When you purchase through links on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate deputation . Here ’s how it works .
NASAscientists on Earth have repair the creepy black " wanderer " that litter the Earth’s surface of Mars . The breakthrough leave the researchers " shrieking " with joyfulness and could assist unveil further arcanum about the occult structures .
" wanderer on Mars " is the name give to a geological feature , known as araneiform terrain , that is visible inmultiple fix on the Red Planet . In these berth , hundreds of dour crack - same structures seem on the satellite ’s surface , each with potentially hundreds of case-by-case lines , or " leg . " When reckon from above , these tightly grouped deformations , which can be more than 3,300 feet ( 1,000 meters ) wide , see like a hoard of spiders scuttle across the Martian landscape painting .
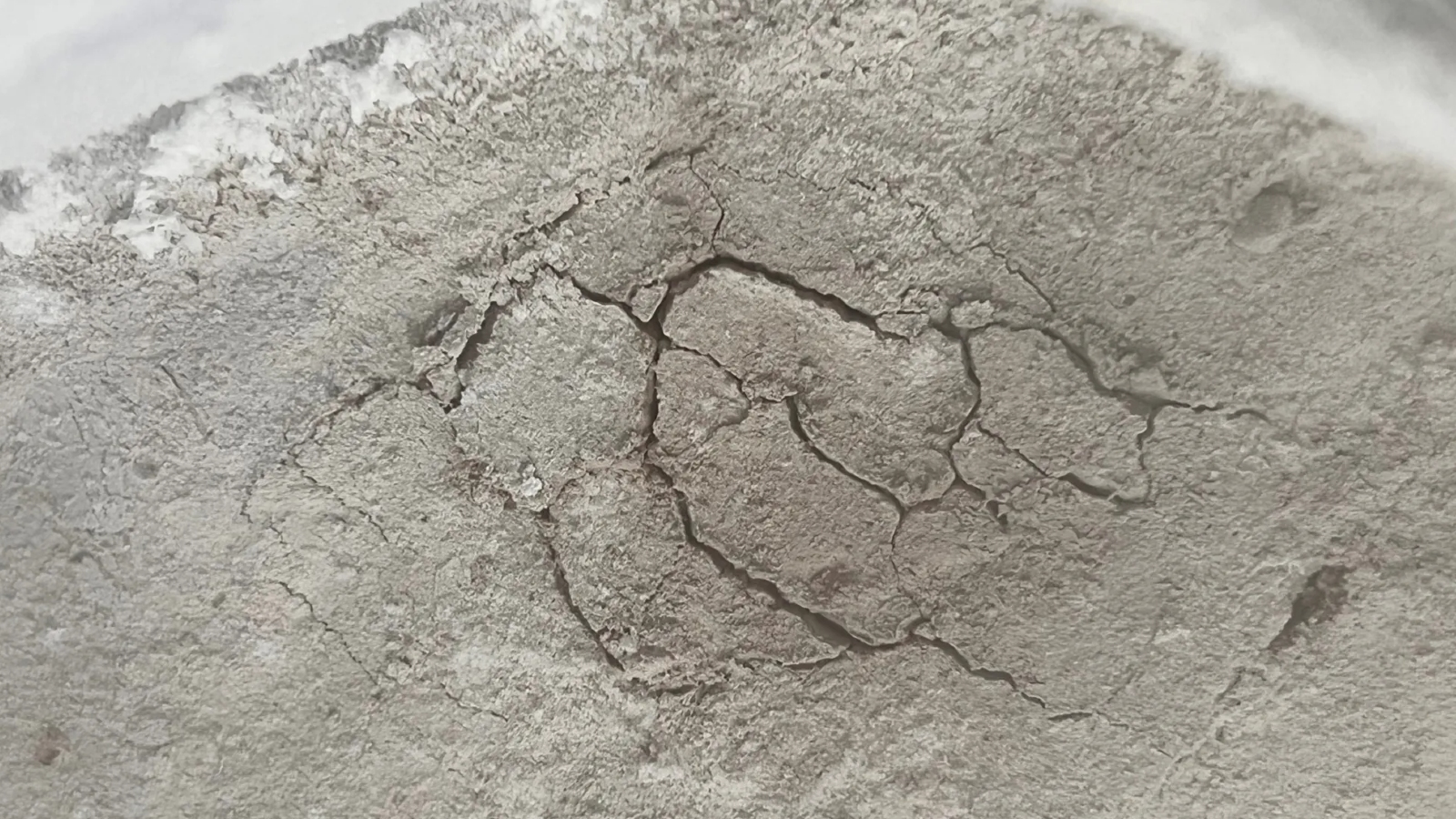

Researchers created this crack within a simulated Martian substrate using a specialized laboratory chamber to mimic conditions on the Red Planet. The end result is nearly identical to the famous “spiders on Mars."
