When you buy through links on our site , we may take in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
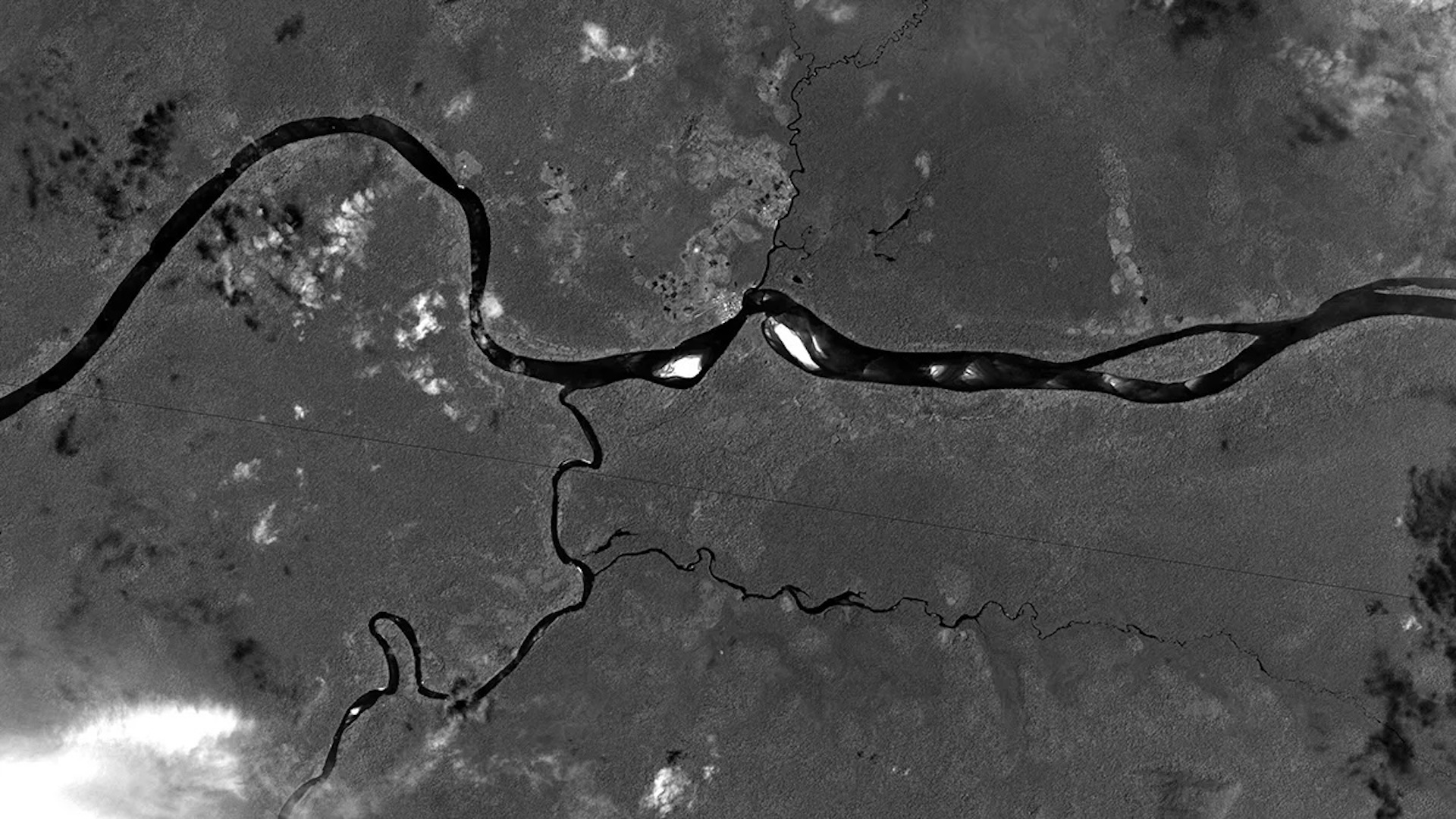
A subduction geographical zone below the Gibraltar Strait is creeping westwards and could one day " invade " the Atlantic Ocean , cause the ocean to slow conclude up , new research suggest .
Thesubduction zona , also make out as the Gibraltar discharge or trench , currently sits in a narrow sea corridor between Portugal and Morocco . Its westward migration began around 30 million year ago , when a subduction geographical zone formed along the northerly seacoast of what is now the Mediterranean Sea , but it has stalled in the last 5 million years , prompting some scientist to question whether the Gibraltar electric arc is still active today .
