When you purchase through links on our site , we may garner an affiliate perpetration . Here ’s how it works .
A giant impactor that severely dented Mars ' surface roughly 2.3 million years ago also carve out 2 billion smaller craters on the Red Planet as it shattered the ground , a new written report finds .
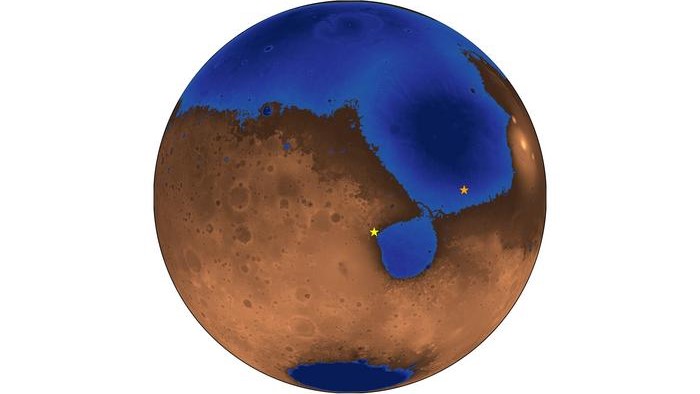
The primary impact crater , eff as Corinto , step around 8.7 land mile ( 14 kilometre ) in diam and is located in Elysium Planitia — a broad plain that straddlesMars ' equator . Asteroids equal to of pull up stakes such a gigantic mark are estimated to only dash into the Martian Earth’s surface every 3 million yr or so , meaning Corinto may be the untried crater of its size on the Red Planet , researchers divulge at the 55th annualLunar and Planetary Science Conferencein Texas sooner this month .
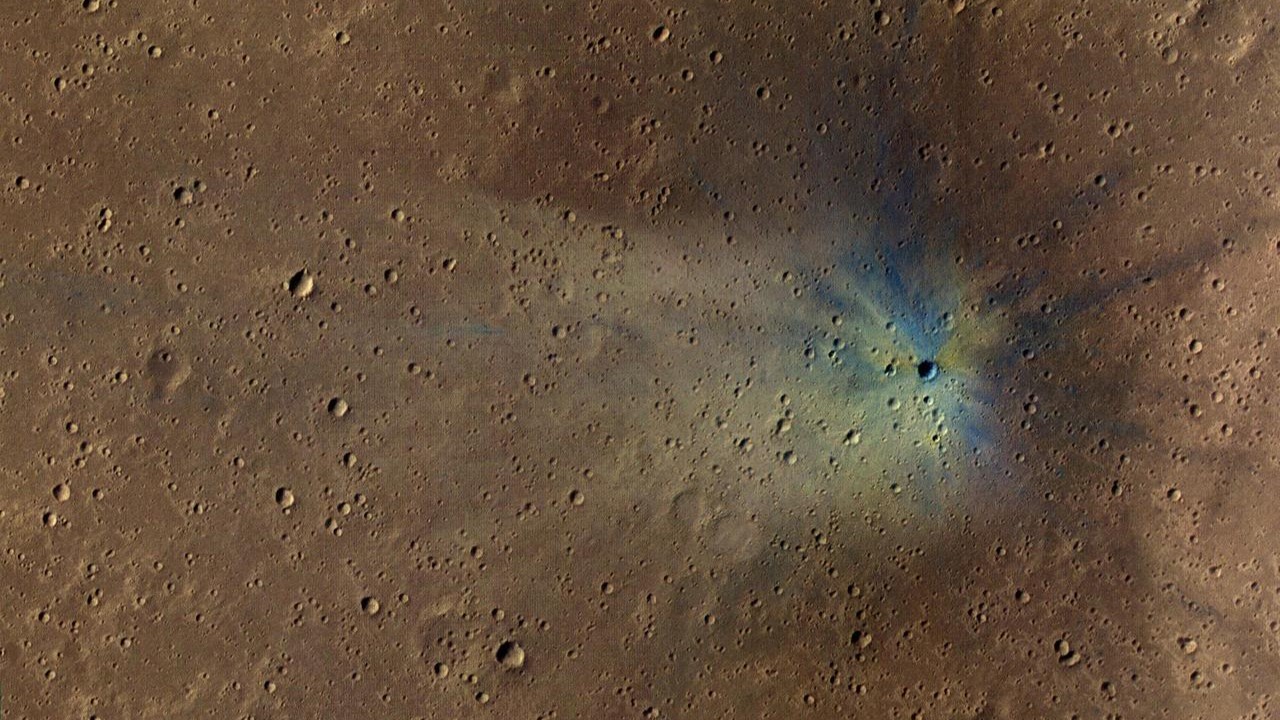