Mars artificial satellite first spotted the wanderer in 2003 , and the lineament have continuallypopped up in satellite imagesever since . At first , these stationary arachnids were a pure mystery , but scientists finally determined that the spiders form when carbon dioxide ( CO2 ) sparkler on the planet ’s airfoil of a sudden sublimates — or turns into gasoline without first melting into liquidity .
In a unexampled study , published Sept. 11 inThe Planetary Science Journal , researchers mimic this process on a smaller scale using a specialized laboratory bedchamber to make a near - perfect miniature translation of the spiders .
For the study ’s lead authorLauren Mc Keown — a planetary geomorphologist at NASA ’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory ( JPL ) in California , who has been work out on hearten these spider for five years — the here and now of finally birthing the Martian critter was almost too much to handle .
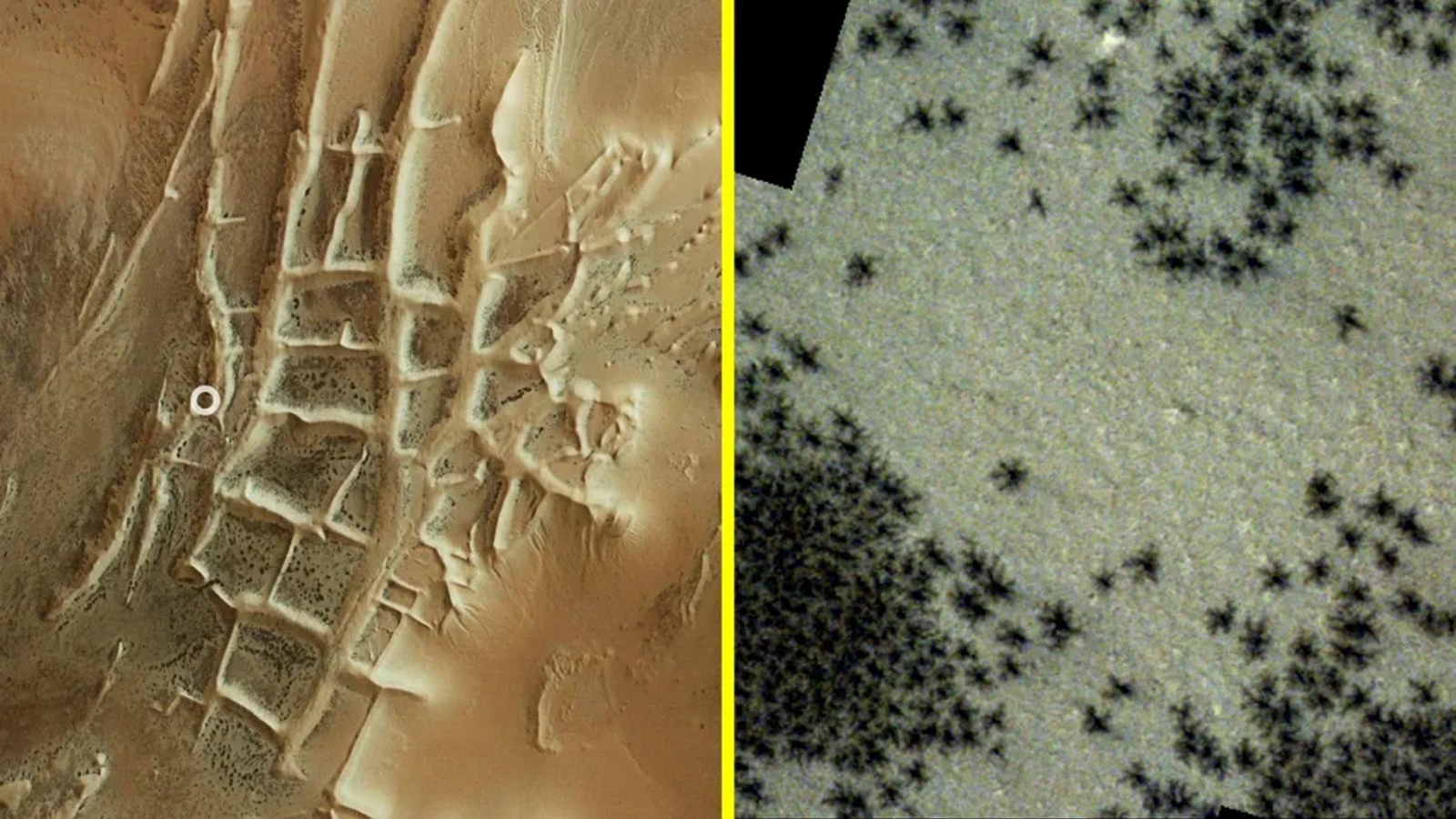
From space, araneiform terrain looks like hundreds of spiders running across the Red Planet’s surface. In these images, we see the “spiders on Mars” from orbit(left) and magnified to higher detail (right).
" It was previous on a Friday evening [ when the experiment succeeded ] and the lab director explode in after hearing me shrieking , " Mc Keown tell in astatement . " She thought there had been an stroke . "
Related:15 Martian objects that are n’t what they seem
