When you purchase through link on our site , we may make an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
A temperamental black hole is serve scientist learn more about how galaxies acquire . In a novel subject field print Feb. 1 inThe Astrophysical Journal Letters , researchers key out how an outburst from a remote shameful hole changed its astronomical landscape — and how similar activity may have shaped our own galaxy .
Markarian 817 is a whorled extragalactic nebula located some 430 million clean - years from Earth . Like our galaxy , theMilky Way , it has a massiveblack holeat its center . Such objects assist hold galaxy together , exerting enough graveness on stars , rubble and other material to keep everything slowly orbiting around a key point — and now and then bolt up some of that matter when it falls too close to the black hole ’s outcome skyline . But late , researchers spotted Markarian 817 ’s black pickle doing something unexpected .
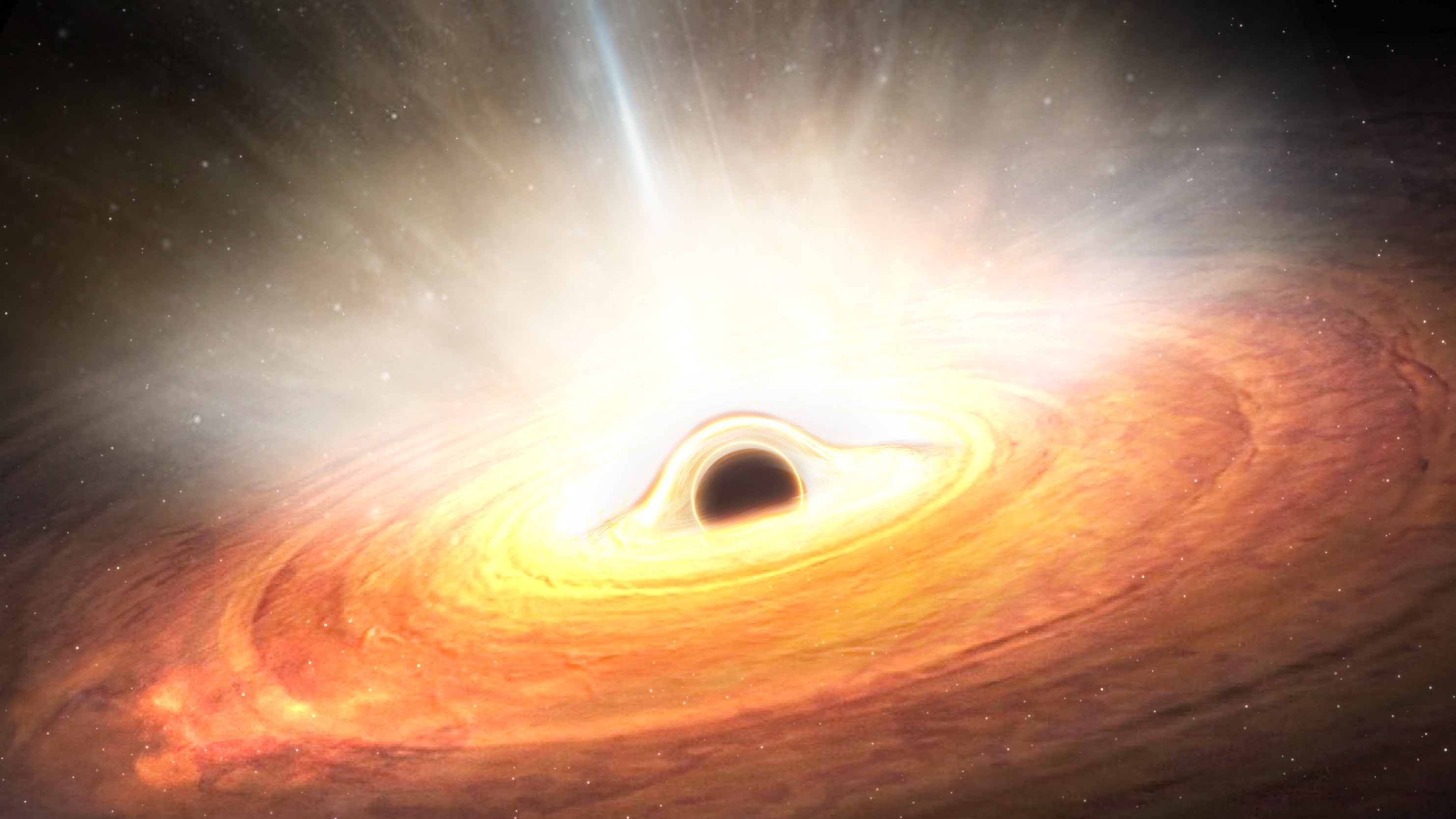

