When you purchase through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Stone Age people in Belgium were track down with spear - thrower more than 30,000 year ago — the earliest have it away evidence of such a weapon in Europe , a raw discipline suggests .
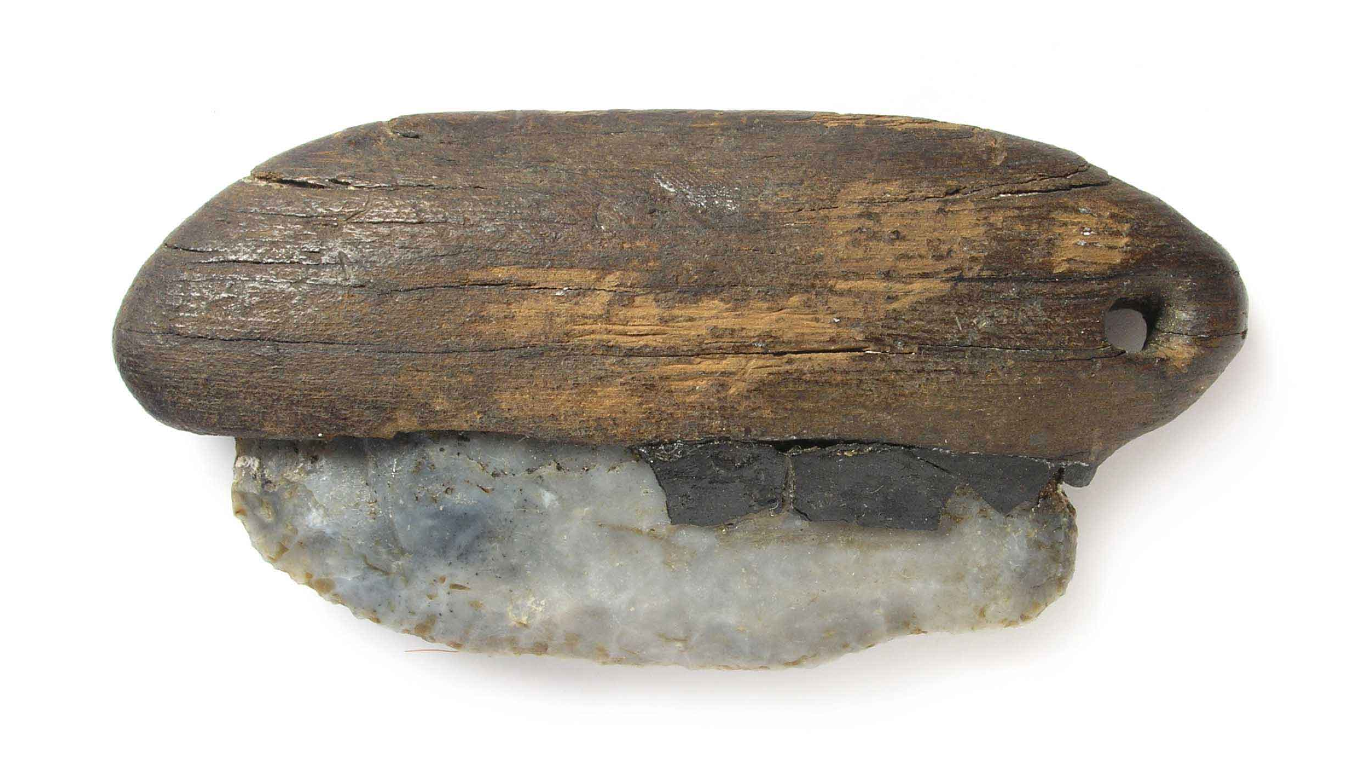
After investigate more than 300 antecedently love Flint River artifact bump at the Maisières - Canal archaeological site in southern Belgium , a research squad documented that 17 have minuscule fractures that betoken they were points for rocket of some type .