In 2021 , Mc Keown led a written report thatfirst explained how the spiders form — via a nerve tract bed as the Kieffer fashion model .
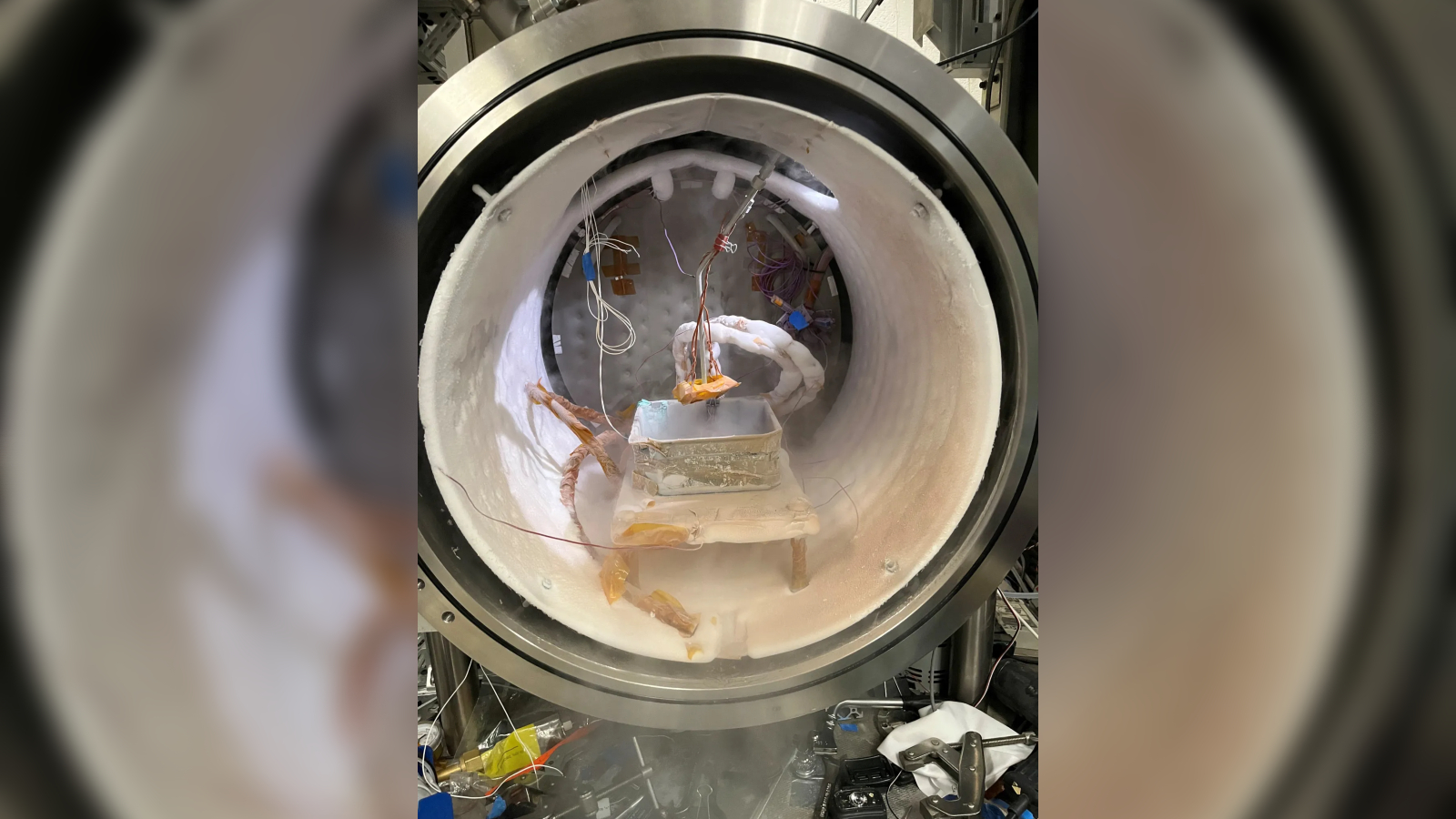

The Dirty Under-vacuum Simulation Testbed for Icy Environments (DUSTIE) replicated the extreme conditions on Mars that allow araneiform terrain to take shape.
This manikin show that , during Martian springtime , sunshine shines through slabs of CO2 ice on the surface , heating the solid ground below . This , in turn , induce some of the sparkler to sublimate into gas , create a pressure buildup within the glass slab . When the pressure gets too high , the methamphetamine hydrochloride crevice , which enables the gas to escape . As the flatulence seep out of the ice , it takes a stream of dismal dust and sand from the surface , leaving behind wanderer - like scars that seem when the deoxyephedrine to the full melts during Mars ' summer .
In the new study , the researcher put the Kieffer model to the test by animate these steps in a wine-coloured barrel - sizing chamber at JPL , known as the Dirty Under - void Simulation Testbed for Icy Environments ( DUSTIE ) , which recreated Mars ' extremely scurvy pressure and temperature — minus 301 degrees Fahrenheit ( minus 185 level Celsius ) .
The squad post a simulated Martian soil into the chamber and cover it with CO2 internal-combustion engine . They then heated the mixture with a lamp placed beneath the simulated dirt to replicate the heating effect of the sun .

" It took many tries before Mc Keown found just the right conditions for the ice to become thick and semitransparent enough for the experimentation to work , " NASA representatives wrote in the statement . But finally , the deoxyephedrine crack open and gas seeped out of the jam for around 10 mo before the frozen CO2 eventually disappeared and go forth behind one of the iconic spiders .
The new study also break a secret footstep in the Kieffer model : Ice also form within the earth , which caused it to crack open along with the ice rink . This could explain why the spider ' leg have such a zig - zag form , the researchers wrote .
— Scientists spot ancient ' smiley cheek ' on Mars — and it could contain signs of life

— Grand Canyon - sizing ' mark ' on Mars revealed like never before in striking new satellite picture
— ' Space potato ' spotted by NASA Mars satellite is really something much cool
" It ’s one of those item that show that nature is a little messier than the schoolbook image , " study co - authorSerina Diniega , a planetal scientist at JPL , said in the statement .

The researchers plan to perform similar experiments to solve the vainglorious remaining mysteries about the Martian spiders , let in why they mould in some topographic point on Mars but not others and why they do n’t seem to be growing in number every year .












