When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Zapping the vagus brass promotes rakehell curdling , fresh enquiry propose .
These finding are the first grounds in humans of a " neural tourniquet , " or a brain - based pathway that could reduce bleeding , said study co - authorDr . Jared Huston , a trauma operating surgeon at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in New York .
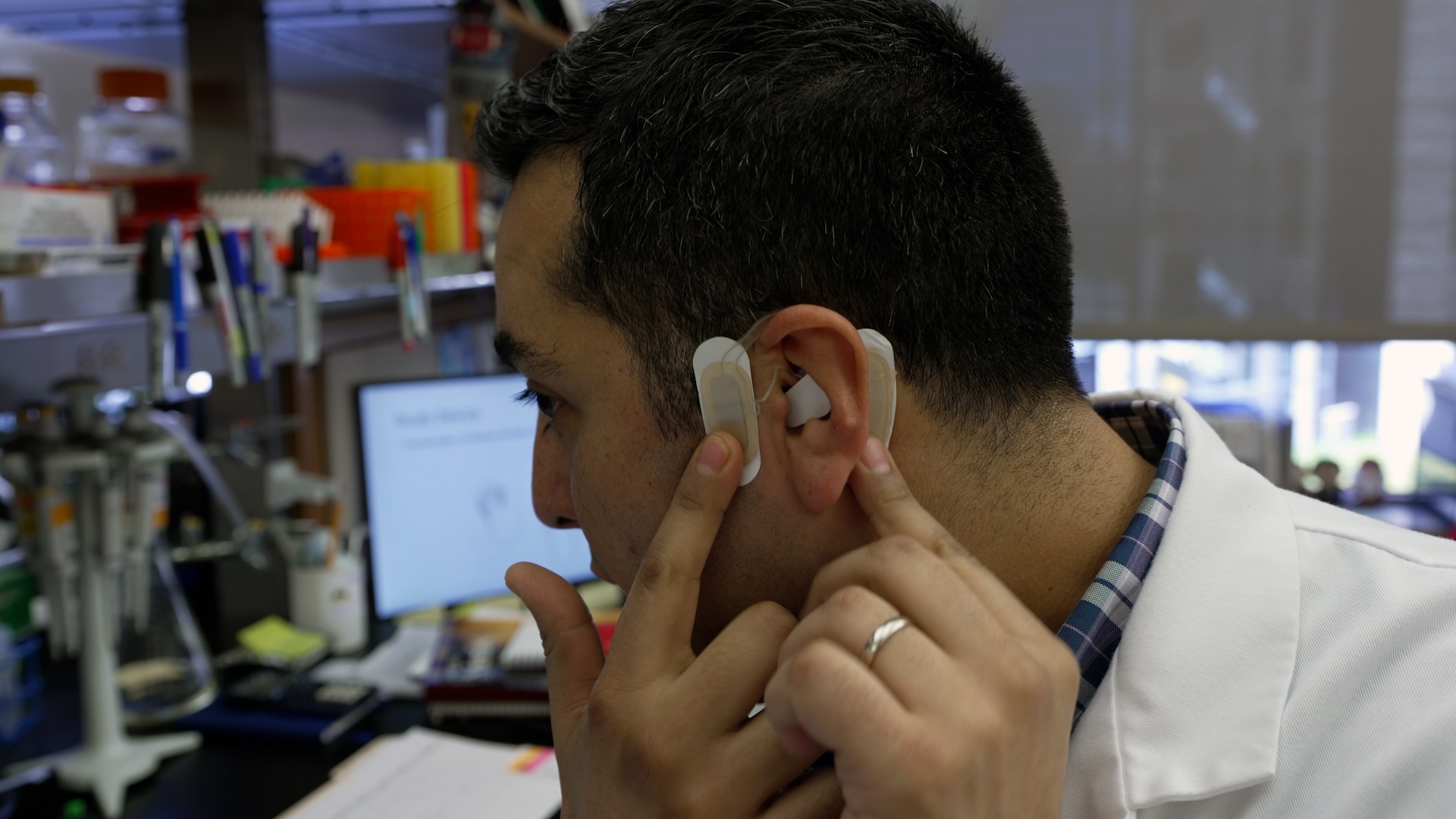