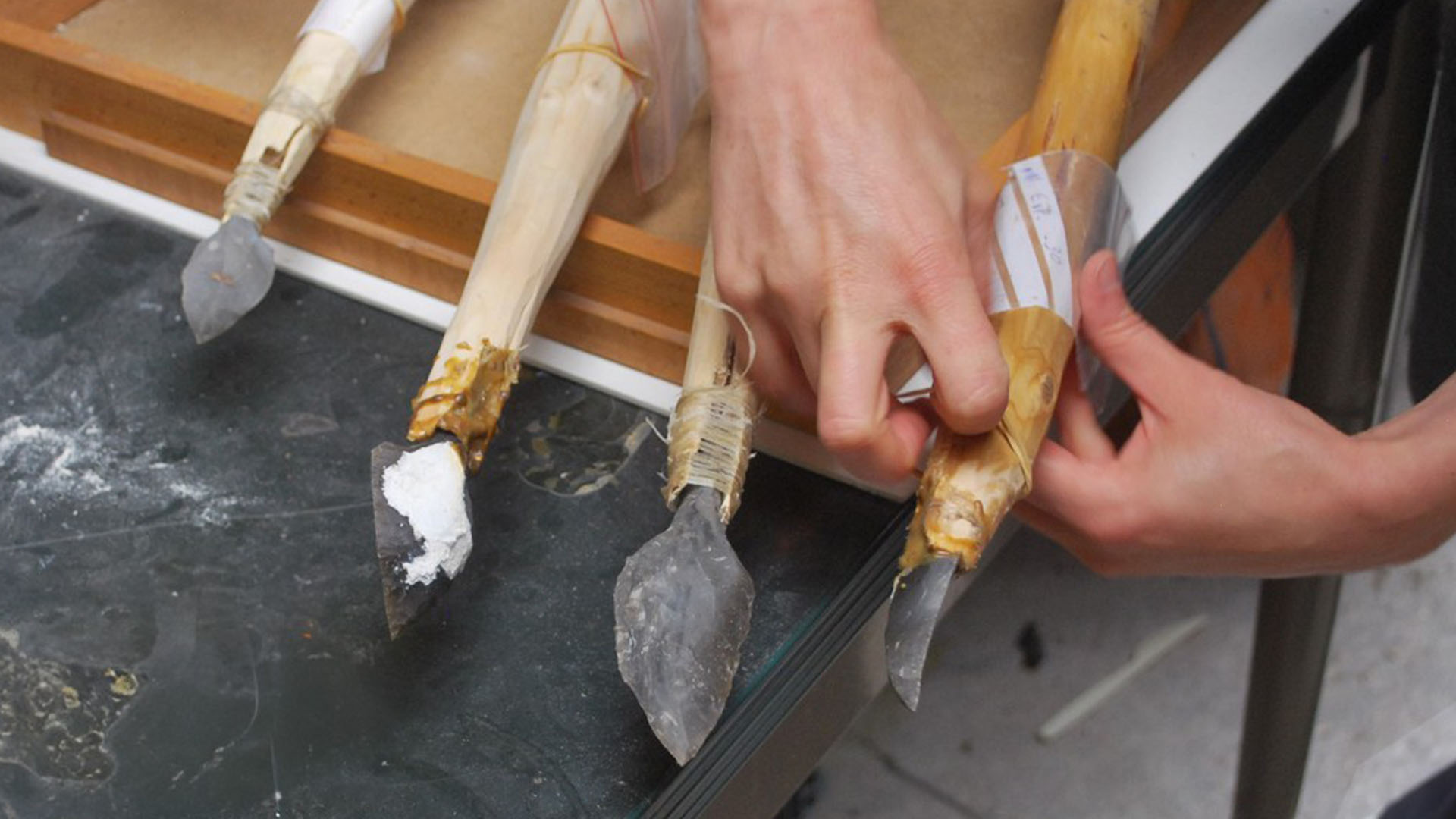

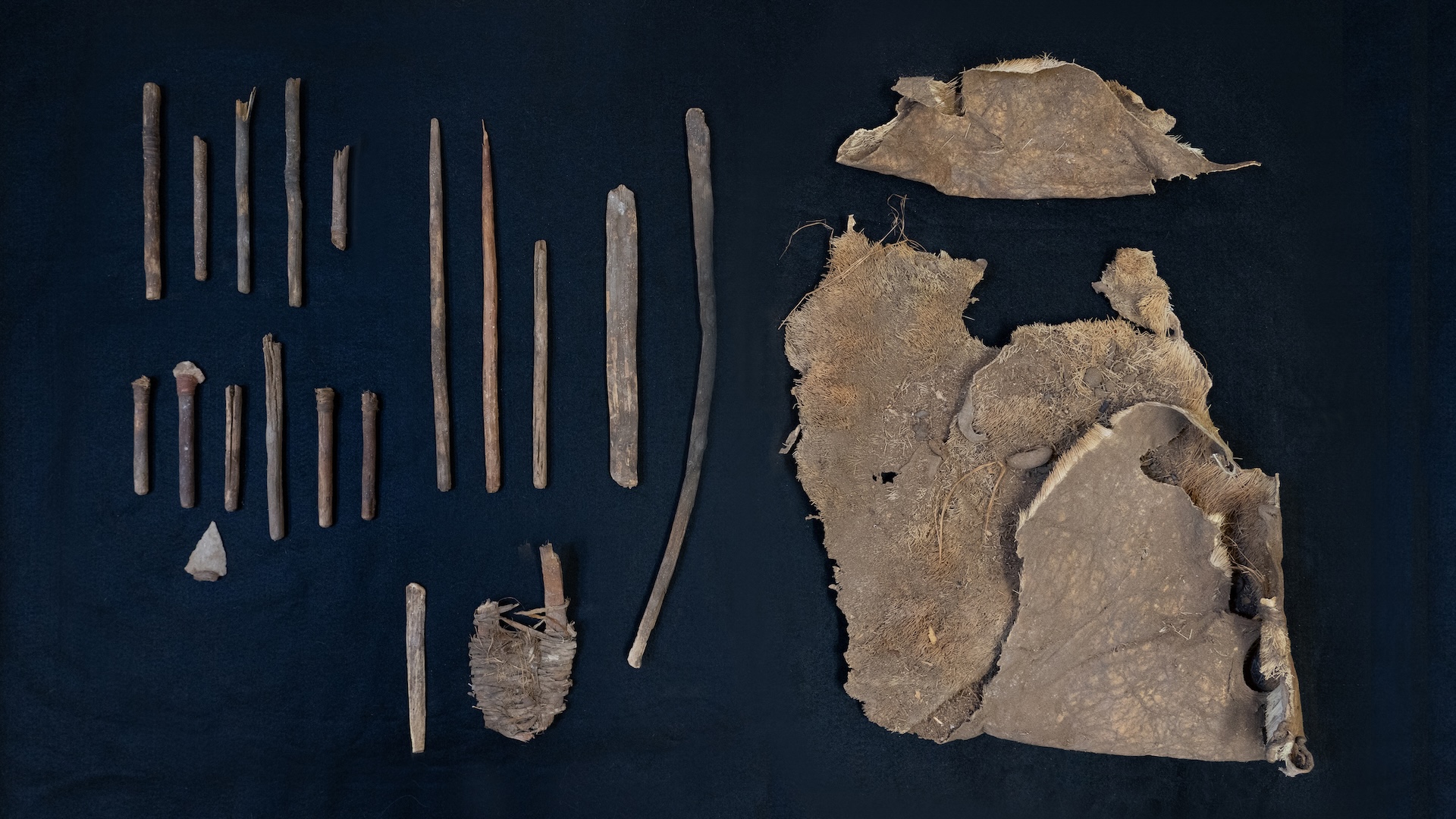
The researchers made reconstructions of Stone Age projectile weapons and threw them at targets containing ballistic gel and bones to determine the pattern of fractures each weapon caused.