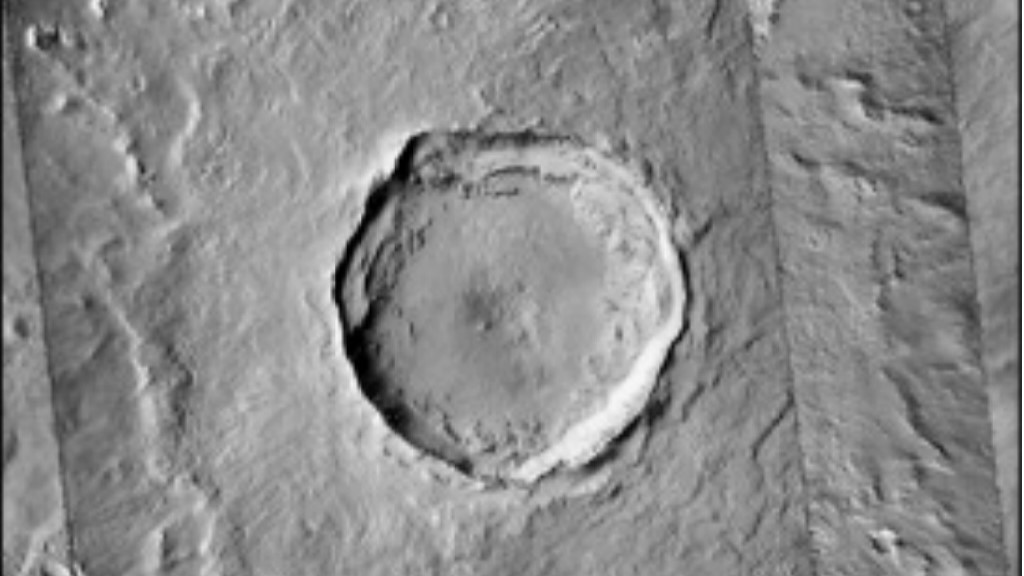
A view of Mars’ young Corinto crater surrounded by hundreds of secondary craters formed during the same ancient impact event, as seen by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
" Corinto is a saucy impact volcanic crater in Elysium Panitia that produced one of the most broad organization of … petty craters on Mars , " the researchers write in astudyreleased at the group discussion .
The team used data point gather by the High Resolution Imaging Experiment ( HiRISE ) and the Context Camera ( CTX ) on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter ( MRO ) to examine Corinto and its milieu .
The target that organize Corinto pockmarked the ring landscape with smaller craters , as ejected fragments of the Martian surface shot outward in ray - like patterns still seeable today , according to the discipline . These secondary crater are centre in an country to the south and sou'-west of Corinto , with the furthest flung ejecta landing 1,150 mi ( 1,850 klick ) from the independent crater .
Mars' Corinto impact crater is located in the Elysium Planitia, a broad plain that straddles the planet’s equator.
Related : Mars crater is ' chock - full ' of opal stone , suggest at far-flung water and possible microbial living
The research worker group the petty craters into four " facies , " base on their form and space from the main volcanic crater . Facies 0 crater , those closest to Corinto , appeared semicircular , whereas the farthermost away , Facies 3 Crater , were long and minute .
" The celebrate difference … with length from the volcanic crater probably result from variations in shock speed and size of ejecta , " the researchers note in the study .

— Eerie exposure of Mars ' purview take NASA 3 months to capture
— Mars ' oldest meteorite traced to foreign double encroachment crater
— monolithic Martian meteor impact was largest ever record in solar system

The flight direction of the ejecta fragment that abound outwards during the impact , together with the slightly elliptical shape of the principal crater , paint a picture the physical object number from the north and rival down on Mars at an devious angle of 30 to 45 degrees , according to the study . The researcher also posit the object was made of " stiff , competent basalt . "
Corinto ’s interior floor , which sits 0.6 Swedish mile ( 1 km ) below the surrounding Martian landscape , features a large telephone number of pits that indicate the area wascovered in water icewhen it was strike . The pits , which are all smaller than 660 feet ( 200 meters ) across , may have mould as a result of intense degassing ( the remotion of dissolved gases from a liquid ) when the water meth was superheated upon impact , the researcher suggested .
This study has not yet been publish in a peer - reexamine diary .