When you buy through links on our site , we may gain an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it works .
Antibiotics treat infections triggered by bacteria — but bacteria can evolve to resist these essential drug . Over meter , the abuse of antibiotics has rapidly accelerated the spread of such insubordinate germs , and widely used antibiotics are becoming less effective .
So until substitute drug to antibiotic are developed , how can we slow the rise of bacterial " Bemisia tabaci " ? The answer : Antibiotic stewardship .
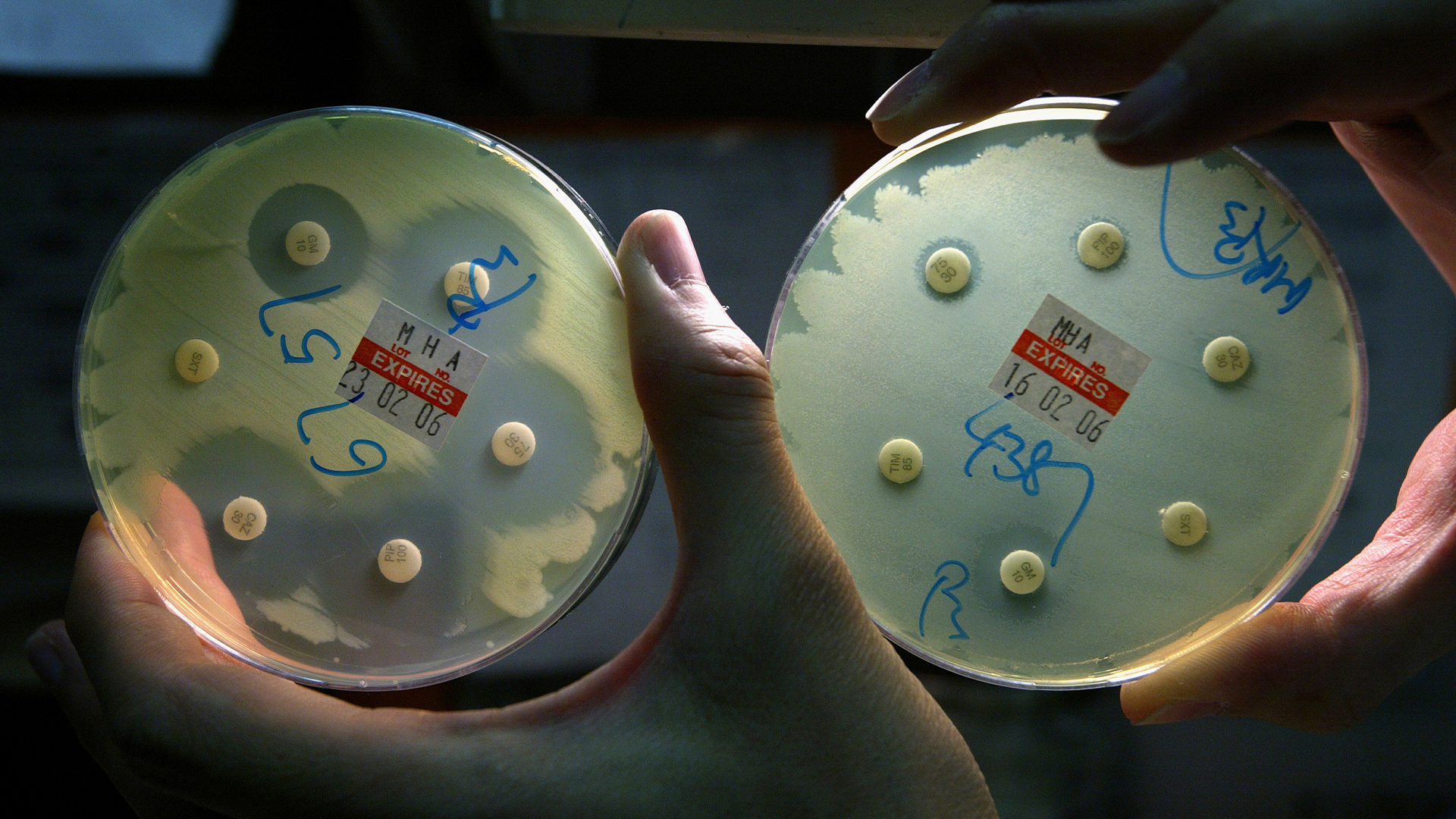
The bacteria on the left show no resistance to the antibiotics in the lab dish, but the bacteria on the right show resistance, as indicated by their growing right next to the drug without issue.
Antibiotic stewardship aim to curb the abuse of antibiotic drug that drive bacteria to develop resistance in the first berth . It ask rig vindicated principles for how doctors prescribe antibiotics and how patient role use them in dissimilar configurations , such as hospitals and nursing homes , and closely track whether those principles are follow , according to theCenters for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC ) .
The finish is to dissuade physician from prescribing antibiotics for viral contagion , which the drugs ca n’t plow , or give a affected role a " broad - spectrum " antibiotic open of killing many bacteria when a " minute - spectrum " drug would work , for example . across-the-board - spectrum antibiotic pose a particular problem because they push a broad range of bacteria in the organic structure to develop impedance . And once they clean up newtools of resistance , the drug - resistant bugs caneasily share themwith a hatful of additional bacteria .
colligate : unsafe ' superbug ' are a growing menace , and antibiotic drug ca n’t stop their rising . What can ?