A device that attaches to the ear can stimulate the vagus nerve, thus promoting blood clotting. The technology, called transcutaneous auricular neurostimulation (tAN), has been tested in an early trial sponsored by the company Five Liters.
If a future clinical test like a shot shows that the nerve stimulation decreases blood loss , the proficiency could be used before plan OR to protect patient role from excessive bleeding , Huston told Live Science .
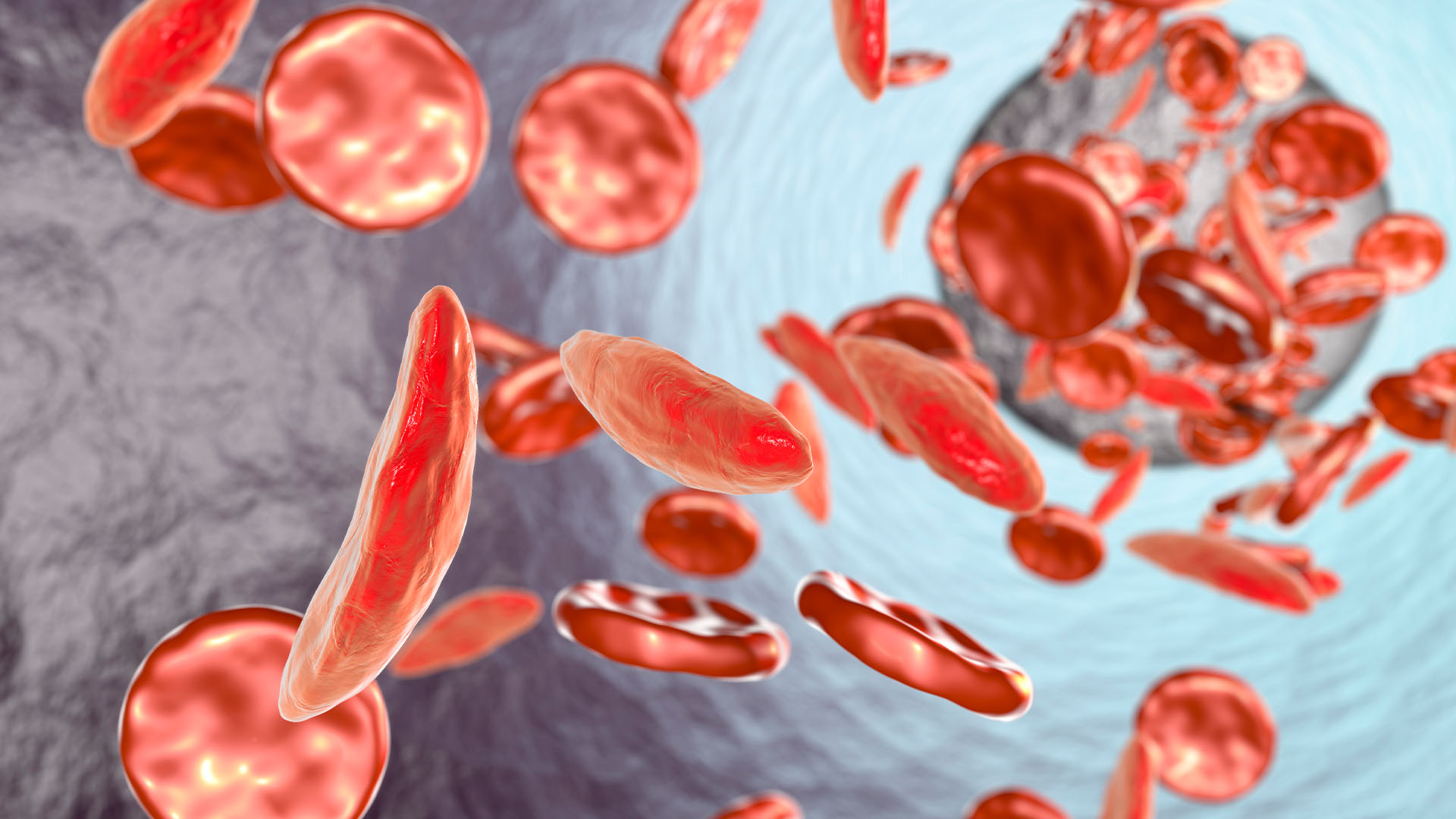
Around 1.5 % of surgeriesare complicated by haemorrhaging , or excessive blood loss , and some degree of hemorrhage is tie in with all surgeries . surgeon currently rely on sutures , bandages andtourniquets — devices that stop parentage from course to part of the body — to steadfast bleeding .
But Huston inquire whether making stock less likely to escape in the first place would make surgery safer . " Preventing a trouble is always better than dealing with it after the fact , " he articulate .