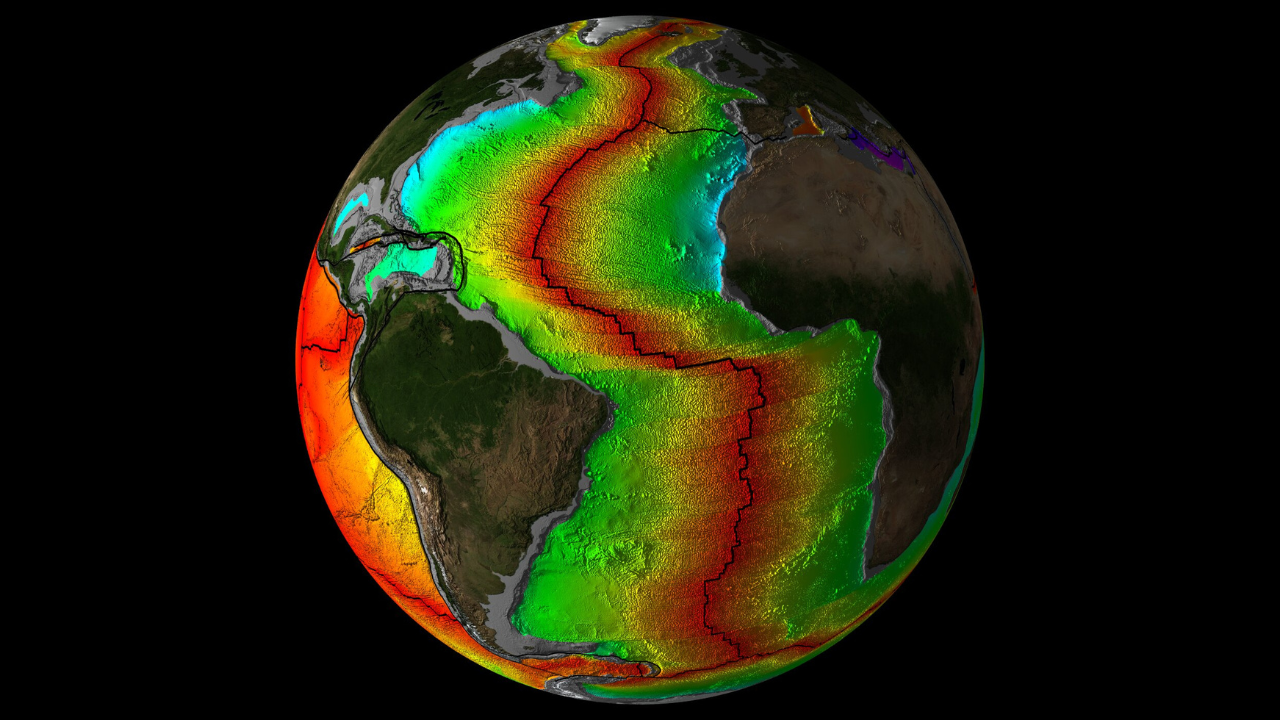
Diagram showing the age of the crust below the Atlantic Ocean (red being newly formed crust and blue being the oldest crust).
It appears , however , that the arc is only in a menstruum of quiet , according to a study write Feb. 13 in the journalGeology . This quiet will in all probability last for another 20 million years , after which the Gibraltar arc could resume its advance and relegate into the Atlantic in a process known as " subduction invasion . "
The Atlantic Ocean host two subduction zones that research worker know of — the Lesser Antilles subduction zone in the Caribbean and the Scotia arc , near Antarctica .