An illustration of ultrafast wind gushing out of a supermassive black hole
Rather than steady ingest the natural gas and dust around it , the black kettle of fish experienced a " temper fit " and suddenly flung the issue aside . This bring out a bald patch in the coltsfoot in which very few new hotshot could imprint . The notice " propose that mordant holes may reshape their host wandflower much more than previously thought,“Elias Kammoun , an astronomer at the Roma Tre University in Italy and co - source of the survey , said in astatement .
Kammoun and his team set out their study with information fromNASA ’s Swift Observatory , which detects light in the X - shaft of light , ultraviolet and da Gamma - ray spectrum . When the investigator noticed a significant fall in the amount ofX - electron beam lightcoming from Markarian 817 , they decide to take a closer look . This time , they used data from the European Space Agency ’s XMM - Newton mission , an extremely sensitive X - beam quad lookout station designed to take galax establishment .
Related : Astronomers blob gigantic black muddle kill a extragalactic nebula ’s star formation at the aurora of fourth dimension
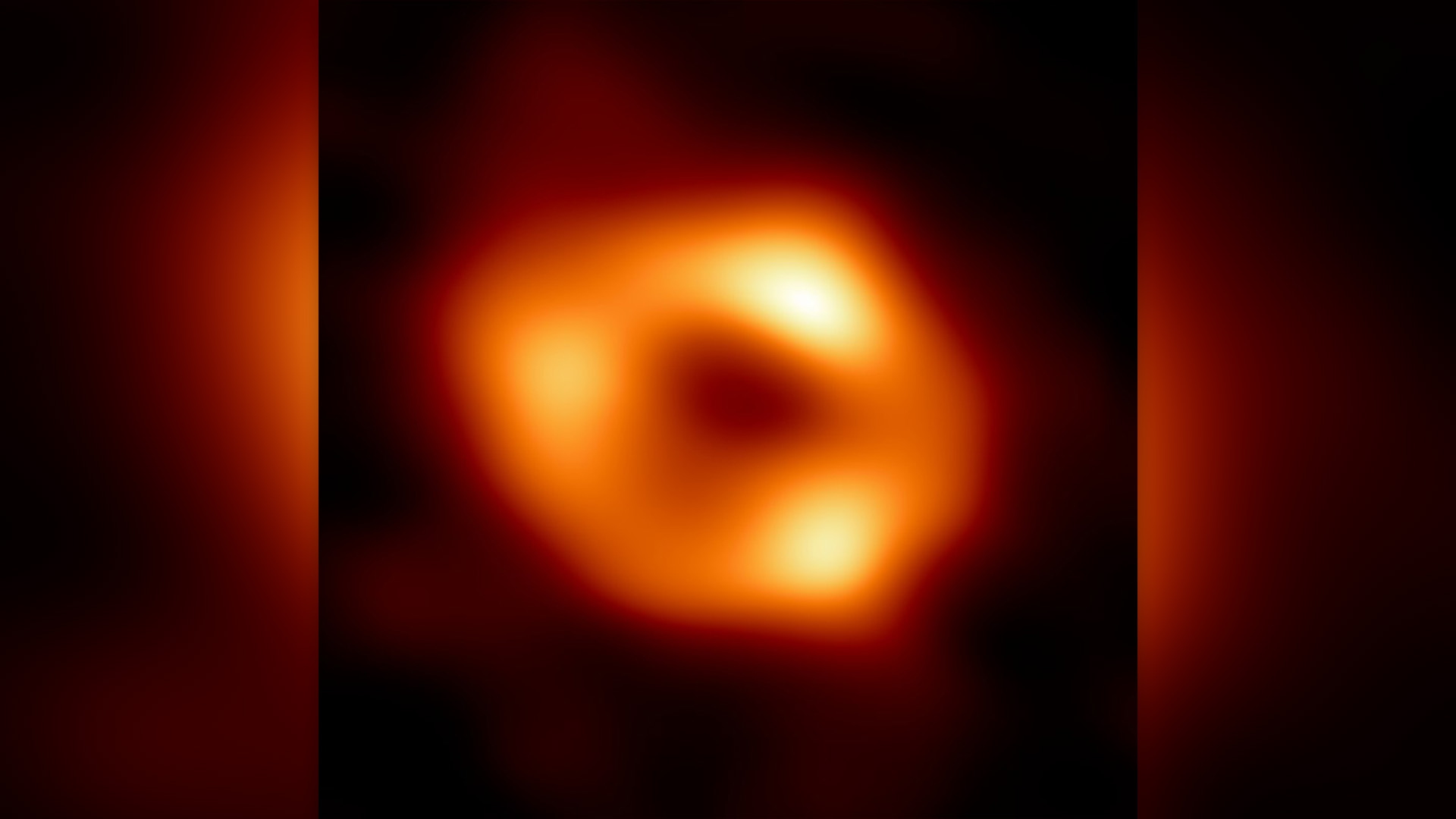

An image of Sag A, the supermassive black hole at the heart of the Milky Way, taken with the Event Horizon Telescope.*
XMM - Newton enabled the team to get to the bottom of the discharge drop . As it turns out , the culprit was a sustained gust of ultrafast cosmic idle words lash around the galaxy ’s black hole at several percent ofthe focal ratio of light , blot out the X - ray light of the galaxy . While it ’s fairly normal for black holes to broadcast out brief " puffs " of gas , such a prolonged tempest — which live on several hundred days — had not been observed before , the researchers said .
— Event Horizon Telescope spies gargantuan energy jets erupting from nearby supermassive black hole
— Scientists may at long last bed where the biggest , Old black holes in the universe derive from

— Faint radio signal from ancient star clustering could be rare ' missing connectedness ' black kettle of fish , uranologist account
When the dust lastly settled , the squad saw that the part of Markarian 817 immediately around its black hole had been largely sort out of dust . This help unlock a primal part of the cognitive process of galaxy formation — namely , that black holes can defeat star formation in extensive swath of the galaxies they inhabit , changing the shape of those galaxies . accord to the researchers , this finding could even excuse the peculiar bald patch surroundingour own coltsfoot ’s supermassive black-market hole , Sagittarius A * .
" This highlights the prime importance of the XMM - Newton mission for the future,“Norbert Schartel , a task scientist for XMM - Newton , say in the program line . " No other missionary work can give up the combining of its high sensitiveness and its power to make long , uninterrupted observations . "