When you purchase through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
One of the modest human relatives ever found has been unearthed in South Africa . stand just 3 feet , 4.5 in ( 1.03 metre ) marvelous , the adultParanthropus robustus , who died 2 million old age ago , is even short than the famously bantam " Lucy " from Ethiopia and the inscrutable grouping of tiny " hobbit " from Indonesia — but researcher are n’t sure why .
" These small early hominin somebody are reconstructed as shorter and thick than modern human being ' Pigmy ' , " or groups of hoi polloi with an average male height under 4 feet , 11 inches inches ( 150 centimeters ) , study principal authorTravis Pickering , a paleoanthropologist at the University of Wisconsin – Madison , assure Live Science in an email . The freshly uncovered soul , designated SWT1 / HR-2 , " was probably similarly built — short and stocky , " he said .

A fragment of a hip bone from the newly discoveredP. robustusskeleton from Swartkrans, South Africa.
The leg bones of this mintage are rarely found , so the new find also bring home the bacon clues about howP. robustuswalked . The researchers describe their finding in the April issue of theJournal of Human Evolution .
The team recollect chunks of sedimentary rock date between 1.7 million and 2.3 million years old from the Swartkrans limestone cave , which is located in South Africa’sCradle of Humankind — a region that encompasses 180 square Admiralty mile ( 470 square kilometers ) and includes more than a 12 major fogy sites . When researchers began to excavate the blocks in the lab , they find three connecting bones — the left rose hip , femoris and tibia — all from one young grownup hominin .
base on the shape of the bones , the research worker think that this individual was a young adult female from the speciesP. robustus , also get it on as a robust australopithecine due to the heavy size of it of its tooth and face . But very few fossils of the body ofP. robustushave ever been find , make the new find authoritative for understanding what they look like and how they moved .
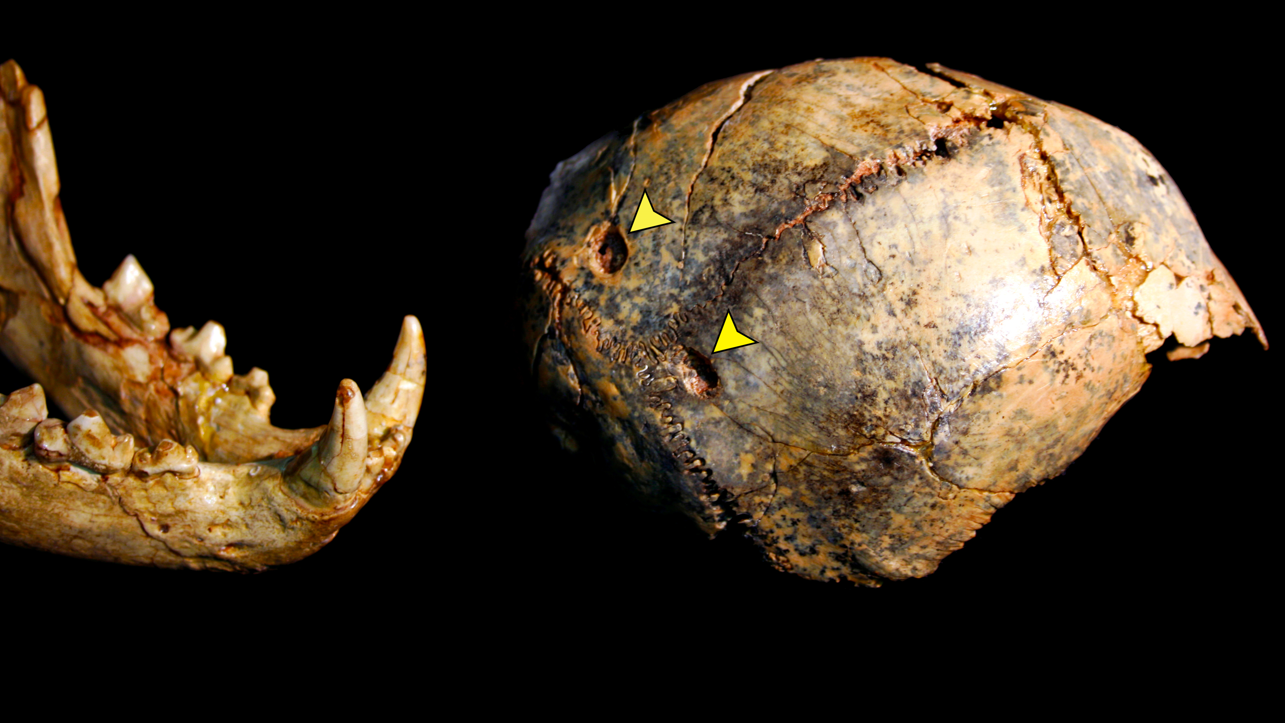
A fossil leopard lower jaw next to a juvenileP. robustusskull fragment from Swartkrans.
Related:1.4 million - yr - previous jaw that was ' a bit weird for Homo ' turns out to be from never - before - seen human relative
" She was sure full-bodied in the pelvis and at the rose hip joint , " Pickering said . " However , her leg off-white are not as singular in this gaze — and this is one of the quizzical things about the fogy . "
Taken together , the racy pelvic girdle bone coupled with the more slim peg bones show that thisP. robustusmoved through the landscape painting on two feet but also likely go up Sir Herbert Beerbohm Tree in search of intellectual nourishment or to evade predators , the researchers said in the report .

Close examination of the bones also revealed the likely cause of this untested female ’s death : A leopard devour her .
Leopards run to cling out in Tree near cave openings and favour to pounce on quarry that count around 55 pounds ( 25 kilograms ) , according to the researchers . This tinyP. robustus , which was find inside a cave , probably press about 60.4 pounds ( 27.4 kg ) . Carnivore tooth marks were also found on the hominin ’s bones , offering further clues about the cause of death . Other fossils at the website also have puncture marks that match leopard teeth , field co - generator C.K. Brain has contend inpast research .
Size is a mystery

Although the leg bones provide important newfangled grounds for what life was like forP. robustus , the researchers are still uncertain why this species was so small .
There is currently no grounds that the species was involve byinsular dwarfism , study co - authorJason Heaton , a paleoanthropologist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham , tell Live Science in an email . That cognitive operation — in which a species evolves to be smaller over time due to competition for resources — may be whyHomo floresiensis , also called thehobbits , were very short .
Rather , forP. robustus , " it may reflect natural variation within the species , universe - degree differences , or environmental influence such as nutrition or developmental restraint , " Heaton read .

— 1.5 million - year - quondam footprint give away our Homo erectus ancestors subsist with a 2nd proto - human specie
— scientist discover what could be the oldest evidence of cannibalism among ancient human relatives
— Ancient human ancestor Lucy was not alone — she lived alongside at least 4 other proto - human mintage , emerging inquiry evoke

More research into the body size ofP. robustusis require , the researcher noted in their cogitation , and further archeological site at Swartkrans could yield more bones from the same someone .
" I think that there is a good chance that much more of the SWT1 / HR-2 skeleton will be recuperate , " Pickering said , " especially if we are right and she was down and eaten by a leopard , since leopards do not loosely consume bones . "
Human evolution quiz: What do you know about Homo sapiens?
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your display name .











