When you buy through links on our web site , we may bring in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
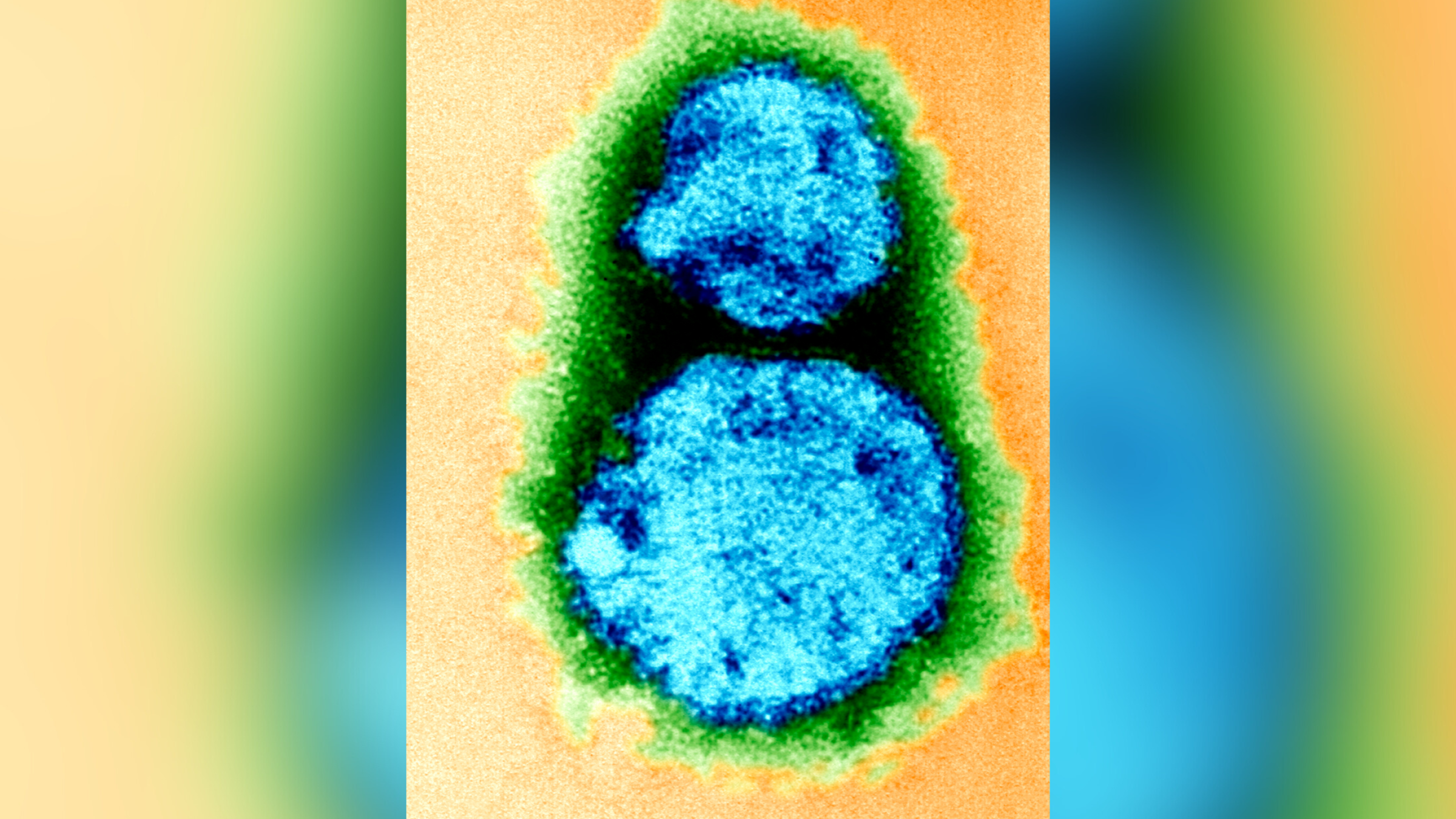
Oropouche computer virus disease , a Zika - like illness that unfold in the Americas , has been detected in Europe for the first time , affecting the great unwashed in Spain , Italy and Germany .
Meanwhile , officials are investigating whether the germ may make pitiable outcomes in pregnancy , similar to those associated with Zika virus .