" When we give hatful of antibiotics , or we give more broad antibiotic than are necessary , then you will breed more antibiotic underground in a patient and in our populations,“Dr . Shruti Gohil , a lead investigator of fourINSPIRE - ASP Trials — federally fund research aim at curbing the overutilisation of antibiotic in hospitals — evidence Live Science .
The hope is that , by reigning in the misuse of antibiotic , we can trim down the rate that people get infect with multidrug - resistant organism ( MDROs ) , while also reducing the opportunities for new MDROs to come forth and spread between people .
" That would be the metric we would all want to see fall out , is a reversal of the prevalence of MDROs , " said Gohil , who is also the associate medical director of the Epidemiology and Infection Prevention political platform at the University of California , Irvine School of Medicine .
How do we do that ? There are a wide grasp of strategies .
One core strategy , of course , is to educate clinicians about how to apply antibiotics appropriately , Gohil said . And to two-fold - check physicians ' work , hospital can expend " deescalation , " which involves agree a patient role ’s initial prescription to see whether a narrow-minded , shorter or lowly - dose antibiotic drug line would be more appropriate . Adjustments are made quickly if a unlike antibiotic is deemed to be a better pick than the one a doctor first picked . " That is presently the mainstay of antibiotic stewardship in the hospital , " she said .
Another common scheme in U.S. hospitals is to provide counselling on the best antibiotics to use for dissimilar contagion within the electronic system that doctors apply to consecrate drugs . hospital may also confine memory access to tops - broad - spectrum drug , call for doctors to seek extra approval to apply them , she added .

Speeding up diagnosis is another mode to help doctor pick the right antibiotic , or skip one altogether for viral infections . When faced with a crazy patient with a yet - undetermined diagnosis , clinicians often " err on the side of caution " by prescribing antibiotic drug that may not be necessitate , Gohil said . " That ’s one of the thing that hobbles us when we ’re trying to make decision , is that uncertainty . "
link up : Could an antibiotic taken after unprotected sex prevent STIs ? What to know about doxy - PEP .
The challenge is that even the very fastest symptomatic tests for bacterial infection take hours to deliver a upshot , she noted . And except in the pillow slip of bloodstream infections , those initial results can only say if a special microbe is present in the trunk , not if it ’s repel the affected role ’s illness . To pass on a definitive diagnosis , doctors must combine these test solution with what they can glean from the patient ’s symptom and extra tests , such as chest X - rays .

In the hereafter , fast diagnostics that give birth result at the bedside could ease this summons , but they ’re far off . " I would not say it ’s unsufferable — I do n’t call up it ’s imminent , " Gohil say .
Beyond hospitals , clinician atnursing homesand outpatient clinics , such as primary care practices anddentist offices , postulate similar education about and regulatory supervising over their purpose of antibiotic drug . Andstate and local wellness departmentsplay a key role in coordinating and influence those movement .
— Scientists cook up ' physique - shifting ' antibiotic to fight deadly superbugs

— What is penicillin , and how was it discovered ?
— bacterium hiding in indoor junk could pass around antibiotic resistivity
item-by-item patient have a role to toy as well — for example , by taking antibiotics as prescribed , not skipping dot and not taking antibiotics originally prescribed to other people , the CDC propose .

" Everybody who has bacterial resistance , for example , can shed and spread their bacteria . So by reduce individual risk , you anticipate that you will strike down the overall population level risk , " Gohil said of antibiotic stewardship programs . " By reducing antibiotic press on a give human , you reduce the likelihood that … that immunity will emerge . "
And beyond the doctor ’s office , antibiotic stewardship is alsocritical in animal factory farm , because MDROs that arise in food - bring out animals can make their way to human .