" My conviction is that all of them are from fishgig - thrower , " subject first authorJustin Coppe , an archeologist at the University of Liège in Belgium , secernate Live Science .
allot to the study , the Flint River head from the Maisières - Canal site , near the town of Mons and the Haine river , show that prehistorical mass were hunting there with spear - thrower between 28,000 and 31,000 years ago ; and that they manifestly favour these to other types of projectile weapon system , such as throw spears ( javelins ) and bows and arrows , he tell .
However , not everyone is pleased with the research , arguing that it brush off the results of other studies on the topic .

Experiments with reconstructed weapons — such as the spear-thrower shown here — revealed that different projectile weapons cause distinctive fractures in their points.
link : Weapons chip at from human bone issue forth from drowned domain bridge between UK and Europe
Until now , the former direct grounds for shaft - thrower in Europe were thought to be stone points from Placard Cave in southwesterly France that date to between 17,000 and 18,000 years ago , the authors wrote . ( The oldest evidence for bow and arrows in Europe , however , isfrom 54,000 years ago . )
The Modern survey on theMaisières - Canal flint artefact , published Oct. 25 in the journalScientific Reports , " pushes back the escort for spear - thrower use in Europe … by over 10,000 years , " the authors indite .
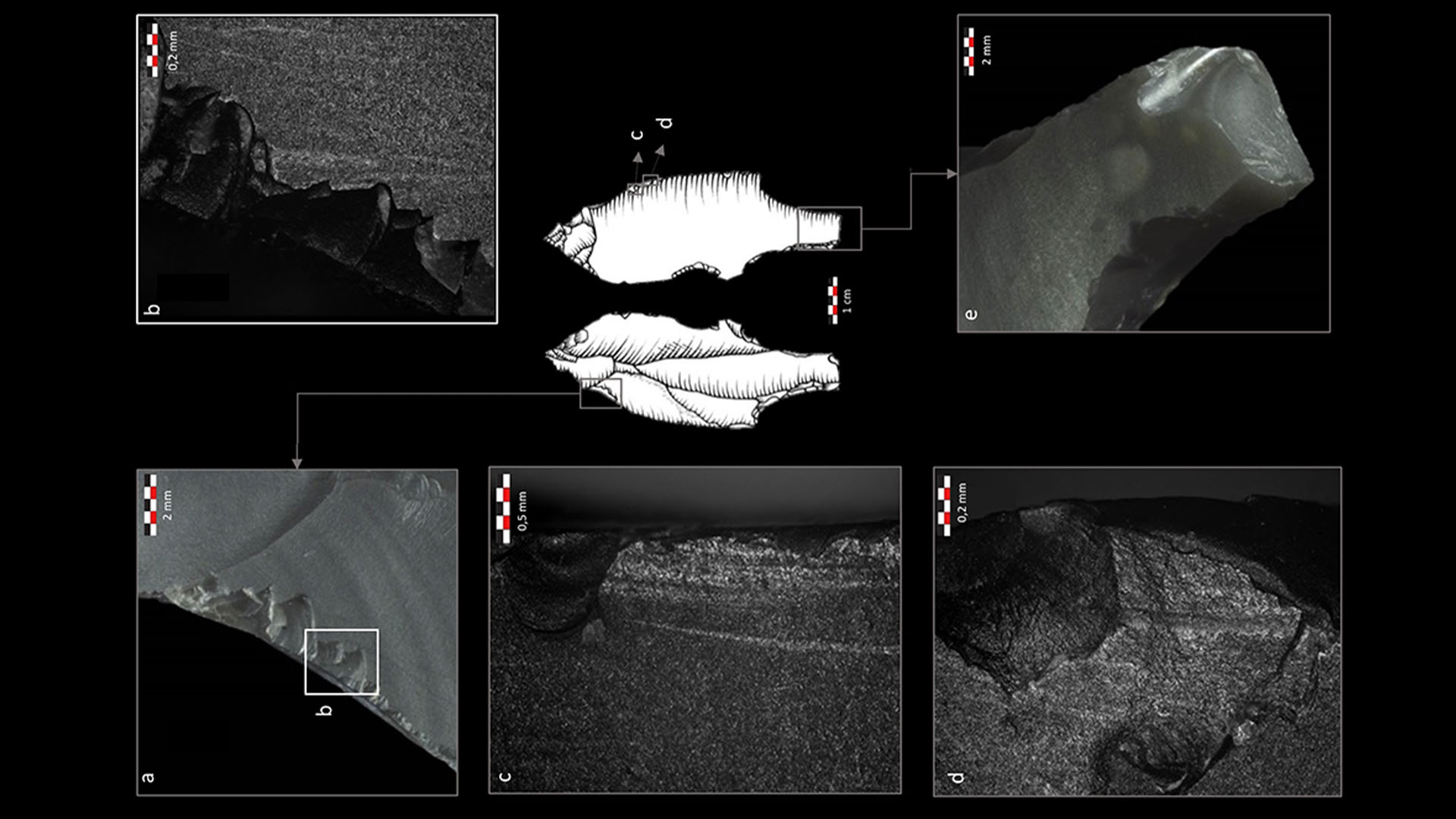
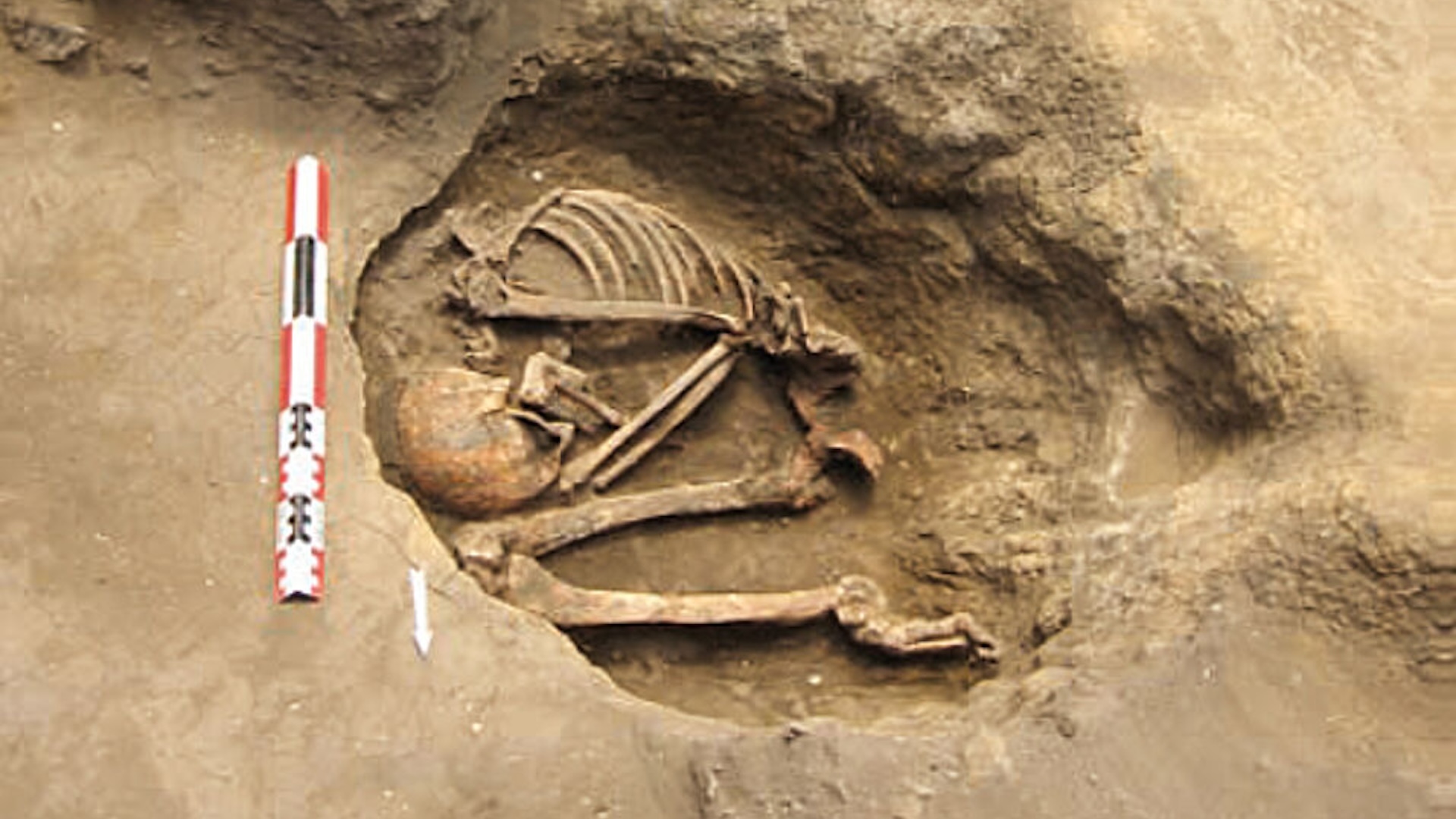
The researchers studied the patterns of fractures on the 31,000 year-old points from the Maisières-Canal archaeological site to determine what type of projectile weapon they were used in.
Spear-throwers
fishgig - throwers , or atlatls , are rarely used these day because most hunter use firearms , but they wereonce a rough-cut weapon . They consist of a shaft with a hook shot or cup on the end that uses leveraging to propel a spear - shaped flit at high speed . The darts are heavy than arrow , which means they can do more price when they hit , but they are smaller and much quicker than cast gig .
Coppe explained that the throwing and flit shafts may have been made of woods but have since rotted away . Only the flint projectile points remain .
Coppe and his colleagues at the University of Liège’sTraceo Labstudied the ancient points by eye and with microscopes to determine their " archaeological fracture signaling . " Experiments with reconstructed weapons had shown that each projectile weapon character — thrown spear , atlatl flit and arrow — bent in unlike ways during flying , which resulted in distinctive fractures , he explicate .

By comparing their fractures to those on the reconstructed artillery , the research worker mold that all 17 of the Maisières - Canal flint points had belike derive from fizgig - ceramicist , he said .
Stone Age hunting
The development of projectile weapons would have had meaning consequences for human evolution because it modify the dieting and societal organization of prehistoric group , Coppe mention . But he cautioned that the pick of projectile weapons may have been based on traditional hunt method rather than on any weapon ’s superiority . Bows and arrows , for example , were ordinarily used by alone hunting watch , but throw spears be given to be favored by hunter in bigger groups , he said .
— 150 - year - honest-to-god mystery story of unusual half - circles from palaeolithic site in France finally solved
— pasty orange coat on a 6,000 - year - old Yukon flit come from a beaver ’s anal sac

Ludovic Slimak , an archeologist at France ’s National Center for Scientific Research ( CNRS ) who was n’t necessitate in the subject area , said the inquiry showed that rocket weapon were old-hat amongHomo sapiensin Europe during the Upper Paleolithic flow , after about 50,000 age ago .
But he was concerned that the author of the report were not familiar enough with or dismiss several other scientific subject on the theme . For case , it was not the cause — as stated in the new field of study — that other studies around the world had considered only the size of it of the item , and not their fracture patterns , he said .
The novel study was fund by the European Research Council and Belgium ’s National Fund for Scientific Research ( FNRS ) .