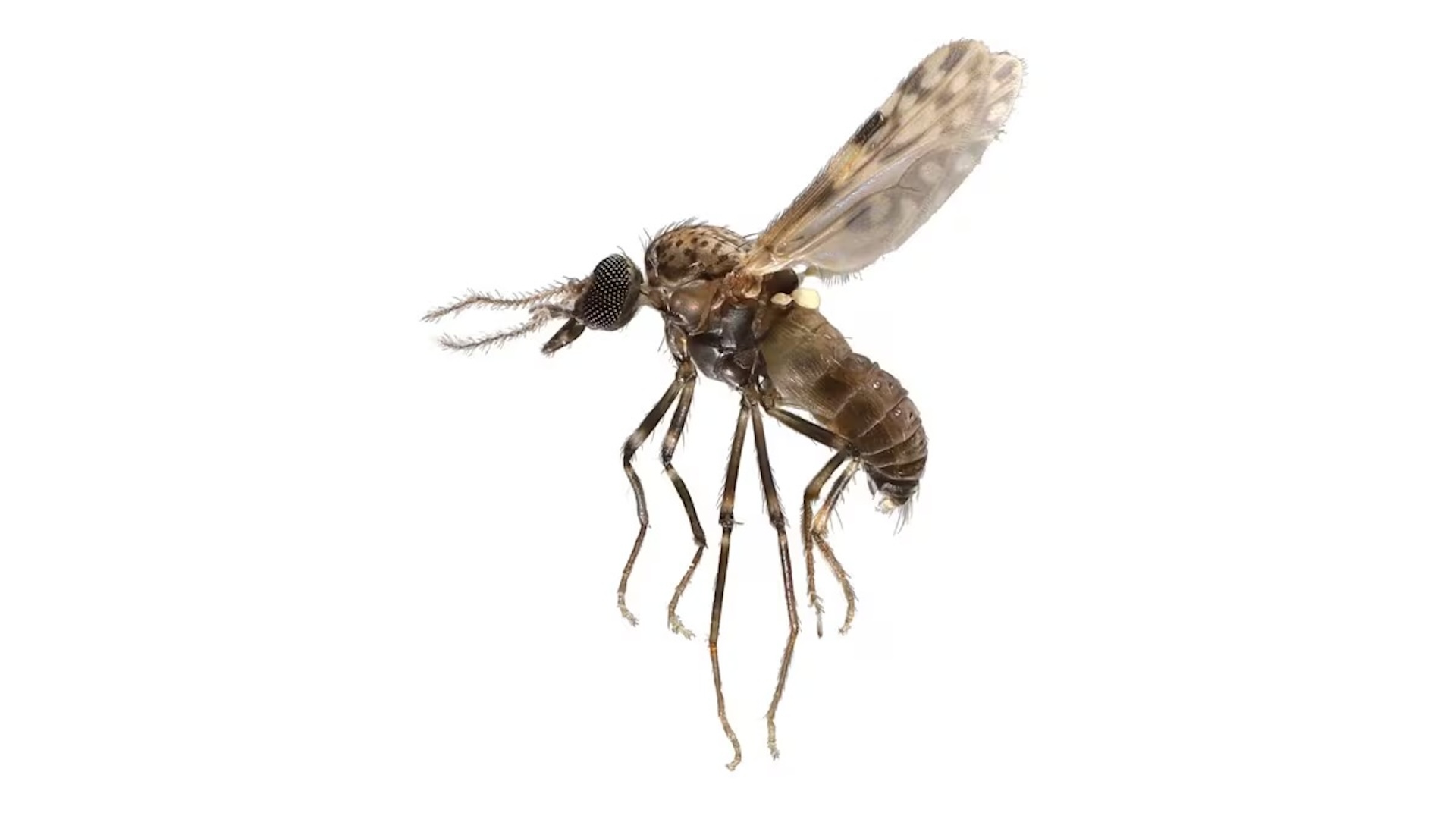

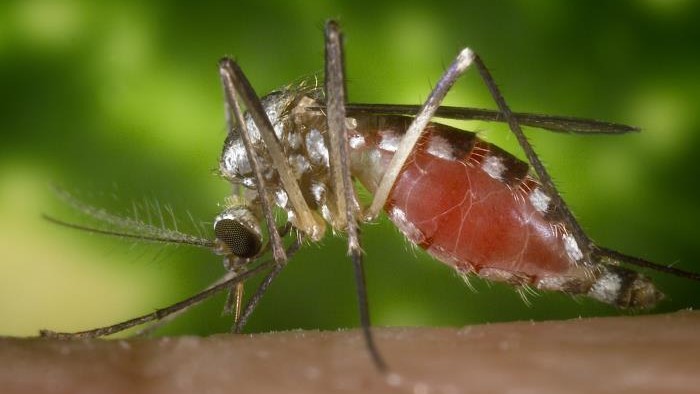
A biting fly called a midge is the main spreader of Oropouche virus to people.
