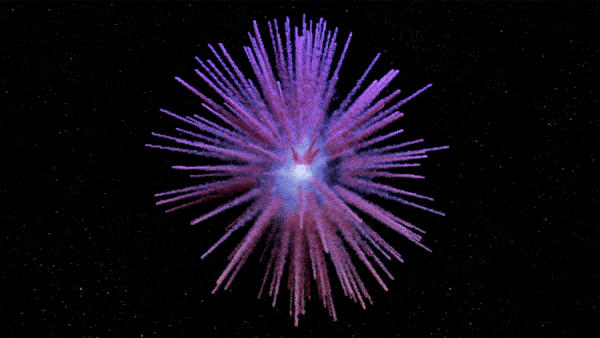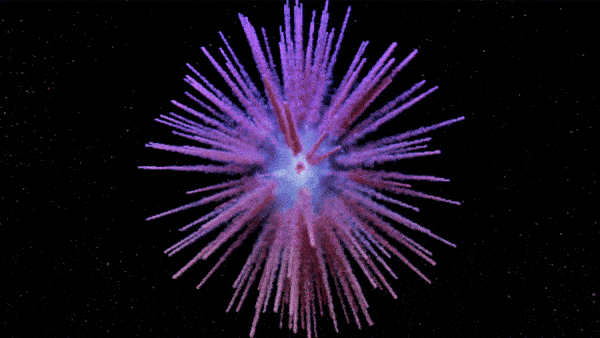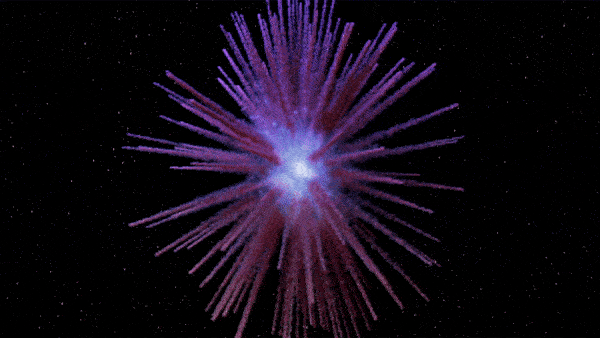
The new map of Pa 30 shows long dandelion-like petals extending outward from the zombie star as matter continually explodes from the remnant.
In a new study , released Thursday ( Oct. 24 ) inThe Astrophysical Journal Letters , astronomers created a new map of Pa 30 using the Keck Cosmic Web Imager ( KCWI ) — a spectrograph place near the acme of Hawaii ’s Mauna Kea volcano .
The resulting figure was extremely elaborated , capture heavy filament resemble " the petals of a blowball " extend from the white nanus to the edge of the nebula , the researchers wrote in a statement sent to Live Science .
By dissect how the light given off by Pa 30 has shifted over fourth dimension , the KCWI also retrace how the nebula has convert shape , thus allowing the investigator to simulate a mini " 3D motion-picture show " of the nebula ’s chronicle . This is the first fourth dimension this has ever been done with a supernova leftover , the researchers write .
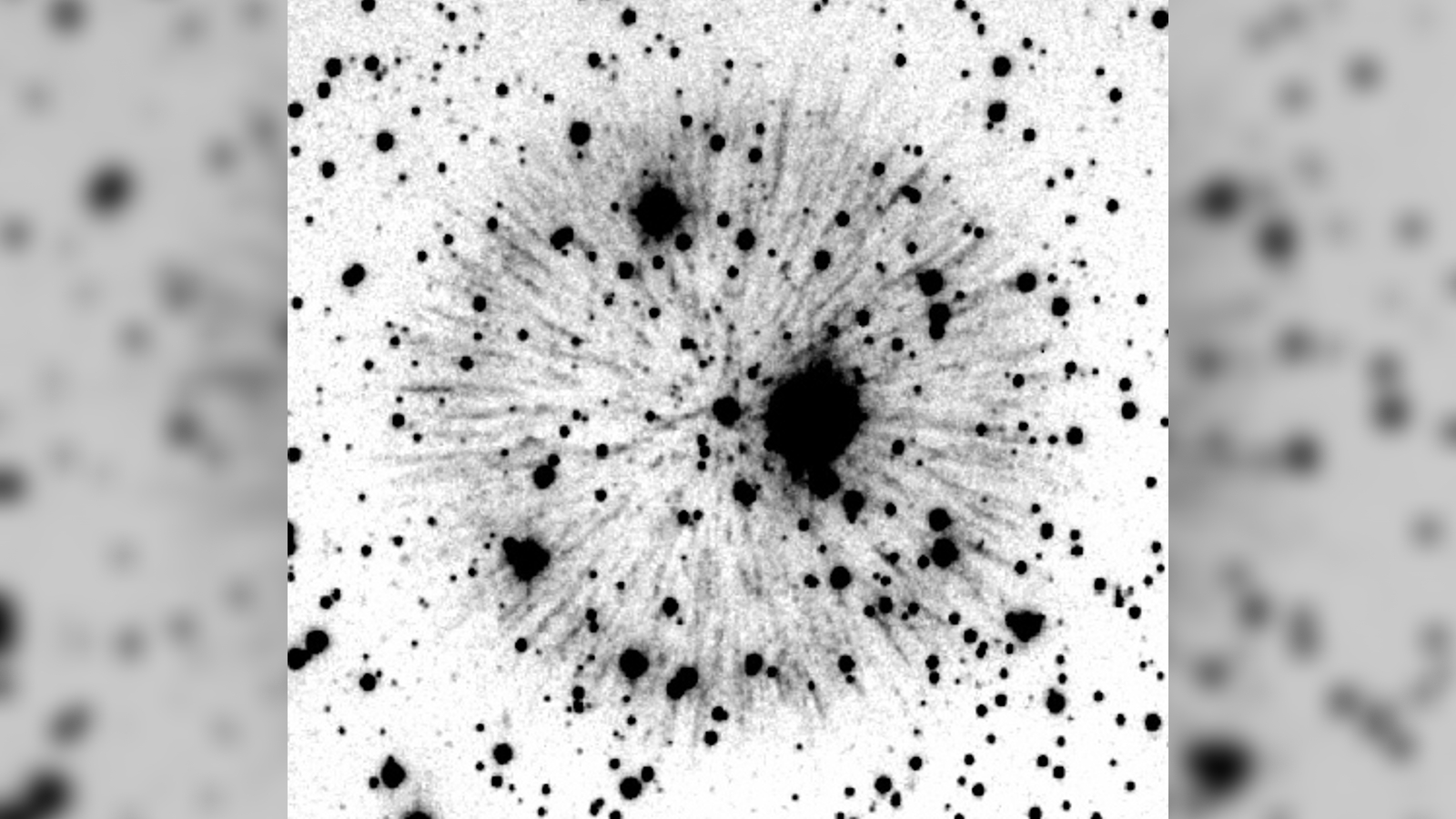