tie in : How much blood is in the human body ?
Huston and his collaborators first enquire if the vagus nerve cheek might promote parentage clotting near 20 years ago , afterthe nervus was found to modulate inflammation . Thevagus nerve , which originates in the brain and branches out to other organs , check theparasympathetic nervous organization — the relaxation - and - compilation counterpart to the " push - or - flight"sympathetic nervous system of rules .
Initial experiments in miceand pigsshowed that stimulating the vagus could , indeed , reduce blood red ink following a diminished cut . " We then drop the better part of a ten assay to figure out exactly how it works , " Huston said .

Last yr , Huston ’s team showedthat vagus nerve stimulation activates a type of resistant cell , called T cells , in thespleen , the organ that help filter germs and erstwhile cells out of blood . These T jail cell then activate blood platelet in the spleen ; thrombocyte are the cell fragments thatset off blood clot formation .
Upon re - entering circulation , the primed platelets are well capable to respond to hurt - relate cues . In computer mouse withhemophilia , a upset in which blood ca n’t clot properly , face input reduced bleeding , the squad get hold .
To test whether the same mechanism subsist in humans , Huston ’s team collaborated with the Dallas - based biomedical companyFive Litersto recruit intelligent volunteer . They used an O.K. machine tozap the auricular branch of pneumogastric face , which runs behind the ear , for 30 minute in each individual . They gather up blood sample before and after the treatment .

These consequence , presented in October at the Society for Neuroscience group discussion in Chicago , show for the first time " that there is a neural compression bandage pathway in humans , " Huston said . " And it look that we can activate this neural compression bandage footpath non - invasively . " More details of the trial can be chance atClinicalTrials.gov .
While the past study solution in creature are " very intriguing , " more work needs to be done to show pneumogastric nerve stimulus can in reality block bleeding in humans , Peder Olofsson , a professor of bioelectronic practice of medicine at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm , Sweden , told Live Science .
" at long last , measurements of bleeding times , bleeding volumes , and patient resultant will be key " to prove the clinical economic value of activating the vagus nerve through the tegument , said Olofsson , who was not involve in the subject field .
Huston agreed . " The next discipline will have to be in an actual clinical disease where the patient are bleeding one way or another , " he said .
Another takings is showing that the stimulators can produce consistent solvent , Olofsson noted . " Non - invasive stimulators " — while much faster and easier to apply than implant stimulators — " often show less consistent physiological effects . "
— Master governor of inflammation found — and it ’s in the brain stem

— How many blood types are there ?
— What ’s the rarest blood type ?
Vagus nerve stimulant is already widely used inepilepsyanddepression , so the risk of side essence is probably low , Huston added . If his finding can be reduplicate and extended in larger trial , surgeons might employ a abbreviated period of nervus vagus nerve stimulation prior to planned surgical procedure .

" We lot antibiotics , so you do n’t get an infection during operating theater . We administer painful sensation medications pre - emptively , so the pain is less , " Huston said . " What is missing is any means to take a normal , intelligent person who ’s undergoing surgery to try and keep hemorrhage forward of fourth dimension . That ’s an tremendous unmet need . "
Ever marvel whysome masses build up muscle more easy than othersorwhy freckles get out in the Dominicus ? Send us your questions about how the human soundbox work tocommunity@livescience.comwith the capable line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your interrogative sentence answered on the website !