When you purchase through liaison on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
almost 35 years after its launch , theHubble Space Telescopeis still revealing newfangled things about the universe .
In a new released series of images , scientists used Hubble to probe a quasar 2.5 billion light - old age aside . The result intensify our understanding of how these inscrutable objects develop — but also reveal " weird things " in the quasar ’s vicinity that research worker can not fully explain , the squad wrote in aNASAstatement .
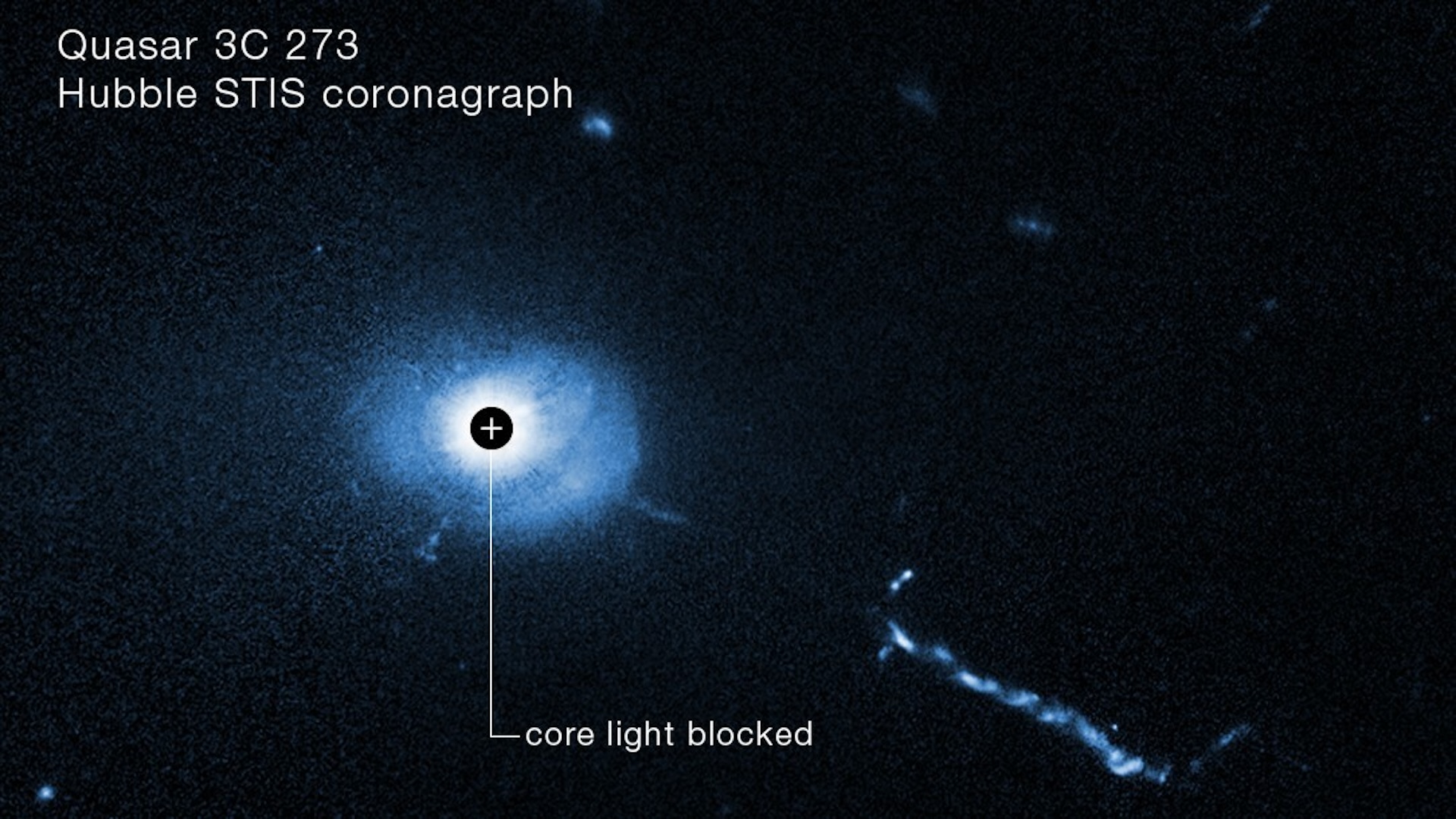
An image of the supermassive black hole-powered quasar 3C 273 with its core light blocked reveals “weird” L-shaped filaments and other mysterious structures.
" We ’ve got a few blobs of unlike size , and a mystifying L - shape filamentary structure,“Bin Ren , an astronomer at the Côte d’Azur Observatory and Côte d’Azur University in Nice , France , said in the instruction . " This is all within 16,000 light - years of the disgraceful hole [ at the quasar ’s center ] . "
Quasar is short for " quasi - stellar radio source " — bright , star - like aim that emit radio waves and are powered by actively feeding supermassiveblack hole . The first quasars were identified in the 1950s , but many of their quality remain mysterious . For example , due to their brightness , researchers do n’t know much about the environments that typically surround quasars . However , Hubble ’s Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph ( STIS ) tool is able to obturate some of this excess lighting , similar to how the synodic month obscures the sun during a totalsolar eclipse .
link up : inglorious hole paradox that stump Stephen Hawking may have a solution , new paper claims

Two views of the black hole-powered quasar 3C 273, with its center blocked (bottom) and not blocked (top).
Researchers pointed STIS at a known quasar named 3C 273 . This particular celestial object was the first quasar to ever be officially realise , in 1963 , and is improbably bright , emit thousands of times more light than the median coltsfoot . scientist theorize that this is because 3C 273 is surround by galactic debris and powered by a massive dark hole devouring the end of the small galaxies in its neighborhood .
— uranologist spot 1 of the most sinewy ' sonic boom ' in the universe as massive beetleweed crashes into its neighbors
— Study of ' twin ' stars see 1 in 12 have killed and eaten a satellite

— freshly observe ' outpouring of youthfulness ' phenomenon may help lead delay death by billions of old age
Hubble ’s instrument block off enough luminousness to canvas the 300,000 - light - year - tenacious jet of fabric streaking out from 3C 273 . Then , the researchers compared the images with Hubble data captured 22 years earlier . They found that the quasi-stellar radio source ’s spurt has travel quicker the farther off it stimulate from the location of the hypothesise black hole . This intimate that the black hole is helping repel the quasar ’s luminance as it raven the remnants of smaller artificial satellite wandflower . The " blob " and cubic decimetre - shaped structures observed in the new range may be the remnants of those galaxies , the squad tot up , but more study is take to identify them conclusively .
" Hubble bridged a interruption between the small - musical scale radio interferometry and large - scale optical tomography observation , and thus we can take an experimental step towards a more consummate understanding of quasar legion morphology , " Ren said .

In coming years , scientists plan to use theJames Webb Space Telescopeto further deepen their agreement of this unique quasi-stellar radio source by peer into its infrared spectrum .