" These subduction zones invaded the Atlantic several million years ago , " pass authorJoão Duarte , a geologist and adjunct professor at the University of Lisbon , enjoin in astatement . " Studying Gibraltar is an invaluable chance because it allows observing the summons in its early stage when it is just happening . "
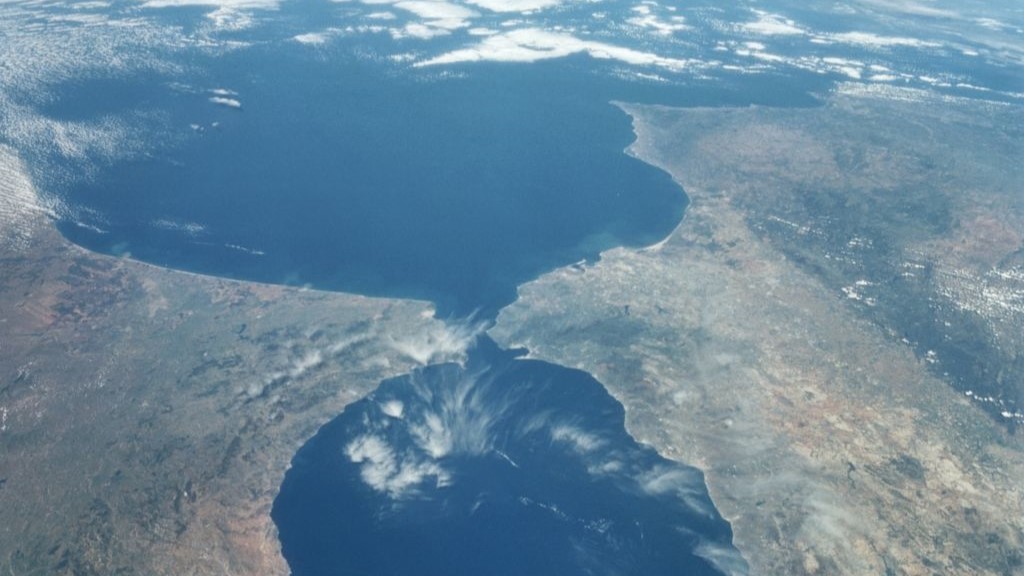

An aerial view of the Gibraltar Strait, which forms a narrow corridor between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
Related:‘We are approaching the tipping decimal point ' : Marker for the crash of key Atlantic current discovered
To test whether the Gibraltar discharge is still active , Duarte and his colleagues built a computer good example that simulate the birth of the subduction zone in the Oligocene epoch ( 34 million to 23 million days ago ) and its phylogeny until present day . The researchers noticed an abrupt fall in the arc ’s speed 5 million year ago , as it approached the Atlantic boundary . " At this stage , the Gibraltar subduction zone seems doomed to go , " they wrote in the study .
The squad then modeled the arc ’s fate over the next 40 million years and found it painstakingly pushes its way through the narrow-minded Gibraltar Strait from the present Clarence Day over the next 20 million twelvemonth . " Strikingly , after this point , the oceanic abyss retreat tardily speeds up , and the subduction zone widen and propagates oceanward , " the research worker wrote in the study .

Modeling of this kind requires advanced tools and computers that were n’t available even a few years ago , Duarte said in the statement . " We can now simulate the formation of the Gibraltar bow with great particular and also how it may evolve in the deep future , " he added .
If the Gibraltar arc intrude on the Atlantic Ocean , it could conduce to mould an Atlantic subduction system analogous to a chain of subduction zones that circles the Pacific Ocean , called the Ring of Fire , according to the statement . A similar chain of mountains organize in the Atlantic would lead to pelagic impudence being recycled into the mantle via subduction on both sides of the Atlantic , gradually swallow and close up up this sea .
The Gibraltar arc ’s cranch advance over the last 5 million years could explicate the proportional want of seismicity and volcanism in the region — which have been used as argumentation to dismiss the estimation that the subduction zona might still be active . The subduction geographical zone ’s architectonic silence is a direct result of its extended catamenia of stalled movement , the authors of the unexampled field of study argue .

— ' lack ' blob of water presage to be in the Atlantic in conclusion obtain
— Do the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean mix ?
— Gulf Stream current could collapse in 2025 , plunging Earth into climate chaos : ' We were actually bewildered '

" If the movement along the subduction interface were small , the accumulation of the seismic strain would be boring and may take 100 of years to accumulate , " they wrote . " This correspond with the long return period figure for gravid earthquakes in the neighborhood . "
Although many smaller earthquakes have been recorded since , the last major earthquake to rock the part was the 1755 Great Lisbon Earthquake , which reached an approximate 8.5 to 9.0 on the moment magnitude scale leaf . An earthquake of this order of magnitude occurring anytime presently is " pretty much out of the doubtfulness , since the last such terrible event was only 250 years ago , " expertspreviously recount Live Science .














