When you purchase through links on our web site , we may pull in an affiliate committal . Here ’s how it work .
On a enceinte scale , the cosmos is like a complex spider internet , full of cosmic filaments of petrol , dust and sorry issue , split by enceinte voids . Now , in a remarkable fresh image , researcher captured one of these cosmic filament connecting two galaxy from when the population was just 2 billion years old . It ’s the most elaborate image of an ancientstrand of the cosmic webever taken .
Cosmic filaments stretch across million of light - years and shape what ’s known as the " cosmic web . " beetleweed are string together to imprint enceinte filaments , and at their intersections are galaxy clusters — the densest regions of the entanglement . These filament funnel gas into galaxies , thereby helping them grow . They also funnel galaxies into galaxy clusters , thus creating thelargest structures in the universe .
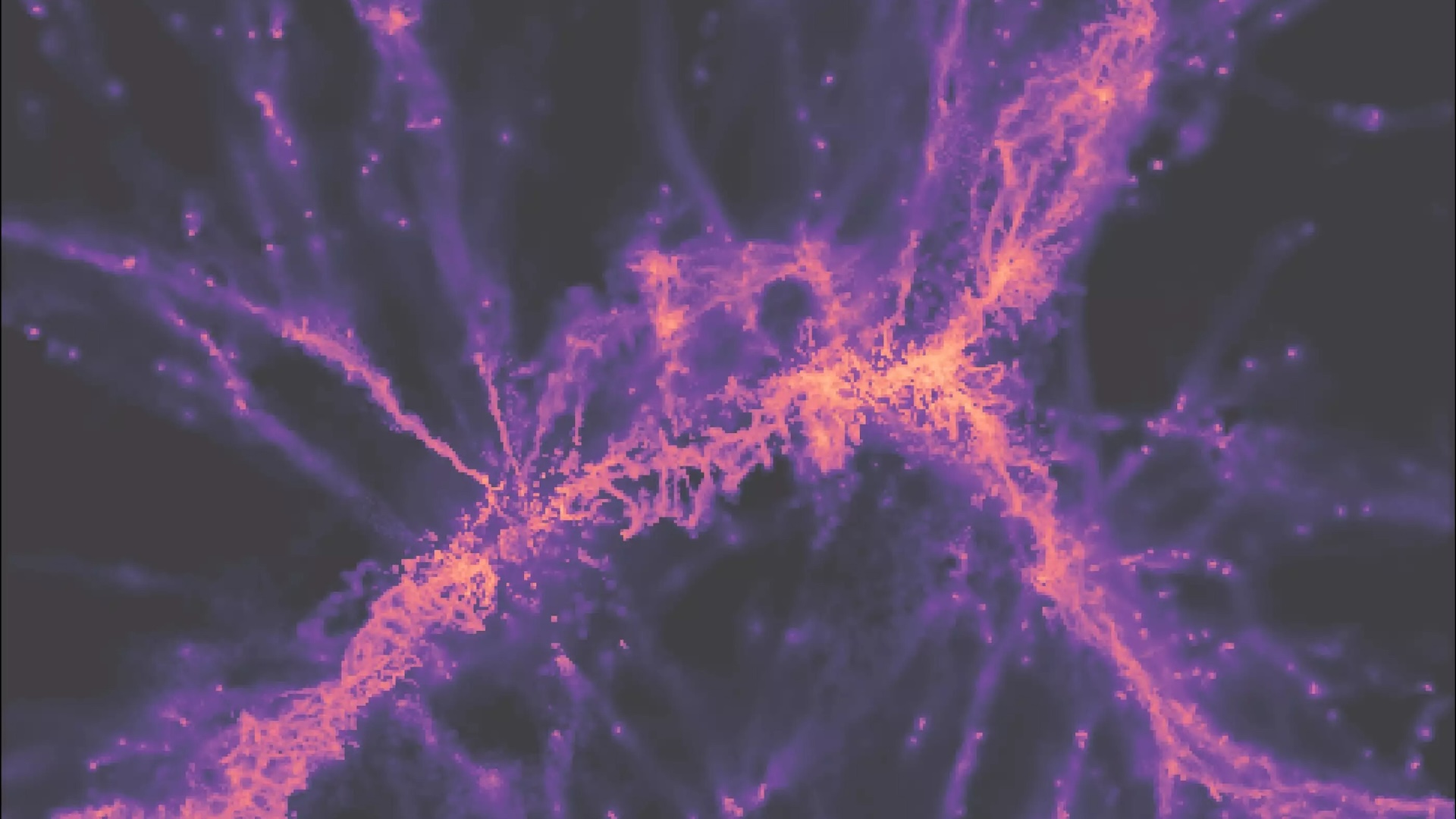