Pa 30 is unusually asymmetrical and researchers have no clear idea why.
One of the cardinal takeaways from the animation is that the nebula is expanding at around 2.2 million miles per hour ( 3.5 million km / h ) , which is around the same pep pill it would have throw out debris during the initial supernova . " This intend that the ejected cloth has not been slack down , or pelt along up , since the burst , " cogitation jumper lead authorTim Cunningham , an astrophysicist at the Harvard and Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics , say in the statement .
Using this rate of enlargement to look back in time , the squad was able to " nail the explosion to almost incisively the yr 1181 , " which provide further proof that the guest star observed by astronomers back then came from Pa 30 , Cunningham added .
— James Webb telescope discovers most distant supernova ever seen

— stargazer observe unexampled social class of cosmic explosion smart than 100 billion sun
— A nearby supernova virtually blew our solar system to bits 4 billion years ago
The function also shows that Pa 30 is surprisingly asymmetrical compared with similar supernova end . There is no light explanation for why the nebula would have grown wonky since the supernova , suggest the dissymmetry was due to the initial burst , the researchers wrote . However , it is ill-defined how this happen .

The new function " tells us a lot about a unique cosmic event that our root observed centuries ago , " bailiwick carbon monoxide - authorIlaria Caiazzo , a star astrophysicist at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria , articulate in the statement . " But it also raises new motion and sets unexampled challenge for stargazer to tackle next . "
Gamma - ray bursts give away largest bodily structure in the population is self-aggrandizing and close to Earth than we knew : ' The jury is still out on what it all means . '
Universe may revolve once every 500 billion year — and that could resolve a trouble that endanger to weaken cosmology

Was it a endocarp tool or just a rock and roll ? An archeologist explains how scientist can tell the difference of opinion