In June and July , 19 cases of Oropouche computer virus disease were discover in Europe among travelers returning from Cuba or Brazil , according to the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control ( ECDC ) . The illness is overspread to humans by midge , a type of biting fly , as well as mosquitoes .
" The prognosis for recovery is good and fatal outcomes are extremely rarefied , " the agency state in arisk assessment published Aug. 9 .
touch : WHO may declare new , deadlier mpox outbreak an international emergency
Oropouche computer virus can cause symptoms like to Zika , including sudden fever , muscle aches , light sensitivity , eye pain , puking and rash . In close to 4 % of cases , the computer virus can infect the nervous system , get excitement around the spinal cord and brainiac or within the mentality itself . Nonetheless , most hoi polloi retrieve within several day to a month .
That order , lately , Brazil reported a handful of case that investigatorssuspect passed from mother to fetusduring pregnancy . These infection were tentatively link up to poor outcomes , including pregnancy loss andmicrocephaly , which causes a baby ’s top dog to be much smaller than ordinary .
However , due to restriction in the information , the link between inadequate pregnancy outcomes and Oropouche computer virus has not yet been confirm . The U.S. CDC and the Pan American Health Organization arecurrently inquire the potential risk .

Oropouche computer virus was first detect in 1955 in Trinidad and Tobago , and it ’s since caused eruption in various countries in South America , Central America and the Caribbean . So far this twelvemonth , outbreak have been reported in Brazil , Bolivia , Colombia and Peru , and Cuba reported its first - ever known cases .
Direct scatter of the computer virus from person to someone has never been documented . alternatively , people most often catch the disease from a midge coinage calledCulicoides paraensis . In addition , a handful of mosquito species can hold and spread the virus to people .
The midges that circularize the disease are n’t found in Europe , and " to date , there has been a lack of evidence as to whether European midge or mosquitoes could transmit the computer virus , " the ECDC take note in its risk assessment . This lack of evidence , combined with the fact that the virus does n’t spread between mass , makes catching the disease topically in Europe very unlikely .

The peril of catching the disease abroad is " temperate , " however , and the ECDC recommends that people traveling to places where Oropouche virus spreads take precautions . Safety measures admit using dirt ball repellent and wearing long - sleeved shirts and long pants when outside . Insecticide - treated bed nets should also be considered in rooms that are not adequately screen or air - conditioned . There is no vaccinum for Oropouche computer virus .
— In world 1st , computer virus blot attached to 2nd computer virus
— The deadliest virus in history
— gentleman’s gentleman in critical condition after catching deadly ' B virus ' from wild monkeys in Hong Kong
Although the risks of catching Oropouche computer virus during gestation are n’t yet clear , Zika virus — which does haveclear risks if contracted during pregnancy — spread in the same area . Therefore , the same safety wind would give for preventing both infections , according to the ECDC .
Some headline have referred to Oropouche virus as " sloth computer virus " or " sloth fever . " That ’s because the pale - throated sloth ( Bradypus tridactylus ) may be a key brute host for the virus , with insects spend it from sloths to humans and back .

However , the principal fauna hosts of the Oropouche virushaven’t yet been confirmed . A few competition besides sloths admit various angry birds and a few primates , such as capuchin ( Cebus ) and howler ( Alouatta ) monkeys .
This clause is for informational determination only and is not meant to propose medical advice .
Ever wonder whysome hoi polloi build muscle more easily than othersorwhy freckles come out in the Lord’s Day ? air us your question about how the human body figure out tocommunity@livescience.comwith the dependent pedigree " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your interrogative sentence answered on the website !