A filament of the “cosmic web” seen in a recent supercomputer simulation. The simulation matches almost exactly a real piece of the cosmic web captured in new telescope observations.
The cosmic web ’s structure is n’t random . It ’s determine bydark matter , the mysterious entity that account for 85 % of all the topic in the creation . Dark matter is gravid and does n’t interact with twinkle , so it ’s tough to observe . But it does interact with normal , seeable matter gravitationally ; it pull on it in way we can see . Because of this , dreary topic dominates normal matter . It holds everything together and gives it social system . It also shapes the cosmic World Wide Web ’s filaments .
The flow of gas within the filaments can provide insight into how galaxies form and evolve . However , it ’s difficult to maintain the gas within these filum because even the most abundant element , atomic number 1 , emits very swooning light .
Related:5 place discoveries that scientist are struggling to explain
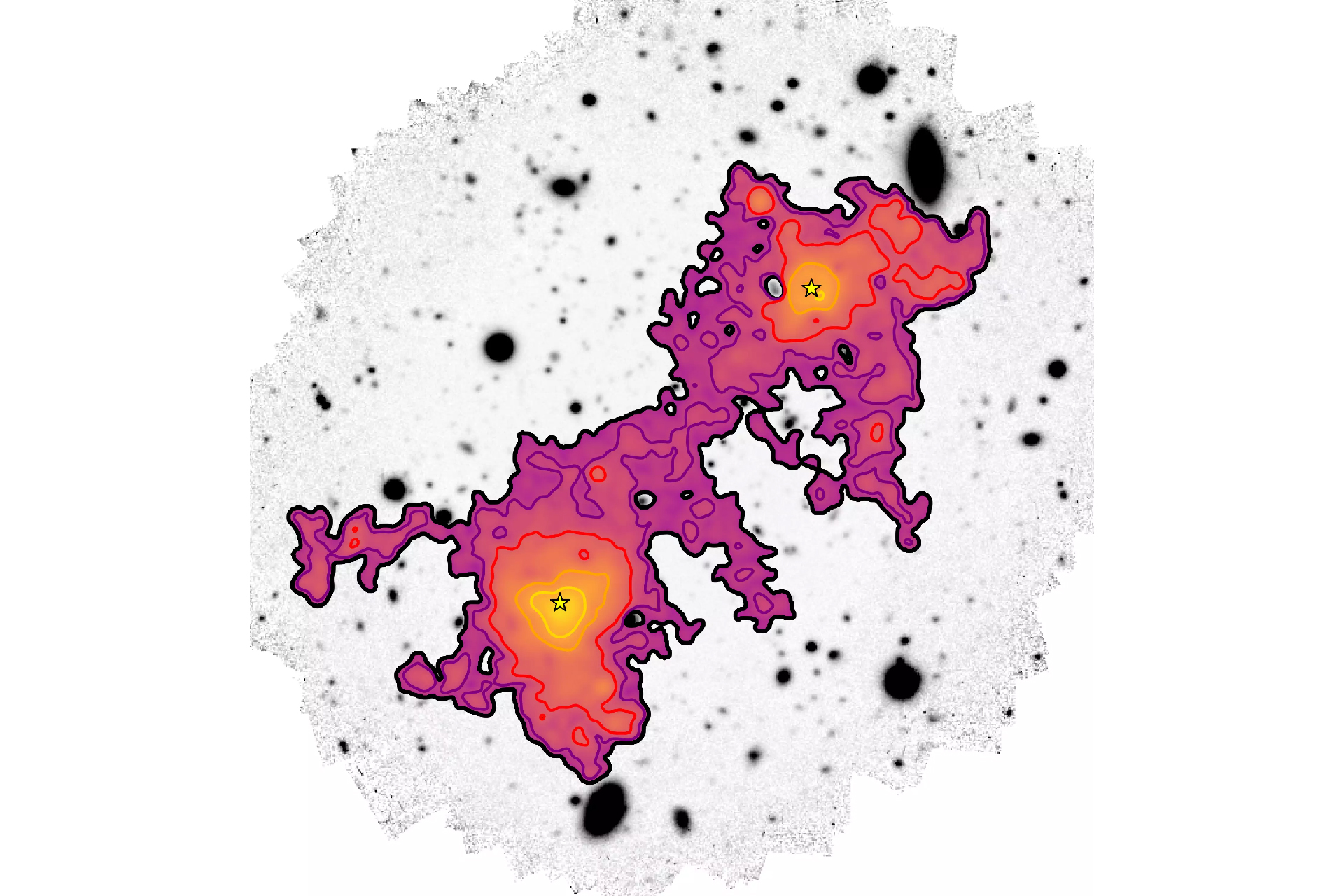
This image from the new study reveals a single ancient filament of the cosmic web, with diffuse gas (yellow to purple) connecting two galaxies (yellow stars) over an enormous distance of roughly 3 million light-years.
Unraveling “the web”
To capture the new prototype , astronomers from the University of Milano - Bicocca in Italy and the Max Planck Institute ( MPA ) in Germany utilized 150 hours of observations from the Multi - Unit Spectroscopic Explorer ( MUSE ) instrumental role at the European Southern Observatory ’s Very Large Telescope in Chile to capture a highly detailed portrait of a cosmic filament extend about 3 million light-colored - eld across and connect two galaxies with supermassiveblack holes .
From these notice , the researcher traced the boundary between the gas in the Galax urceolata and the cloth in the cosmic web through direct measurement for the first meter , lead authorDavide Tornotti , a doctorial student at the University of Milano - Bicocca , saidin a statement . The remarkable sensitivity of MUSE countenance the squad to capture the filament ’s light after it had locomote for almost 12 billion years to turn over Earth , the team explained in astudypublished Jan. 29 , 2025 , in the journal Nature Astronomy .
— Astronomers discover ' Quipu ' , the single large bodily structure in the known population

— Euclid scope spots rare ' Einstein ring ' hiding near Earth — and an ancient , unnamed galaxy behind it
— stargazer catch black holes ' cook ' their own meal in bizarre , eternal feeding bike
Based on the current cosmological model , the squad simulate the expected filamentary structure within the cosmic web . " When equate to the novel high - definition image of the cosmic web , we find solid agreement between current possibility and observation , " Tornotti said . This adds bread and butter to the standard model of cosmology , which some researchers have start out to question thanks topuzzling James Webb Space Telescope observationsof the very early universe .

The laconic image and its strong coalition with predictions open up unexampled opportunities to study gas distribution in cosmic filaments and its impact on the formation of galaxies . Study cobalt - author and MPA staff scientistFabrizio Arrigoni Battaiaadded that the squad contrive to distinguish more filaments in next observations to get a complete scene of how natural gas flow within the cosmic web .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be incite to enter your exhibit name .














